







 these graphs are for number 3 please help me
these graphs are for number 3 please help me
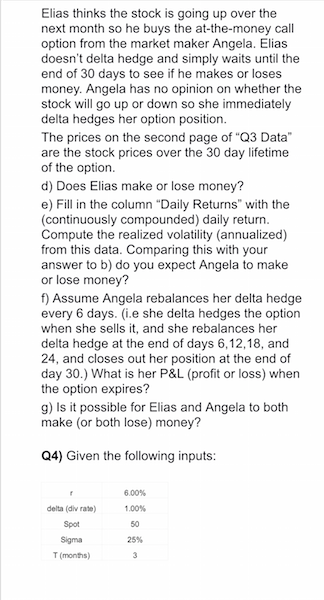
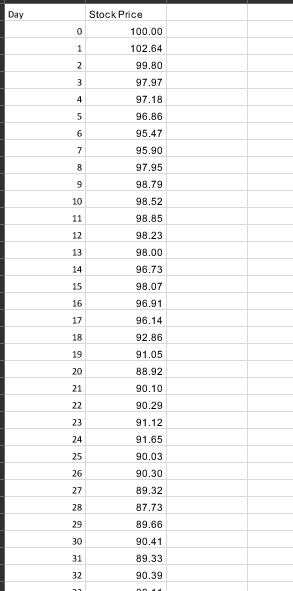
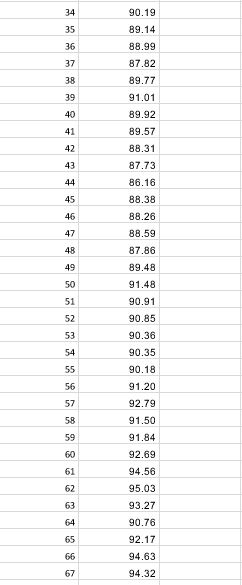
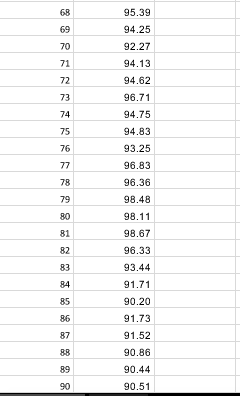
Q1) Given the following inputs: "TO 0.50% 0.40% 1.30 10% Spot USD/CAD Sigma T(months) Option Type 6 Call a) What is the T month forward USD/CAD exchange rate? b) Use the Black-Scholes formula to compute the price of a T month, at the money European style option of the type specified (put or call) on $1 million USD. (That is, the right to sell (put) /buy (call) $1 million USD and receive (put)/pay (call) the Spot(USD/CAD) * 1 million CAD.) Is the buyer of this option hoping that the US dollar will go up or down relative to the Canadian dollar? c) Compute the values for u, d. Pup Pon and use them to construct a 2 step, a 4 step, and a 10 step binomial tree, and then price the European option using each of these trees. Compare your answers to the answer you got using Black-Scholes. Do they get better as the number of time steps in the tree increase? d) Assume the option is American style instead of European style. Build 2 step, 4 step, and 10 step binomial trees to price the option. e) Assume the option is Bermuda style, with possible exercise times of T/2 and T. Build 2 step, 4 step, and 10 step binomial trees to price the option f) We know that American style >= Bermuda style >= European style. If, using the given inputs, you get the same value for any two of these, change and/or (within reason, i.e. 20% > >0) and see if you can get different answers for all three (Am style> Berm style > Euro style). Whatra andr, work for you? Why? Q2) Given the following inputs for TFS: 5099 dela divrate) 200% Sot 40% Timonths) Option Type Put a) Use the Black-Scholes formula to compute the price for the given option. Graph the payoff and profit diagrams, computing all key points. b) Suppose the bid price of the option is $0.10 less than the option price from a). Find the implied volatility corresponding to this price. This is called the bid volatility. Do the same for the ask volatility assuming the ask price is $0.10 more than the option price from c) Assume the stock price increases by 10%. Compute the new option price (using the input volatility Compute the combidiask c) Assume the stock price increases by 10%. Compute the new option price (using the input volatility). Compute the new bid/ask prices for the option using the bid/ask volatilities from b). Do the same if the stock price decrease by 10%. d) Are the new bid/ask spreads (prices) roughly the same as the initial bid/ask spread? Are the new option prices roughly in the middle of the new bid/ask spreads? Do you see why option market makers think in terms of volatilities (which change slowly) instead of prices (which change quickly)? e) Find Delta for the original option at the original spot price, and construct the delta hedged portfolio. Graph the payoff and profit diagrams, computing all key points. f) (Hard!) Show that the delta hedged portfolio has the exact same profit and payoff as an asymmetric straddle (long n1 puts, long n2 calls both at the same strike as the original option - you must find n1 and n2). Can you explain why / prove it using Put Call Parity? Q3) See the first page of the spreadsheet "Q3 Data" with 3 months (30 days/month) of price data for TFS. a) Fill in the column "Daily Returns" with the (continuously compounded) daily return. b) Compute the annualized historical volatility based on this data. c) Price a 1 month (30 day) at-the-money European call option using the Black-Scholes formula and the following inputs: 5.00% 2.00% delta (civ rate) Elias thinks the stock is going up over the next month so he buys the at-the-money call option from the market maker Angela. Elias doesn't delta hedge and simply waits until the end of 30 days to see if he makes or loses money. Angela has no opinion on whether the stock will go up or down so she immediately delta hedges her option position. The prices on the second page of "Q3 Data" are the stock prices over the 30 day lifetime of the option. d) Does Elias make or lose money? e) Fill in the column "Daily Returns" with the (continuously compounded) daily return. Compute the realized volatility (annualized) from this data. Comparing this with your answer to b) do you expect Angela to make or lose money? f) Assume Angela rebalances her delta hedge every 6 days. (ie she delta hedges the option when she sells it, and she rebalances her delta hedge at the end of days 6,12,18, and 24, and closes out her position at the end of day 30.) What is her P&L (profit or loss) when the option expires? g) Is it possible for Elias and Angela to both make (or both lose) money? Q4) Given the following inputs: 6.00% 1,00% delta (div rate) Spot Sigma T(months) Yuri constructs a portfolio that implements the following option strategy (the options are priced using the Black-Scholes formula): Butterly Spread K -10% K, Spot K-Spot - 10% a) Graph the payoff and profit diagrams, computing key points. b) Compute delta and construct the delta hedged portfolio. Also, compute omega for each individual option and for the portfolio C) Assume time doesn't change. Find the range of stock prices for which the delta hedged portfolio shows a profit, the range where it shows a loss, and the breakeven points. (Yuri never rebalances the delta hedge.) d) The same as c) but this time, find the breakeven points and the profit and loss ranges at the time the option expires. (Yuri never rebalances the delta hedge.) e) For the initial delta hedged portfolio find the range of stock prices for which gamma is positive, the range where it is negative, and the points where gamma = 0. f) The same as e) but for theta instead of gamma. Q5) Given the following inputs: 5.COM 2.00% data divate) and the following option prices Suike Call Price Put Price a) If possible, construct an arbitrage portfolio. Graph the profit and payoff diagrams, computing key points. For the next set of options, assumer, delta (div rate) as above plus Expiry Crears) 0.5 Given the following option prices (and r and delta as above) Stile Callie 1153 Put Price 1043 12.70 b) If possible construct an arbitrage portfolio. Graph the profit and payoff diagrams, computing key points. c) Compute the implied volatilities for each of these options (not the ones from part a)). Are these volatilities consistent with what we expect from fat tails and skew" in the real world? Q6) Given the following inputs for TFS: et de 25% Sigma Tooth) Option Type Put a) Find ud. p. and pe, and construct a 2 step tree to price the option. b) Compute the replicating portfolio Delta and B, at every node (except for the final set of nodes att-T. In the case of the 2 step tree, this means only for the node att = 0, but for the 3 step and 4 step trees below, you will have to compute values at 3 and 6 separate nodes respectively.) c) Compute the price and delta using the Black-Scholes formula at each node prior to expiry and compare those to your answers from a) (price) and b) (Delta). d) Do the same for the 3 stop and 4 step binomial trees. e) At time t = 0, Lin delta hedges her portfolio using the Delta from the replicating portfolio from the 4 step binomial tree. The stock price at each time step is as follows (u and d from parta): O Stock Price Spot (from inputs above) u Spot du Spot ddu Spot dudu Spot At each time step, h = T/4, 2n, 3h Lin rebalances her portfolio using the Delta from the replicating portfolio at the current node of the binomial tree, and at time t = T she closes out her portfolio. What is her net profit or e) Can you compute the value of a straddle (with the above strike and expiry) without using a separate tree for each of the two options? Q7) Recall, a binomial option pays 1 if the stock price at expiry is above the strike price, O if the stock price at expiry is at or below the strike price. Given the following inputs: 3.00 0.50% celta dive ) Spot Strike price Sigma T months) Option type omil Option a) Price the option using a 4 step binomial tree. Compute the replicating portfolio Delta and B (for a single time step) at t = 0. b) Price the option using the appropriate formula assuming the Black-Scholes framework holds. Derive the formula for Delta and compute it. b) Price the option using the bull spread approximation with n = 1 and strike prices KL = KK = K + 1 = K + 1. Compute Delta. c) Same as b) with n 4K-K, K K + 1 = K +0.25 0505 delta (vrate) Spot Strke price Sigma T months) Option type SOS Bromial Option a) Price the option using a 4 step binomial tree. Compute the replicating portfolio Delta and B (for a single time step) at t = 0. b) Price the option using the appropriate formula assuming the Black-Scholes framework holds. Derive the formula for Delta and compute it. b) Price the option using the bull spread approximation with n = 1 and strike prices K = KK = K + 1 = K + 1. Compute Delta c) Same as b) with n = 4, K = K, K = K + 1 = K +0.25 d) How big would n have to be so your prices from c) and b) were accurate to within $0.01. Day WwN Stock Price 100.00 102.64 99.80 97.97 97.18 96.86 95.47 95.90 97.95 98.79 98.52 98.85 98.23 98.00 96.73 98.07 96.91 96.14 92.86 91.05 88.92 90.10 90.29 91.12 91.65 90.03 90.30 89.32 87.73 89.66 90.41 89.33 90.39 90.19 89.14 88.99 87.82 69.77 91.01 89.92 89.57 88.31 87.73 86.16 8.38 88.26 88.59 87.86 89.48 91.48 90.91 90.85 90.36 90.35 90.18 31.20 2.79 91.50 91.84 92.69 94.56 95.03 93.27 0.76 92.17 94.63 94.32 95.39 94.25 92.27 94.13 94.62 96.71 94.75 94.83 93.25 96.83 96.36 98.48 98.11 98.67 96.33 93.44 91.71 90.20 91.73 91.52 90.86 90.44 90.51 Q1) Given the following inputs: "TO 0.50% 0.40% 1.30 10% Spot USD/CAD Sigma T(months) Option Type 6 Call a) What is the T month forward USD/CAD exchange rate? b) Use the Black-Scholes formula to compute the price of a T month, at the money European style option of the type specified (put or call) on $1 million USD. (That is, the right to sell (put) /buy (call) $1 million USD and receive (put)/pay (call) the Spot(USD/CAD) * 1 million CAD.) Is the buyer of this option hoping that the US dollar will go up or down relative to the Canadian dollar? c) Compute the values for u, d. Pup Pon and use them to construct a 2 step, a 4 step, and a 10 step binomial tree, and then price the European option using each of these trees. Compare your answers to the answer you got using Black-Scholes. Do they get better as the number of time steps in the tree increase? d) Assume the option is American style instead of European style. Build 2 step, 4 step, and 10 step binomial trees to price the option. e) Assume the option is Bermuda style, with possible exercise times of T/2 and T. Build 2 step, 4 step, and 10 step binomial trees to price the option f) We know that American style >= Bermuda style >= European style. If, using the given inputs, you get the same value for any two of these, change and/or (within reason, i.e. 20% > >0) and see if you can get different answers for all three (Am style> Berm style > Euro style). Whatra andr, work for you? Why? Q2) Given the following inputs for TFS: 5099 dela divrate) 200% Sot 40% Timonths) Option Type Put a) Use the Black-Scholes formula to compute the price for the given option. Graph the payoff and profit diagrams, computing all key points. b) Suppose the bid price of the option is $0.10 less than the option price from a). Find the implied volatility corresponding to this price. This is called the bid volatility. Do the same for the ask volatility assuming the ask price is $0.10 more than the option price from c) Assume the stock price increases by 10%. Compute the new option price (using the input volatility Compute the combidiask c) Assume the stock price increases by 10%. Compute the new option price (using the input volatility). Compute the new bid/ask prices for the option using the bid/ask volatilities from b). Do the same if the stock price decrease by 10%. d) Are the new bid/ask spreads (prices) roughly the same as the initial bid/ask spread? Are the new option prices roughly in the middle of the new bid/ask spreads? Do you see why option market makers think in terms of volatilities (which change slowly) instead of prices (which change quickly)? e) Find Delta for the original option at the original spot price, and construct the delta hedged portfolio. Graph the payoff and profit diagrams, computing all key points. f) (Hard!) Show that the delta hedged portfolio has the exact same profit and payoff as an asymmetric straddle (long n1 puts, long n2 calls both at the same strike as the original option - you must find n1 and n2). Can you explain why / prove it using Put Call Parity? Q3) See the first page of the spreadsheet "Q3 Data" with 3 months (30 days/month) of price data for TFS. a) Fill in the column "Daily Returns" with the (continuously compounded) daily return. b) Compute the annualized historical volatility based on this data. c) Price a 1 month (30 day) at-the-money European call option using the Black-Scholes formula and the following inputs: 5.00% 2.00% delta (civ rate) Elias thinks the stock is going up over the next month so he buys the at-the-money call option from the market maker Angela. Elias doesn't delta hedge and simply waits until the end of 30 days to see if he makes or loses money. Angela has no opinion on whether the stock will go up or down so she immediately delta hedges her option position. The prices on the second page of "Q3 Data" are the stock prices over the 30 day lifetime of the option. d) Does Elias make or lose money? e) Fill in the column "Daily Returns" with the (continuously compounded) daily return. Compute the realized volatility (annualized) from this data. Comparing this with your answer to b) do you expect Angela to make or lose money? f) Assume Angela rebalances her delta hedge every 6 days. (ie she delta hedges the option when she sells it, and she rebalances her delta hedge at the end of days 6,12,18, and 24, and closes out her position at the end of day 30.) What is her P&L (profit or loss) when the option expires? g) Is it possible for Elias and Angela to both make (or both lose) money? Q4) Given the following inputs: 6.00% 1,00% delta (div rate) Spot Sigma T(months) Yuri constructs a portfolio that implements the following option strategy (the options are priced using the Black-Scholes formula): Butterly Spread K -10% K, Spot K-Spot - 10% a) Graph the payoff and profit diagrams, computing key points. b) Compute delta and construct the delta hedged portfolio. Also, compute omega for each individual option and for the portfolio C) Assume time doesn't change. Find the range of stock prices for which the delta hedged portfolio shows a profit, the range where it shows a loss, and the breakeven points. (Yuri never rebalances the delta hedge.) d) The same as c) but this time, find the breakeven points and the profit and loss ranges at the time the option expires. (Yuri never rebalances the delta hedge.) e) For the initial delta hedged portfolio find the range of stock prices for which gamma is positive, the range where it is negative, and the points where gamma = 0. f) The same as e) but for theta instead of gamma. Q5) Given the following inputs: 5.COM 2.00% data divate) and the following option prices Suike Call Price Put Price a) If possible, construct an arbitrage portfolio. Graph the profit and payoff diagrams, computing key points. For the next set of options, assumer, delta (div rate) as above plus Expiry Crears) 0.5 Given the following option prices (and r and delta as above) Stile Callie 1153 Put Price 1043 12.70 b) If possible construct an arbitrage portfolio. Graph the profit and payoff diagrams, computing key points. c) Compute the implied volatilities for each of these options (not the ones from part a)). Are these volatilities consistent with what we expect from fat tails and skew" in the real world? Q6) Given the following inputs for TFS: et de 25% Sigma Tooth) Option Type Put a) Find ud. p. and pe, and construct a 2 step tree to price the option. b) Compute the replicating portfolio Delta and B, at every node (except for the final set of nodes att-T. In the case of the 2 step tree, this means only for the node att = 0, but for the 3 step and 4 step trees below, you will have to compute values at 3 and 6 separate nodes respectively.) c) Compute the price and delta using the Black-Scholes formula at each node prior to expiry and compare those to your answers from a) (price) and b) (Delta). d) Do the same for the 3 stop and 4 step binomial trees. e) At time t = 0, Lin delta hedges her portfolio using the Delta from the replicating portfolio from the 4 step binomial tree. The stock price at each time step is as follows (u and d from parta): O Stock Price Spot (from inputs above) u Spot du Spot ddu Spot dudu Spot At each time step, h = T/4, 2n, 3h Lin rebalances her portfolio using the Delta from the replicating portfolio at the current node of the binomial tree, and at time t = T she closes out her portfolio. What is her net profit or e) Can you compute the value of a straddle (with the above strike and expiry) without using a separate tree for each of the two options? Q7) Recall, a binomial option pays 1 if the stock price at expiry is above the strike price, O if the stock price at expiry is at or below the strike price. Given the following inputs: 3.00 0.50% celta dive ) Spot Strike price Sigma T months) Option type omil Option a) Price the option using a 4 step binomial tree. Compute the replicating portfolio Delta and B (for a single time step) at t = 0. b) Price the option using the appropriate formula assuming the Black-Scholes framework holds. Derive the formula for Delta and compute it. b) Price the option using the bull spread approximation with n = 1 and strike prices KL = KK = K + 1 = K + 1. Compute Delta. c) Same as b) with n 4K-K, K K + 1 = K +0.25 0505 delta (vrate) Spot Strke price Sigma T months) Option type SOS Bromial Option a) Price the option using a 4 step binomial tree. Compute the replicating portfolio Delta and B (for a single time step) at t = 0. b) Price the option using the appropriate formula assuming the Black-Scholes framework holds. Derive the formula for Delta and compute it. b) Price the option using the bull spread approximation with n = 1 and strike prices K = KK = K + 1 = K + 1. Compute Delta c) Same as b) with n = 4, K = K, K = K + 1 = K +0.25 d) How big would n have to be so your prices from c) and b) were accurate to within $0.01. Day WwN Stock Price 100.00 102.64 99.80 97.97 97.18 96.86 95.47 95.90 97.95 98.79 98.52 98.85 98.23 98.00 96.73 98.07 96.91 96.14 92.86 91.05 88.92 90.10 90.29 91.12 91.65 90.03 90.30 89.32 87.73 89.66 90.41 89.33 90.39 90.19 89.14 88.99 87.82 69.77 91.01 89.92 89.57 88.31 87.73 86.16 8.38 88.26 88.59 87.86 89.48 91.48 90.91 90.85 90.36 90.35 90.18 31.20 2.79 91.50 91.84 92.69 94.56 95.03 93.27 0.76 92.17 94.63 94.32 95.39 94.25 92.27 94.13 94.62 96.71 94.75 94.83 93.25 96.83 96.36 98.48 98.11 98.67 96.33 93.44 91.71 90.20 91.73 91.52 90.86 90.44 90.51











 these graphs are for number 3 please help me
these graphs are for number 3 please help me 





