Question
This case study will provide a thorough illustration as to the concepts of consolidations on the date of acquisition. On this date, an ensuing Consolidated
This case study will provide a thorough illustration as to the concepts of consolidations on the date of acquisition. On this date, an ensuing Consolidated Balance Sheet is created, whereby the acquiring and the acquired companies are combined as a single entity. Interestingly, there are options as to the consolidation basis which may be utilized, which also includes the push-down method of accounting. The pushdown method was illustrated in a previous case study and it is highly recommended that the reader resort to this, which can be found in Harris & Dilling (2015). An overview of this critical topic will be discussed, followed by a comprehensive illustration demonstrating the results of consolidated results as of the date of acquisition. Note that the resulting Balance Sheet will be the same with the push-down accounting result. This case study is recommended as a group project for an Advanced Accounting course as well as for a graduate Financial Statement Analysis class.
Facts: On December 31, 2011, PA. Inc. purchased 95 percent of Sub. Inc. for $120,000 cash. The Balance Sheet of each corporation just prior to the acquisition is presented below. Additionally, book value and fair value for all of Sub’s assets and liabilities are equal, with the exception of Property, Plant and Equipment, whose fair value is $47,000.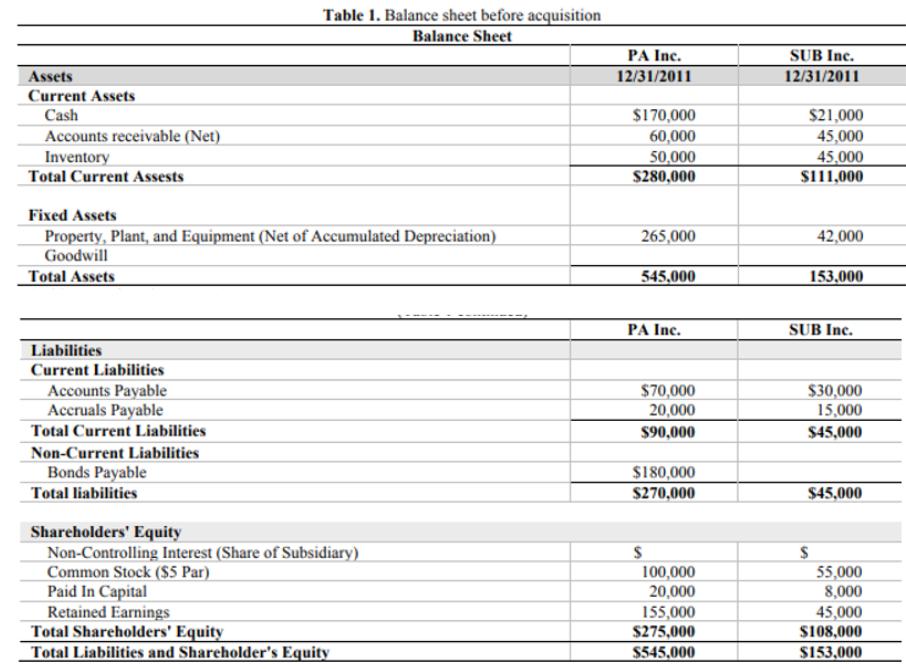
Can you calculate the ROE for this acquisition? Start by defining the ROE, listing the formula and its three main components. Then, define what factors are missing and where to find them?
Table 1. Balance sheet before acquisition Balance Sheet PA Inc. SUB Inc. Assets 12/31/2011 12/31/2011 Current Assets $21,000 45,000 45,000 $111,000 Cash $170,000 Accounts receivable (Net) Inventory Total Current Assests 60,000 50,000 $280,000 Fixed Assets Property, Plant, and Equipment (Net of Accumulated Depreciation) Goodwill Total Assets 265,000 42,000 545,000 153,000 PA Inc. SUB Inc. Liabilities Current Liabilities Accounts Payable Accruals Payable $70,000 20,000 $90,000 $30,000 15,000 Total Current Liabilities $45,000 Non-Current Liabilities Bonds Payable $180,000 $270,000 Total liabilities $45,000 Shareholders' Equity Non-Controlling Interest (Share of Subsidiary) Common Stock ($5 Par) Paid In Capital Retained Earnings Total Shareholders' Equity Total Liabilities and Shareholder's Equity 100,000 20,000 155,000 $275,000 55,000 8,000 45,000 $108,000 $545,000 $153,000
Step by Step Solution
3.52 Rating (152 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Return n equity Frmul Net inme bk vlue f equity Return n equity r RE fr shrt is simly the munt f inm...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


