Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
This class uses Geankoplis, Transport Processes and Separations Process Principles, 5th Edition. Please use *only* this book to develop the answer as we are allowed

 This class uses Geankoplis, Transport Processes and Separations Process Principles, 5th Edition. Please use *only* this book to develop the answer as we are allowed the book on the exam. When an equation is used, please indicated where it was taken from so I can follow along.
This class uses Geankoplis, Transport Processes and Separations Process Principles, 5th Edition. Please use *only* this book to develop the answer as we are allowed the book on the exam. When an equation is used, please indicated where it was taken from so I can follow along.
I have no idea where to start. I failed the section on heat transport last semester and now similar terms and ideas are showing up again through diffusion. We are learning about unsteady state transfer.
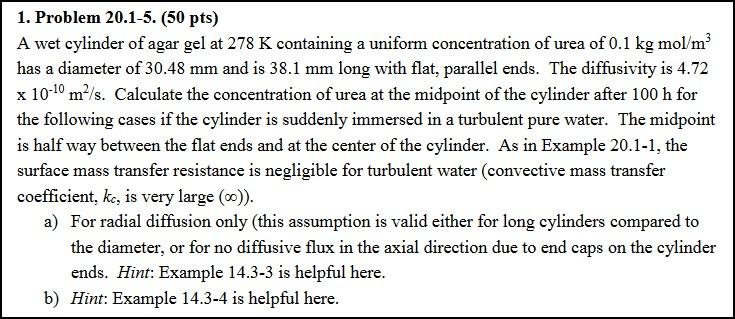
20.1-5. Unsteady-State Diffusion in a Cylinder of Agar Gel. A wet cylinder of agar gel at 278 K containing a uniform concentration of urea of 0.1 kg mol/m2 has a diameter of 30.48 mm and is 38.1 mm long with flat, parallel ends. The diffusivity is 4.72 10-10 m/s. Calculate the concentration at the midpoint of the cylinder after 100 h for the following cases if the cylinder is suddenly immersed in turbulent pure water: a. For radial diffusion only. b. Diffusion occurs radially and axially. 1. Problem 20.1-5. (50 pts) A wet cylinder of agar gel at 278 K containing a uniform concentration of urea of 0.1 kg mol/m has a diameter of 30.48 mm and is 38.1 mm long with flat, parallel ends. The diffusivity is 4.72 x 10-10 m-/s. Calculate the concentration of urea at the midpoint of the cylinder after 100 h for the following cases if the cylinder is suddenly immersed in a turbulent pure water. The midpoint is half way between the flat ends and at the center of the cylinder. As in Example 20.1-1, the surface mass transfer resistance is negligible for turbulent water (convective mass transfer coefficient, kc, is very large (0)). a) For radial diffusion only (this assumption is valid either for long cylinders compared to the diameter, or for no diffusive flux in the axial direction due to end caps on the cylinder ends. Hint: Example 14.3-3 is helpful here. b) Hint: Example 14.3-4 is helpful hereStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


