



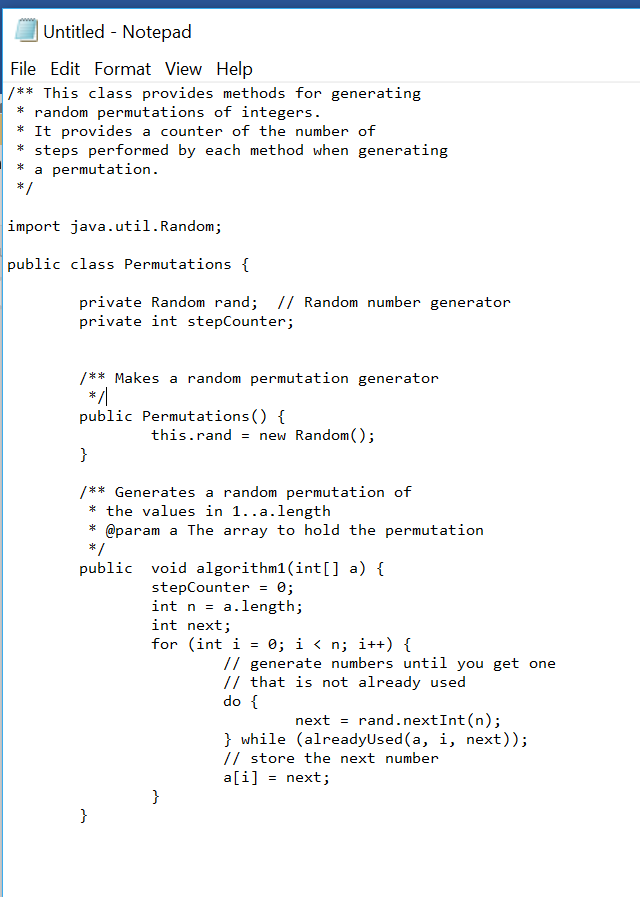

This exercise involves several algorithms for generating random permutations of the integers in 1.N. For example, when N-5, [3, 1, 5,4,2] and [1, 5, 2,4, 3] are legal permutations, but [4, 2,1, 5, 1 is not because the integer 1 is duplicated and 3 is missing. The files Permutations iava and exercise. Create a new Java project in Eclipse and load these files into it. contain most of the code for the The Random class has methods for generating pseudo-random numbers. The method nextInt (n) returns a random integer in 0..n-1 Tracing in debug mode Open the PermutationTester class in an editor windo. Double-click in the left margin next to the statement p.algorithm1 (a) This should display a blue dot next to the statement, which marks a "break point". When run in debug mode, the program will pause at this line. Click to start execution of the program. The program will stop the bug icon at the breakpoint. Eclipse will also change to the "Debug perspective" that shows panel with a list of al1 visible variables and their values in the upper right corner 1) What values are stored in array perm? Click the Step Over iconto execute the method call. 2) What values are stored in array perm now? It is not correct according to the problem specifications described above. What is wrong? The error is in the statement inside the do-while loop in the algorithml method of the Permutations class. Fix the ercheck the Javadoc for the nextInt method if necessary) and run the tester in debug mode again to make sure it is now correct. Add two more statements to the main method to also run algorithm2 and algorithm3. Run the program in debug mode again and execution will pause at the breakpoint. 3) Advance one statement and write down the contents of array perm after algorithml executes. Do the same for algorithm2 and algorithm Measuring Algorithm Performance The most significant factor affecting the performance of these algorithms is the number of loop interations performed. The Permutations class has a variable stepCounter that wil1 be used to count the loop iterations This exercise involves several algorithms for generating random permutations of the integers in 1.N. For example, when N-5, [3, 1, 5,4,2] and [1, 5, 2,4, 3] are legal permutations, but [4, 2,1, 5, 1 is not because the integer 1 is duplicated and 3 is missing. The files Permutations iava and exercise. Create a new Java project in Eclipse and load these files into it. contain most of the code for the The Random class has methods for generating pseudo-random numbers. The method nextInt (n) returns a random integer in 0..n-1 Tracing in debug mode Open the PermutationTester class in an editor windo. Double-click in the left margin next to the statement p.algorithm1 (a) This should display a blue dot next to the statement, which marks a "break point". When run in debug mode, the program will pause at this line. Click to start execution of the program. The program will stop the bug icon at the breakpoint. Eclipse will also change to the "Debug perspective" that shows panel with a list of al1 visible variables and their values in the upper right corner 1) What values are stored in array perm? Click the Step Over iconto execute the method call. 2) What values are stored in array perm now? It is not correct according to the problem specifications described above. What is wrong? The error is in the statement inside the do-while loop in the algorithml method of the Permutations class. Fix the ercheck the Javadoc for the nextInt method if necessary) and run the tester in debug mode again to make sure it is now correct. Add two more statements to the main method to also run algorithm2 and algorithm3. Run the program in debug mode again and execution will pause at the breakpoint. 3) Advance one statement and write down the contents of array perm after algorithml executes. Do the same for algorithm2 and algorithm Measuring Algorithm Performance The most significant factor affecting the performance of these algorithms is the number of loop interations performed. The Permutations class has a variable stepCounter that wil1 be used to count the loop iterations












