Question: This has to be in the java program. Can you label sections of the code with commented descriptions. Also, explain the program. Thank you ahead
This has to be in the java program. Can you label sections of the code with commented descriptions. Also, explain the program. Thank you ahead of time:-)
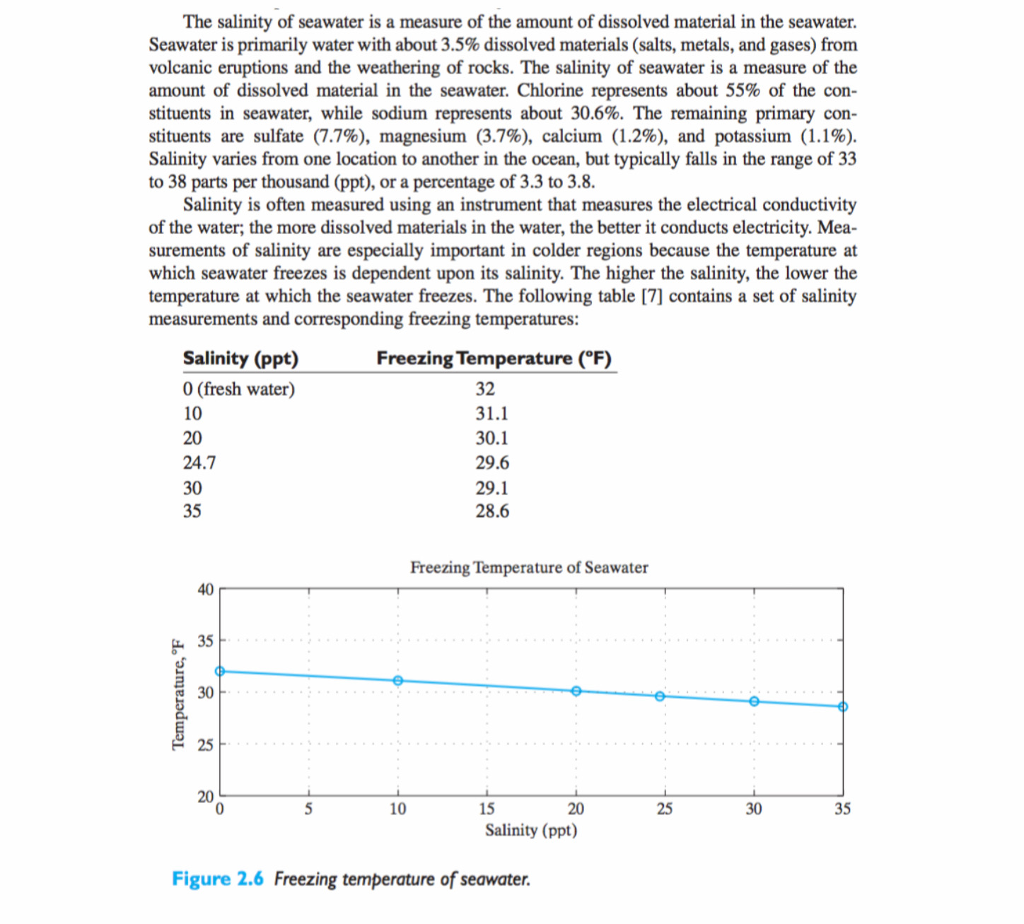

The salinity of seawater is a measure of the amount of dissolved material in the seawater. Seawater is primarily water with about 3.5% dissolved materials (salts, metals, and gases) from volcanic eruptions and the weathering of rocks. The salinity of seawater is a measure of the amount of dissolved material in the seawater. Chlorine represents stituents in seawater, while sodium stituents are sulfate (7.7%), magnesium (3.7%), calcium (1.2%), and potassium (1.1%). Salinity varies from one location to another in the ocean, but typically falls in the range of 33 to 38 parts per thousand (ppt), or a percentage of 3.3 to 3.8 about 55% of the con sents about 30.6%. The remaining primary con repre Salinity is often measured using an instrument that measures the electrical conductivity of the water; the more dissolved materials in the water, the better it conducts electricity. Mea surements of salinity are especially important in colder regions because the temperature at which seawater freezes is dependent upon its salinity. The higher the salinity, the lower the temperature at which the seawater freezes. The following table [7] contains a set of salinity measurements and corresponding freezing temperatures: Salinity (ppt) 0 (fresh water) 10 20 24.7 Freezing Temperature (F) 32 31.1 30.1 29.6 29.1 28.6 35 Freezing Temperature of Seawater 40 35 25 20 10 15 Salinity (ppt) 20 25 30 35 Figure 2.6 Freezing temperature of seawater Suppose that we want to determine the freezing temperature for water with a salinity meas- urement of 33 ppt. From the data, we see that this point falls between 30 and 35 ppt: a 30 29.1f(a) b 33 35 28.6 rc) f(b) Using the linear equation formula, we can compute f(b): 29.1 +3/5. (28.6- 29.1) = 28.8. Problem: Use linear interpolation to compute a new freezing temperature for water with a specified salinity. The user is asked to enter a and fa), c and f(c), and b. Your program should calculate and displays f(b). If the user provides a salinity value that is below 0 or above 35, display an appropriate error Sample Output: Enter the lower salinity and associated freezing point temperature: 30 29.1 Enter the upper salinity and associated freezing point temperature: 35 28.6 Enter the salinity for which the associated freezing point temperature is desired: New freezing temperature is 28.8 degrees F Enter the lower salinity and associated freezing point temperature: 5 30.3 SALINITY VALUE IS OUT OF RANGE VALUE SHOULD BE BETWEEN 0 AND 35
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


