This is a lab I did. The graph below says pH is 13.1. Is this the end point being asked for in question 1b? I'm not sure if my numbers or math are correct, so please check every question over and let me know if it is right and if anything isn't, please show your work on how you did or found something.
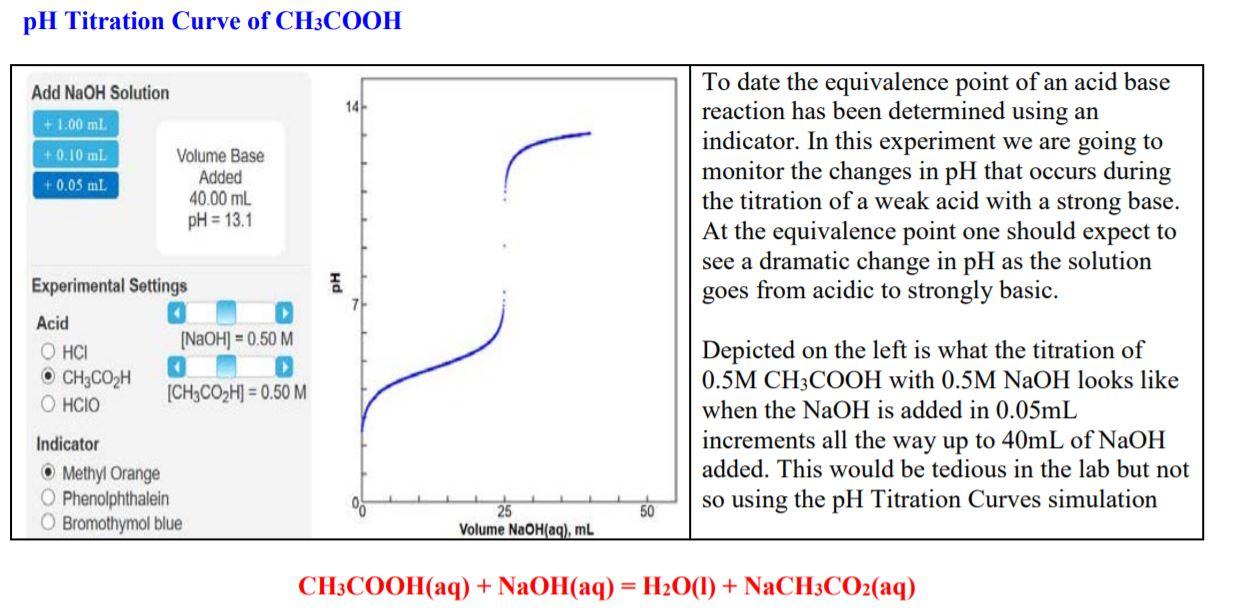
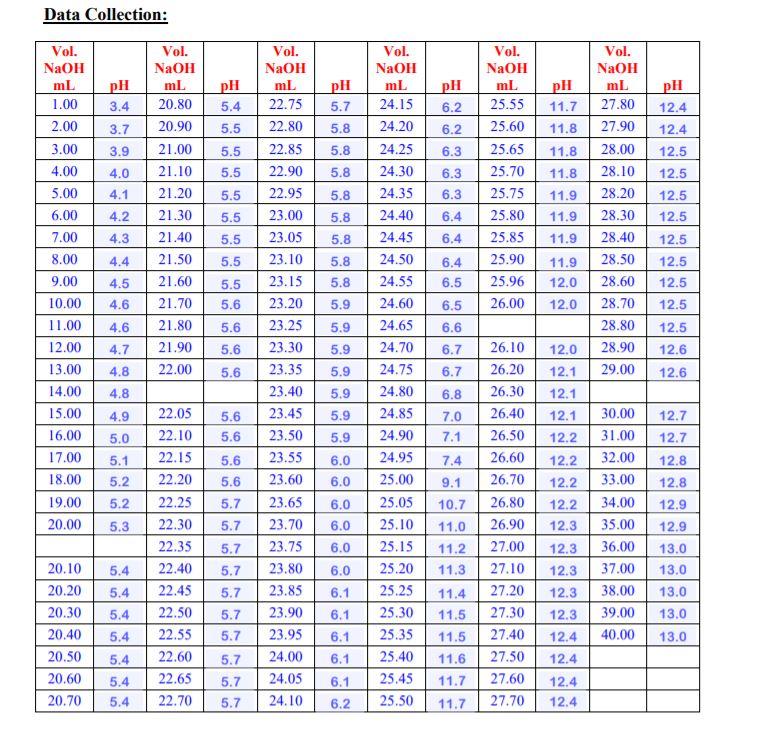
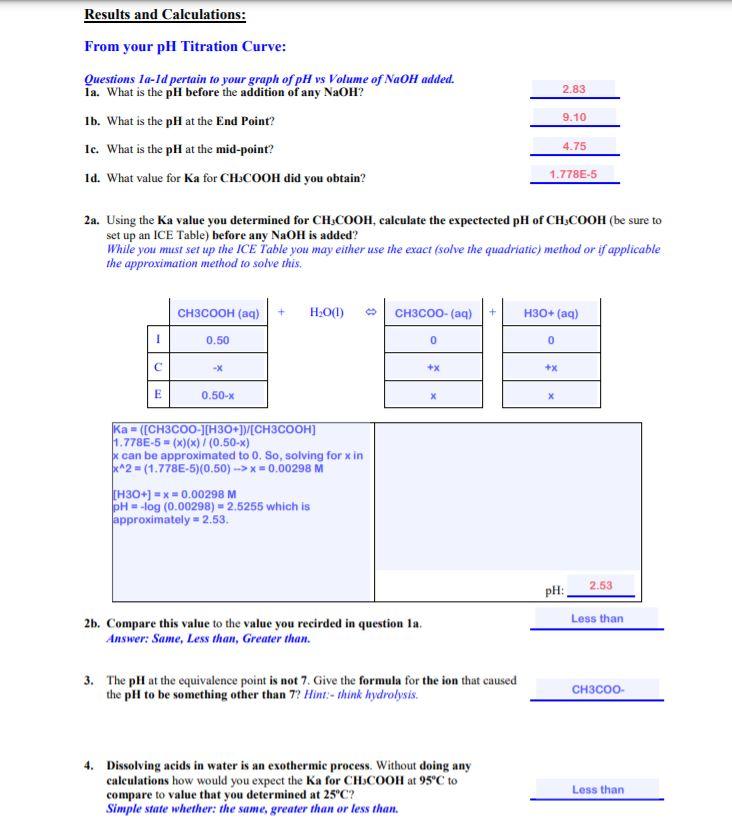
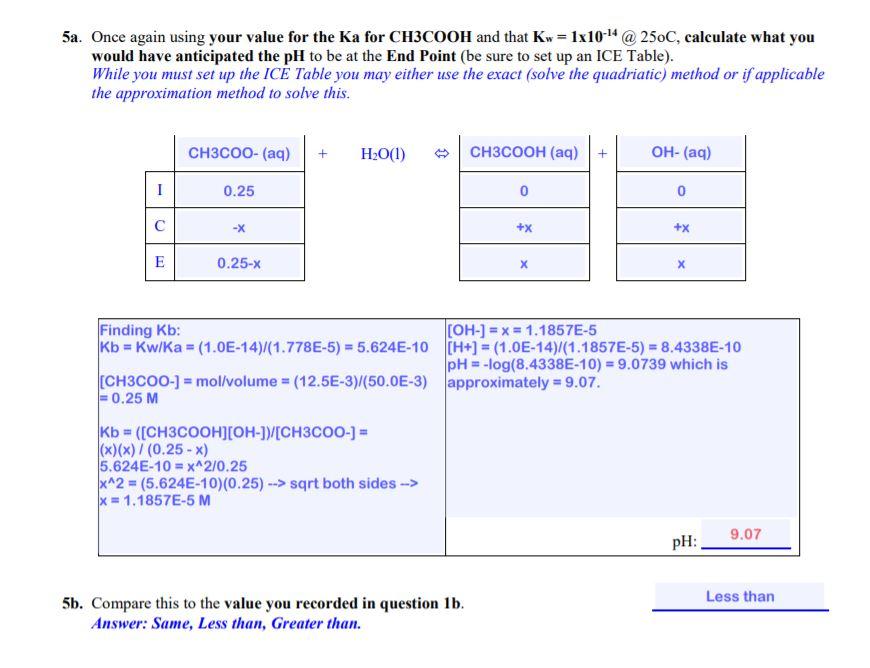
pH Titration Curve of CH3COOH Add NaOH Solution 14 +1.00 ml +0.10 ml +0.05 ml Volume Base Added 40.00 mL pH = 13.1 To date the equivalence point of an acid base reaction has been determined using an indicator. In this experiment we are going to monitor the changes in pH that occurs during the titration of a weak acid with a strong base. At the equivalence point one should expect to see a dramatic change in pH as the solution goes from acidic to strongly basic. Experimental Settings [NaOH] = 0.50 M Acid OHCI CH3COH HCIO [CH3CO2H] = 0.50 M Depicted on the left is what the titration of 0.5M CH3COOH with 0.5M NaOH looks like when the NaOH is added in 0.05mL increments all the way up to 40mL of NaOH added. This would be tedious in the lab but not so using the pH Titration Curves simulation Indicator Methyl Orange O Phenolphthalein O Bromothymol blue 50 Volume NaOH(aq), ml CH3COOH(aq) + NaOH(aq) = H2O(l) + NaCH3CO2(aq) Data Collection: pH 5.4 5.5 5.5 5.5 pH 5.7 5.8 5.8 5.8 5.8 pH 6.2 6.2 6.3 6.3 6.3 Vol. NaOH ml 20.80 20.90 21.00 21.10 21.20 21.30 21.40 21.50 21.60 21.70 21.80 21.90 22.00 Vol. NaOH ml 25.55 25.60 25.65 25.70 25.75 25.80 25.85 25.90 25.96 26.00 pH 12.4 12.4 12.5 12.5 12.5 12.5 Vol. NaOH mL 1.00 2.00 3.00 4.00 5.00 6.00 7.00 8.00 9.00 10.00 11.00 12.00 13.00 14.00 15.00 16.00 17.00 18.00 19.00 20.00 pH 11.7 11.8 11.8 11.8 11.9 11.9 11.9 11.9 12.0 12.0 5.8 6.4 pH 3.4 3.7 3.9 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.6 4.7 4.8 4.8 4.9 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.2 5.3 Vol. NaOH mL 27.80 27.90 28.00 28.10 28.20 28.30 28.40 28.50 28.60 28.70 28.80 28.90 29.00 6.4 6.4 5.5 5.5 5.5 5.5 5.5 5.6 5.6 5.6 5.6 5.8 5.8 5.8 5.9 12.5 12.5 12.5 12.5 5.9 Vol. NaOH ml 22.75 22.80 22.85 22.90 22.95 23.00 23.05 23.10 23.15 23.20 23.25 23.30 23.35 23.40 23.45 23.50 23.55 23.60 23.65 23.70 23.75 23.80 23.85 23.90 23.95 24.00 24.05 24.10 Vol. NaOH mL 24.15 24.20 24.25 24.30 24.35 24.40 24.45 24.50 24.55 24.60 24.65 24.70 24.75 24.80 24.85 24.90 24.95 25.00 25.05 25.10 25.15 25.20 25.25 25.30 25.35 25.40 25.43 25.50 12.5 12.6 12.6 5.9 5.9 5.9 5.9 5.6 5.6 5.9 6.0 22.05 22.10 22.15 22.20 22.25 22.30 22.35 22.40 22.45 22.50 22.55 22.60 22.65 22.70 5.6 5.6 5.7 5.7 5.7 5.7 5.7 5.7 5.7 5.7 6.5 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.7 6.8 7.0 7.1 7.4 9.1 10.7 11.0 11.2 11.3 11.4 11.5 11.5 11.6 11.7 11.7 26.10 26.20 26.30 26.40 26.50 26.60 26.70 26.80 26.90 27.00 27.10 27.20 27.30 27.40 27.50 27.60 27.70 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.0 6.1 6.1 6.1 6.1 12.0 12.1 12.1 12.1 12.2 12.2 12.2 12.2 12.3 12.3 12.3 12.3 12.3 12.4 12.4 12.4 12.4 30.00 31.00 32.00 33.00 34.00 35.00 36.00 37.00 38.00 39.00 40.00 20.10 20.20 20.30 20.40 20.50 20.60 20.70 12.7 12.7 12.8 12.8 12.9 12.9 13.0 13.0 13.0 13.0 13.0 5.4 5.4 5.4 5.4 5.4 5.4 5.4 5.7 6.1 5.7 6.2 2.83 Results and Calculations: From your pH Titration Curve: Questions 1a-1d pertain to your graph of pH vs Volume of NaOH added. ia. What is the pH before the addition of any NaOH? Ib. What is the pH at the End Point? Ic. What is the pH at the mid-point? 1d. What value for Ka for CHCOOH did you obtain? 9.10 4.75 1.778E-5 2a. Using the Ka value you determined for CH.COOH, calculate the expectected pH of CH3COOH (be sure to set up an ICE Table) before any NaOH is added? While you must set up the ICE Table you may either use the exact (solve the quadriatic) method or if applicable the approximation method to solve this. CH3COOH (aq) + H2O(1) CH3COO- (aq) H30+ (aq) 1 0.50 0 0 C -X +x +x E 0.50-X X Ka = ([CH3COO-JH3O+][CH3COOH] 1.778E-5 - (x)(x)/(0.50-x) x can be approximated to 0. So, solving for xin x^2 = (1.778E-5)(0.50) --> x=0.00298 M [H3O+] = -0.00298 M pH = -log(0.00298) - 2.5255 which is approximately -2.53. pH: 2.53 Less than 2b. Compare this value to the value you recirded in question la Answer: Same, Less than, Greater than. 3. The pH at the equivalence point is not 7. Give the formula for the ion that caused the pH to be something other than 7? Hint-think hydrolysis. CH3COO- 4. Dissolving acids in water is an exothermic process. Without doing any calculations how would you expect the Ka for CH3COOH at 95C to compare to value that you determined at 25C? Simple state whether the same, greater than or less than. Less than 5a. Once again using your value for the Ka for CH3COOH and that Kw = 1x10-4 @ 250C, calculate what you would have anticipated the pH to be at the End Point (be sure to set up an ICE Table). While you must set up the IC Table you may either use the exact (solve the quadriatic) method or if applicable the approximation method to solve this. CH3COO- (aq) + H2O(1) CH3COOH (aq) + OH- (aq) 1 0.25 0 0 +x +x E 0.25-x X Finding Kb: [OH-] = x = 1.1857E-5 Kb = Kw/Ka = (1.0E-14)/(1.778E-5) = 5.624E-10 (H+) = (1.0E-14)/(1.1857E-5) = 8.4338E-10 pH = -log(8.4338E-10) = 9.0739 which is CH3COO-) = mollvolume = (12.5E-3)/(50.0E-3) approximately = 9.07. = 0.25 M Kb = ([CH3COOH][OH-]Y[CH3COO-) = (x)()/(0.25 - x) 5.624E-10 = x^2/0.25 x^2 = (5.624E-10)(0.25) --> sqrt both sides --> x = 1.1857E-5 M pH: 9.07 Less than 5b. Compare this to the value you recorded in question 1b. Answer: Same, Less than, Greater than










