Question
This is a Physics Lab. About Force Table. You don't need to give me the calculation or explanation. You just need to fill in table
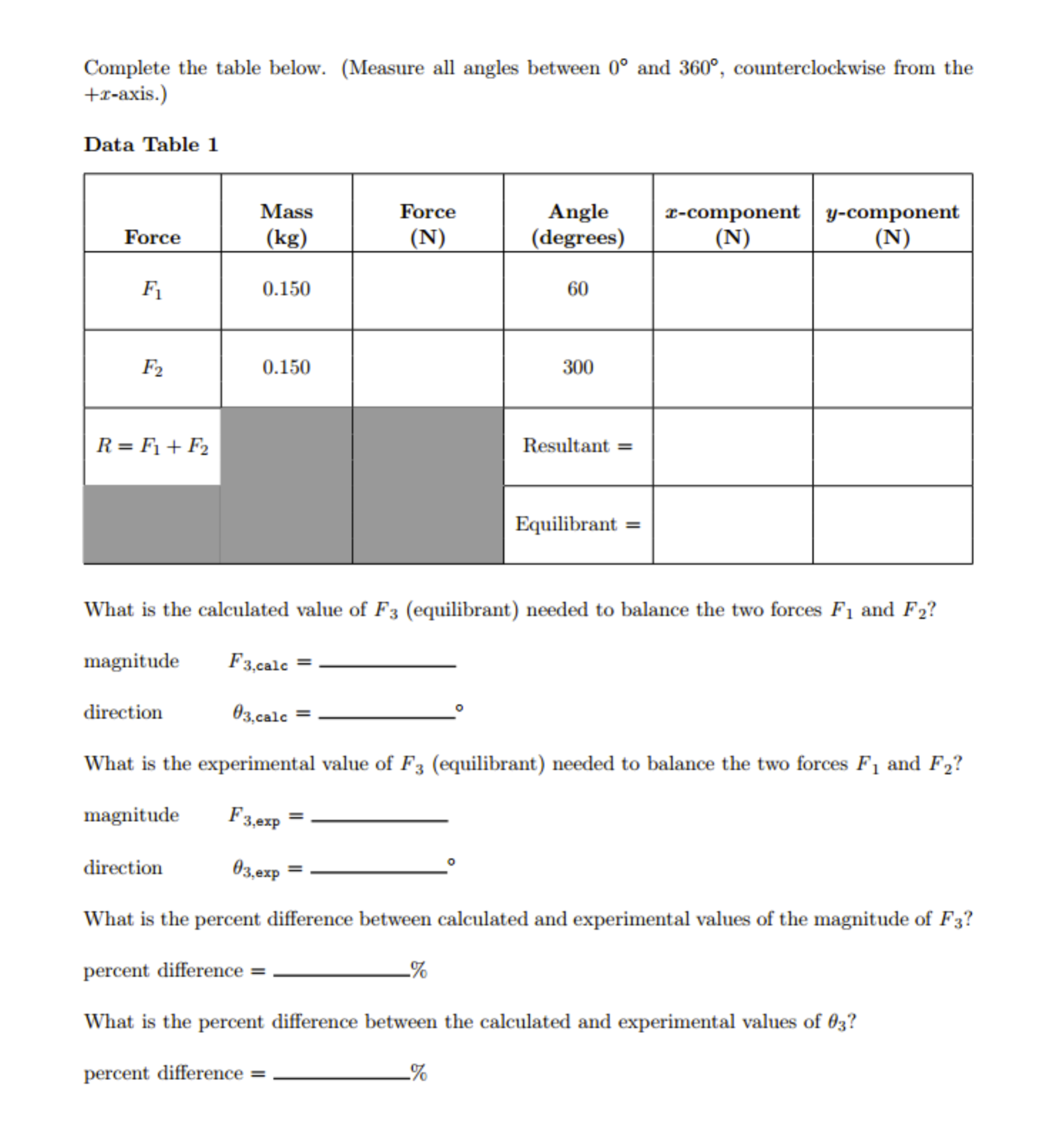
This is a Physics Lab. About Force Table.
You don't need to give me the calculation or explanation. You just need to fill in table 1 based on the information below. It may need some small calculations.
This is the additional data my instructor gave:
"The data you need from me is Data Table 1:
Equilibrant x-component - 1.446 N, y-component - 0.025
Magnitude of F3,exp =1.446 N
direction, theta3,exp = 179 deg."
This is the Lab Procedure and Questions:
"To make it easier to read the angles, assume the x-axis to be from the 180 mark to the 0 mark, with 0 being the positive x-direction, and the y-axis to be from the 270 mark to the 90 mark with 90 being the positive y-direction.
Procedure A: Finding the Equilibrant of Two Known Forces
1. Use the bubble level to check if the circular platform is horizontal. Use the leveling screws, if necessary, to make the necessary adjustments.
2. You are given two 150 g masses that are to be placed at 60 and 300.
Remember that the weight hangers have a mass of 50 g each and this needs to be included as part of the hanging mass. You will determine the magnitude (in Newtons) and angle of the third force needed to balance the forces due to these two masses.
3. Represent these forces as vectors on the diagram in the worksheet. Be sure to include the axes. Each vector in the diagram should be drawn so that the larger the vector the bigger the force it represents.
4. Calculate the x and y components (to the nearest thousandth of a newton) and enter these values in Data Table 1 on the worksheet.
5. Find the x and y components of the resultant of the two vectors and enter these values in Data Table 1 on the worksheet.
6. Now calculate the x and y components of the equilibrant of these two vectors and enter these values on the worksheet.
7. Using Equation (9) (A^2 = Ax^2 + Ay^2) and (12) 0 = tan^-1 (Ay/Ax) to calculate the magnitude and angle of the equilibrant. Enter these values on the worksheet. These are the calculated value of the third force.
8. Add this vector to your diagram to represent the third force.
9. Position the third string at the angle you determined in step 6 and hang the mass (including the hanger mass) corresponding to the calculated third force to represent the third force.
Make adjustments (if needed) to the mass and the angle until the ring is at the center. Record this value on the worksheet.
10. Compare the calculated and experimental values for the third force by computing the percent difference between the two values. See Appendix B.
11. Compare the calculated and experimental values of the angle for the third force by computing the percent difference between the two angle values.
Thanks so much in advance!
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


