This is for Java:
Example:
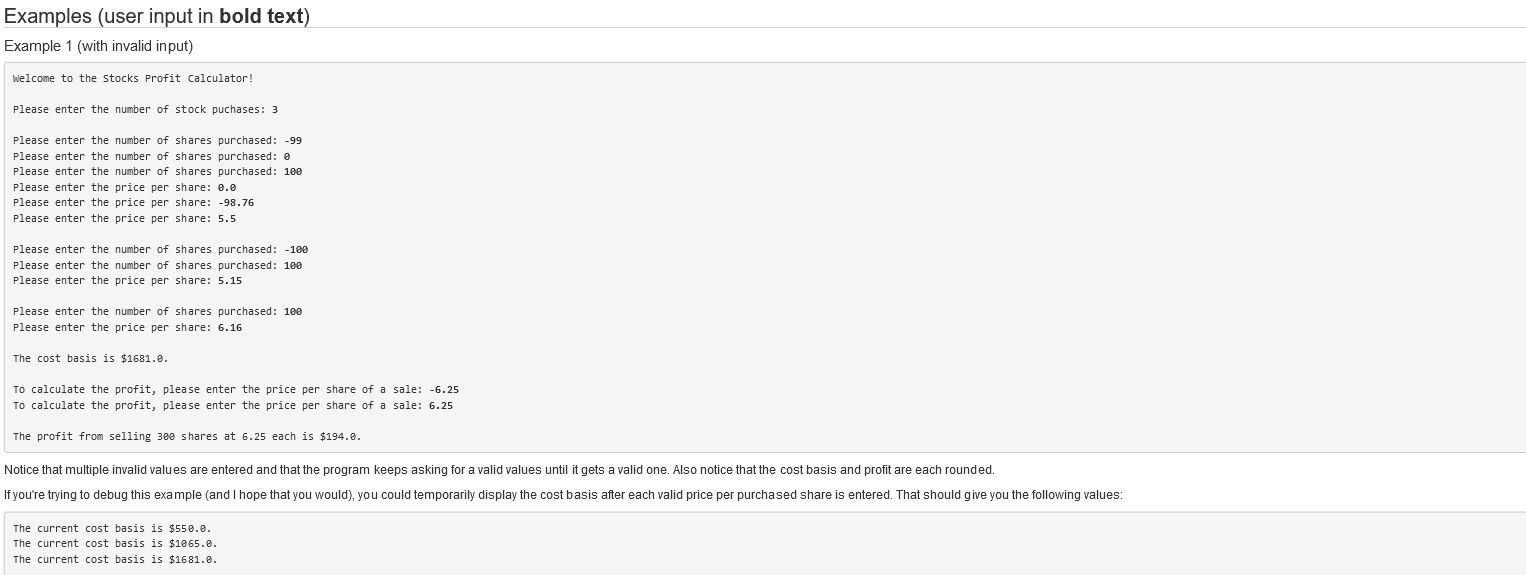
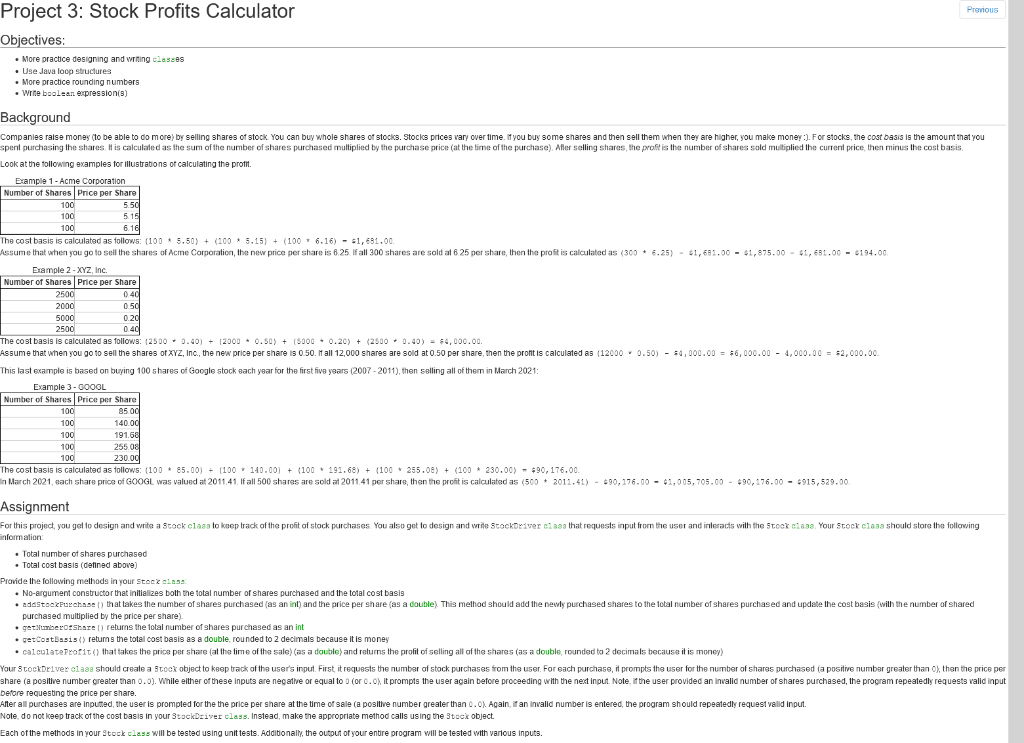
Previous Project 3: Stock Profits Calculator Objectives: . More practice designing and writing classes Use Java loop structures More practice rounding numbers Write boolean expression(s) Background Companies raise money to be able to do more) by selling shares of stock You can buy whole shares of stocks. Stocks prices vary over time. If you buy some shares and then sell them when they are higher, you make money :). For stocks, the cost basis is the amount that you spent purchasing the shares. It is calculated as the sum of the number of shares purchased multiplied by the purchase price (at the time of the purchase) After selling shares the profit is the number of shares sold multiplied the current price, then minus the cost basis Look at the following examples for illustrations or calculating the profit Example 1 - Acme Corporation Number of Shares Price per Share 100 5.50 100 5.15 100 6.16 The cost basis is calculated as follows: (100 * 5.50) + (100 5.15) + (100 - 6.16) - $1,631.00 Assume that when you go to sell the shares of Acme Corporation, the new price per share is 8 25 If all 300 shares are sold at 6 25 per share, then the profit is calculated as (300 * 6.25) - $1,681.00 - $1,875.00 - $1,631.00 - $194.00 Example 2 - XYZ, Inc. Number of Shares Price per Share 2500 0 40 2000 0.50 5000 0.20 2500 0.40 The cost basis is calculated as follows: 2500 0.40) + 12000 - 0.50) + (5000 -0.20) + (2500 0.40) = $4,000.00 Assume that when you go to sell the shares of XYZ, Inc., the new price per share is 0.50. If all 12,000 shares are sold at 0.50 per share, then the prontis calculated as (12000 - 0.50) - 34,000.00 = $6,000.00 - 4,000.00 = $2,000.00 This last example is based on buying 100 shares of Google stock sach year for the first five years (2007-2011), then selling all of them in March 2021: Example 3 - GOOOL Number of Shares Price per Share 100 85.00 100 140.00 100 191.68 100 255.08 100 230.00 The cost basis is calculated as follows: (100 85.00) + (100 140.00) + (100 191.68) + (100255.08) + (100 230.00) - $90, 176.00 In March 2021, sach share price of GOOGL was valued at 2011.41. If all 500 shares are sold at 2011.41 per share, then the profit is calculated as (500 + 2011.41) - $90,176.00 - 41,005,705.00 - $90,176.00 - 4915,529.00 Assignment For this project, you get to design and write a Stock class to keep track of the profit of stock purchases. You also get to design and write cockriver class that requests input from the user and interacts with the stock claas Your Stock class should store the following information: Total number of shares purchased Total cost basis (defined above) Provide the following methods in your stock class No-argument constructor that initializes both the total number of shares purchased and the total cost basis .addStockPurchase that takes the number of shares purchased as an ind) and the price per share (as a double). This method should add the newly purchased shares to the total number of shares purchased and update the cost basis with the number of shared purchased multiplied by the price per share) getumero:Share) returns the total number of shares purchased as an int .getCostasis) returns the total cost basis as a double, rounded to 2 decimals because it is money calculateprofit() that takes the price per share (at the time of the sale) (as a double) and returns the profit of selling all of the shares (as a double, rounded to 2 decimals because it is money) Your StockDriver class should create a stock object to keep track of the user's input. First, it requests the number of stock purchases from the user. For each purchase, it prompts the user for the number of shares purchased a positive number greater than o), then the price per share (a positive number greater than 0.0). While either of these inputs are negative or equal to (or 0.0), it prompts the user again before proceeding with the next input. Note, in the user provided an invalid number of shares purchased, the program repeatedly requests valid input before requesting the price per share. After all purchases are inputted, the user is prompted for the the price per share at the time of sale (a positive number greater than 0.0). Again, an invalid number is entered the program should repeatedly request valid input. Note do not keep track of the cost basis in your StockDriver class. Instead, make the appropriate method calls using the stock object Each of the methods in your stock class will be tested using unit tests. Additionally, the output of your entire program will be tested with various inputs. . Examples (user input in bold text) Example 1 (with invalid input) Welcome to the stocks Profit Calculator! Please enter the number of stock puchases: 3 Please enter the number of shares purchased: -99 Please enter the number of shares purchased: Please enter the number of shares purchased: 100 Please enter the price per share: 0.0 Please enter the price per share: -98.76 Please enter the price per share: 5.5 Please enter the number of shares purchased: -100 Please enter the number of shares purchased: 100 Please enter the price per share: 5.15 Please enter the number of shares purchased: 100 Please enter the price per share: 6.16 The cost basis is $1681.0. To calculate the profit, please enter the price per share of a sale: -6.25 To calculate the profit, please enter the price per share of a sale: 6.25 The profit from selling 300 shares at 6.25 each is $194.8. Notice that multiple invalid values are entered and that the program keeps asking for a valid values until it gets a valid one. Also notice that the cost basis and profit are each rounded. If you're trying to debug this example (and I hope that you would), you could temporarily display the cost basis after each valid price per purchased share is entered. That should give you the following values: The current cost basis is $550.8. The current cost basis is $1065.0. The current cost basis is $1681.0








