This is question about x86-64 assembly language, please help me understand this, thanks!
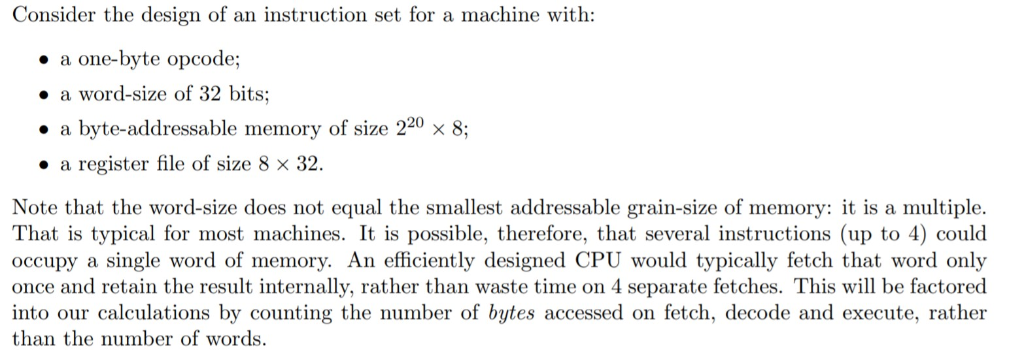

Consider the design of an instruction set for a machine with . a one-byte opcode; . a word-size of 32 bits . a byte-addressable memory of size 220 8; a register file of size 8 32. Note that the word-size does not equal the smallest addressable grain-size of memory: it is a multiple. That is typical for most machines. It is possible, therefore, that several instructions (up to 4) could occupy a single word of memory. An efficiently designed CPU would typically fetch that word only once and retain the result internally, rather than waste time on 4 separate fetches. This will be factored into our calculations by counting the number of bytes accessed on fetch, decode and execute, rather than the number of words. (d) 3 marks] Write a program that, for a trio of 32-bit values x, y, z, computes z-(x+y)* (x - y). You may also use sub and mul, which will have the same instruction format as add. Write two versions: one for the 3-operand machine and one for the 2-operand machine. Total the number of bytes of memory access that are done during each of fetch + decode, and execute, and conclude which system is better. Consider the design of an instruction set for a machine with . a one-byte opcode; . a word-size of 32 bits . a byte-addressable memory of size 220 8; a register file of size 8 32. Note that the word-size does not equal the smallest addressable grain-size of memory: it is a multiple. That is typical for most machines. It is possible, therefore, that several instructions (up to 4) could occupy a single word of memory. An efficiently designed CPU would typically fetch that word only once and retain the result internally, rather than waste time on 4 separate fetches. This will be factored into our calculations by counting the number of bytes accessed on fetch, decode and execute, rather than the number of words. (d) 3 marks] Write a program that, for a trio of 32-bit values x, y, z, computes z-(x+y)* (x - y). You may also use sub and mul, which will have the same instruction format as add. Write two versions: one for the 3-operand machine and one for the 2-operand machine. Total the number of bytes of memory access that are done during each of fetch + decode, and execute, and conclude which system is better








