This is the last question I have this month on course hero, (sorry that there are 2) I will upvote and I am very grateful for any assistance. I mainly need help with the top one but any help with the second one is just a hope. Thank you very much for your time.
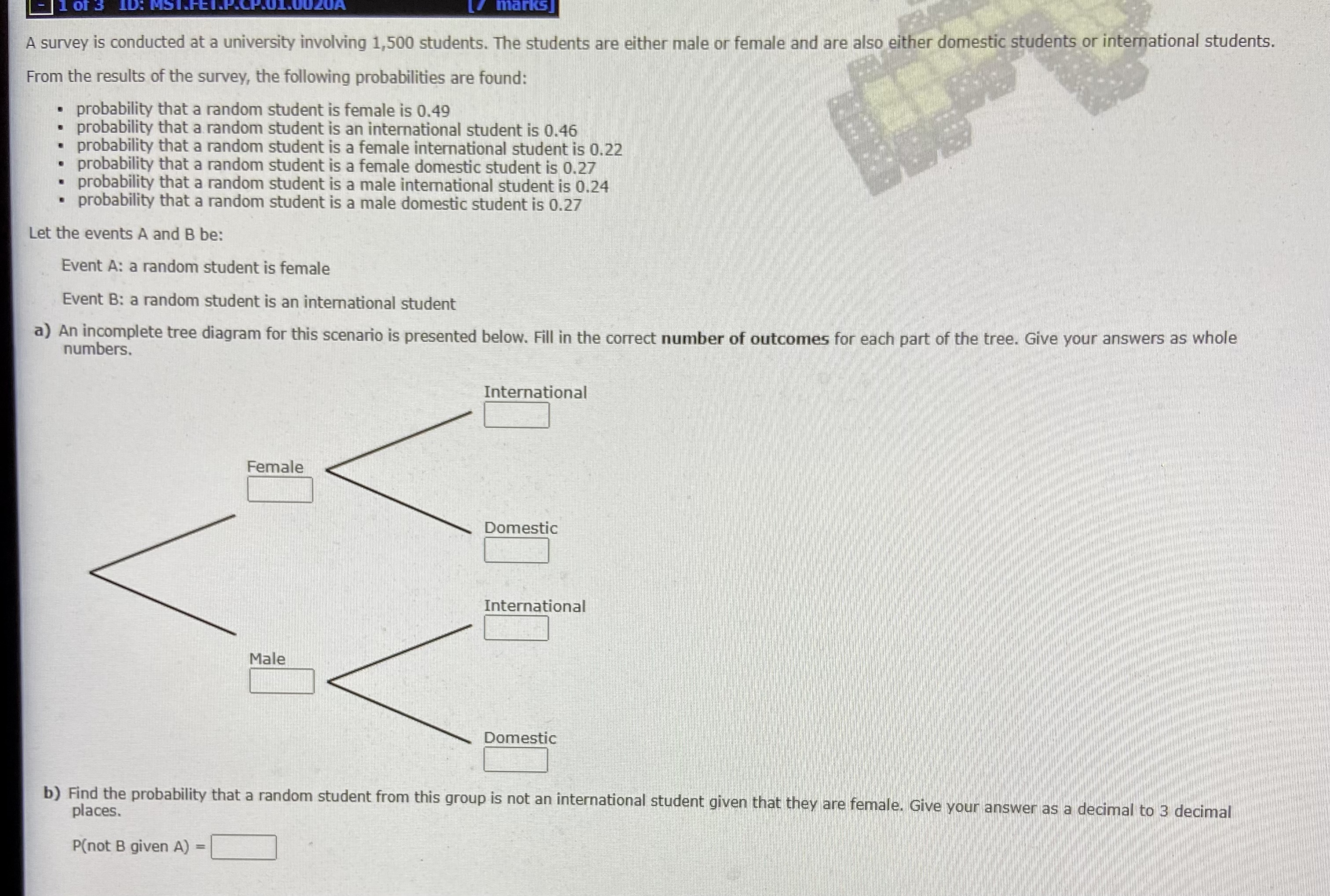
1of 3 ID: MST.FEI. marks] A survey is conducted at a university involving 1,500 students. The students are either male or female and are also either domestic students or international students. From the results of the survey, the following probabilities are found: probability that a random student is female is 0.49 probability that a random student is an international student is 0.46 probability that a random student is a female international student is 0.22 probability that a random student is a female domestic student is 0.27 probability that a random student is a male international student is 0.24 probability that a random student is a male domestic student is 0.27 Let the events A and B be: Event A: a random student is female Event B: a random student is an international student a) An incomplete tree diagram for this scenario is presented below. Fill in the correct number of outcomes for each part of the tree. Give your answers as whole numbers. International Female Domestic International Male Domestic b) Find the probability that a random student from this group is not an international student given that they are female. Give your answer as a decimal to 3 decimal places. P(not B given A) =2 of 3 ID: MST.FET.P.CP.02.0020A [6 marks] A large group of 100 people sit down at a function to a two-course meal. Each course has two options: guests can choose to have either Main A or Main B, and they can choose to have either Dessert A or Dessert B. After the function, the chef notes that 30 chose Main A, while the remaining 70 chose Main B. And of the people that chose main A, 16 chose Dessert A and 14 chose Dessert B. Of the people that chose Main B, 16 chose Dessert A and 54 chose Dessert B. a) A tree diagram describing this situation has been drawn up, and some probabilities have been filled in. Complete the tree diagram for this scenario by filling in the appropriate probability for each part of the tree. Give your answers as decimals to 2 decimal places. Dessert A Main A 0.30 Dessert B Dessert A Main B 0.70 Dessert B b) Find the probability that a random person from this group selects Main A and Dessert B. Give your answer as a decimal to 2 decimal places. P(Main A and Dessert B) = c) Find the probability that a random person from this group selects Dessert B given that they selected Main A. Give your answer as a decimal to 2 decimal places. P(Dessert B| Main A) = 3 of 3 ID: MST.FET.P.CP.03.0010A [2 marks] For the random process of rolling two six-sided dice and recording the sum, let A and B be the events defined by: A: the result is an even number B: the result is greater than 9 a) Calculate the probability of B given A. Give your answer as a decimal to 2 decimal places. P(BIA) - b) Calculate the probability of A given B. Give your answer as a decimal to 2 decimal places. P(A|B) =