this lab is called a simple pendulum.
table one measures 1 period at a time for 100 times.
table 2 measures 50 period at a time for 2 times.

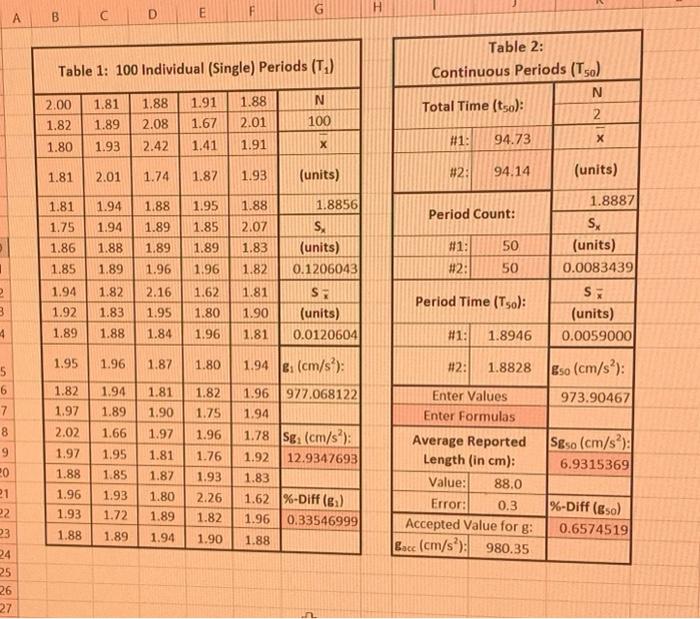
(12 points) There are many "common sense" methods of lowering the randomness reflected in the standard deviation, S, such as using more precise instruments (calipers instead of a ruler, or a telescope instead of binoculars). Our pendulum experiment focuses on a particular strategy that might not be so "common sense." In certain situations, improving fractional error can be used to increase your experimental precision. An error which normally affects a single measurement, S., can be distributed across multiple measurements, n, effectively reducing the error to S. In the case of the pendulum, the uncertainty introduced by starting and stopping the stopwatch is limited by the experimenter's response time, which cannot be easily improved. In the first part of the experiment this imprecision in timing occurs twice for every single measured period. In the second part of the experiment this imprecision in timing occurs twice, but for fifty measured periods. The imprecision in timing in the second part is spread out over a much larger measurement. Assume the error in timing when starting and stopping the stopwatch is +0.2 seconds. So, if a single period is measured, the entire 0.2 second error affects this one period. Suppose the stopwatch is used to record 10 continuous periods, how much of this error affects a single period? How much for 50 continuous periods? b. Describe two changes to the experimental method that would increase the precision of your experimental result for go. a. B A C D E Table 1: 100 Individual (Single) Periods (T.) Table 2: Continuous Periods (To) N Total Time (tso) 2 #1: 94.73 X N 2.00 1.82 1.80 1.81 1.89 1.93 1.88 2.08 2.42 1.91 1.67 1.41 1.88 2.01 100 1.91 1.81 2.01 1.74 1.87 1.93 (units) #2: 94.14 (units) 1.81 1.75 1.86 1.95 1.85 Period Count: 1.94 1.94 1.88 1.89 1.88 1.89 1.89 1.96 1.8856 S, (units) 0.1206043 1.89 #1: 50 50 1 1.88 2.07 1.83 1.82 1.81 1.90 1.81 1.85 1.96 1.62 #2: 1.8887 SX (units) 0.0083439 SE (units) 0.0059000 2 1.82 1.83 1.94 1.92 1.89 2.16 1.95 Period Time (Tso): 3 1.80 S (units) 0.0120604 4 1.88 1.84 1.96 #1: 1.8946 1.95 1.96 1.87 1.80 1.94 . (cm/s): #2: 1.8828 5 6 Eso (cm/s): 973.90467 7 8 1.82 1.97 2.02 1.97 1.94 1.89 1.66 1.81 1.90 1.97 1.82 1.75 1.96 1.81 1.76 1.96 977.068122 1.94 1.78 Sg, (cm/s); 1.92 12.9347693 1.83 1.62 %-Diff (e) 1.96 0.33546999 1.88 S&so (cm/s): 6.9315369 1.88 9 20 21 22 1.87 1.95 1.85 1.93 1.72 Enter Values Enter Formulas Average Reported Length (in cm): Value: 88.0 Error: 0.3 Accepted Value for g: Bacc (cm/s): 980.35 1.93 2.26 1.96 1.93 1.80 1.89 1.94 1.82 %-Diff (go) 0.6574519 23 1.88 1.89 1.90 24 25 26 27








