Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
This lab should be coded in C using linux system calls 2. Exchange PIDs among processes from the same parent Write a C program that
This lab should be coded in C using linux system calls
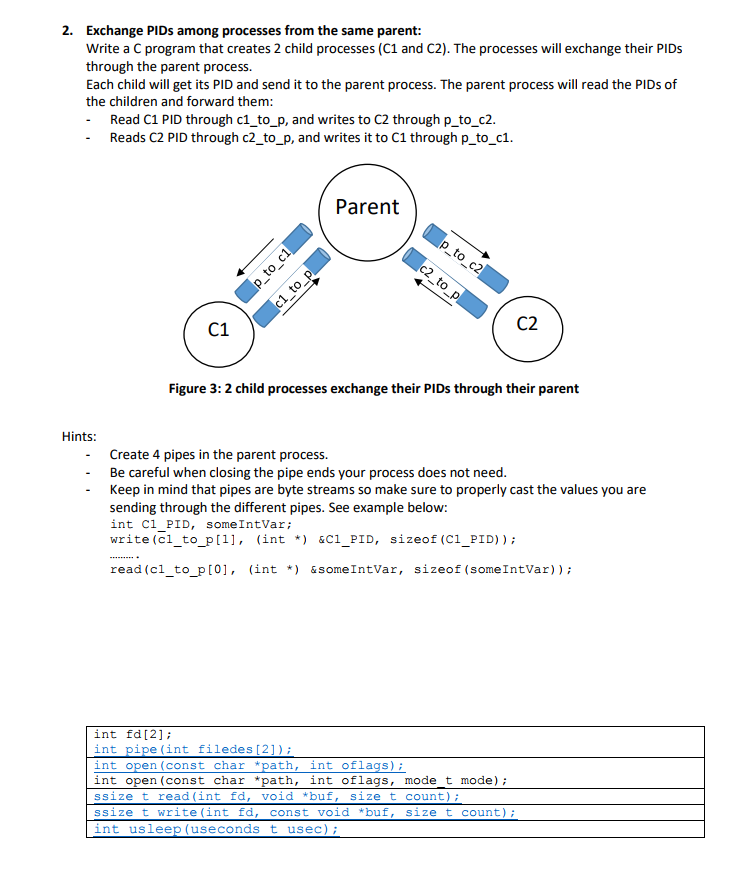
2. Exchange PIDs among processes from the same parent Write a C program that creates 2 child processes (C1 and C2). The processes will exchange their PIDs through the parent process. Each child will get its PID and send it to the parent process. The parent process will read the PIDs of the children and forward them - Read C1 PID through c1_to_p, and writes to C2 through p to_c2 -Reads C2 PID through c2_to_p, and writes it to C1 through p to_c1 Parent C1 C2 Figure 3: 2 child processes exchange their PIDs through their parent Hints: Create 4 pipes in the parent process. - Be careful when closing the pipe ends your process does not need -Keep in mind that pipes are byte streams so make sure to properly cast the values you are sending through the different pipes. See example below: int Cl PID, someIntVar; write (cl_to_p[l], (int *) &Ci_PID, sizeof (C1_PID)) read (cl_to_p [0], (int *) &someIntVar, sizeof (someIntVar)); int fd[2] int pipe (int int open (const char *path, int oflags); int open (const char *path, int oflags, mode t mode); ssize t read(int fd, void *buf, size t count) ssize t write (int fd, const void *buf, size t count) int usleep (useconds t usec); filedes [2] 2. Exchange PIDs among processes from the same parent Write a C program that creates 2 child processes (C1 and C2). The processes will exchange their PIDs through the parent process. Each child will get its PID and send it to the parent process. The parent process will read the PIDs of the children and forward them - Read C1 PID through c1_to_p, and writes to C2 through p to_c2 -Reads C2 PID through c2_to_p, and writes it to C1 through p to_c1 Parent C1 C2 Figure 3: 2 child processes exchange their PIDs through their parent Hints: Create 4 pipes in the parent process. - Be careful when closing the pipe ends your process does not need -Keep in mind that pipes are byte streams so make sure to properly cast the values you are sending through the different pipes. See example below: int Cl PID, someIntVar; write (cl_to_p[l], (int *) &Ci_PID, sizeof (C1_PID)) read (cl_to_p [0], (int *) &someIntVar, sizeof (someIntVar)); int fd[2] int pipe (int int open (const char *path, int oflags); int open (const char *path, int oflags, mode t mode); ssize t read(int fd, void *buf, size t count) ssize t write (int fd, const void *buf, size t count) int usleep (useconds t usec); filedes [2]Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


