Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
This problem involves transfer pricing. Transfer pricing involves the determination of the price used to transfer a product from one division of a company that
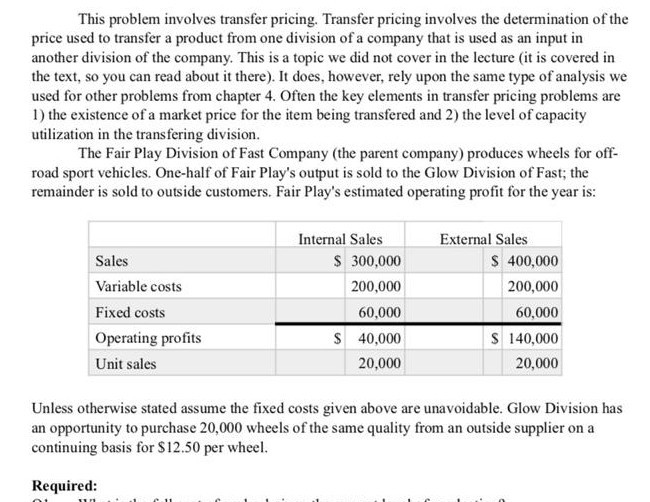
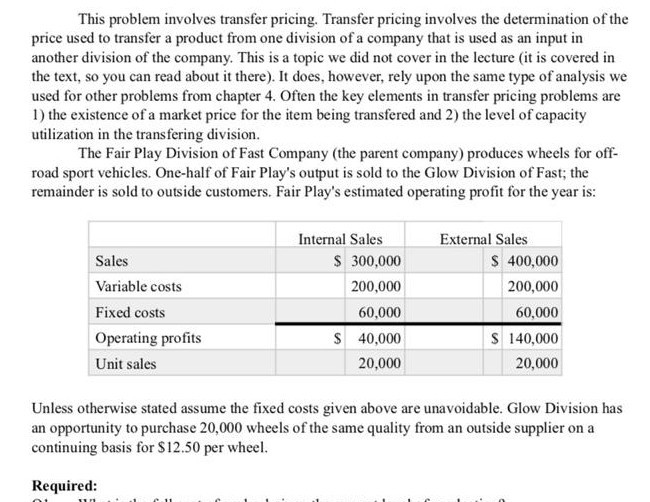
This problem involves transfer pricing. Transfer pricing involves the determination of the price used to transfer a product from one division of a company that is used as an input in another division of the company. This is a topic we did not cover in the lecture (it is covered in the text, so you can read about it there). It does, however, rely upon the same type of analysis we used for other problems from chapter 4. Often the key elements in transfer pricing problems are 1) the existence of a market price for the item being transfered and 2) the level of capacity utilization in the transfering division. The Fair Play Division of Fast Company (the parent company) produces wheels for off- road sport vehicles. One-half of Fair Play's output is sold to the Glow Division of Fast; the remainder is sold to outside customers. Fair Play's estimated operating profit for the year is: Sales Internal Sales $ 300,000 200,000 External Sales $ 400,000 200,000 60,000 S 140,000 20,000 Variable costs Fixed costs Operating profits Unit sales 60,000 $ 40,000 20,000 Unless otherwise stated assume the fixed costs given above are unavoidable. Glow Division has an opportunity to purchase 20,000 wheels of the same quality from an outside supplier on a continuing basis for $12.50 per wheel. Required: This problem involves transfer pricing. Transfer pricing involves the determination of the price used to transfer a product from one division of a company that is used as an input in another division of the company. This is a topic we did not cover in the lecture (it is covered in the text, so you can read about it there). It does, however, rely upon the same type of analysis we used for other problems from chapter 4. Often the key elements in transfer pricing problems are 1) the existence of a market price for the item being transfered and 2) the level of capacity utilization in the transfering division. The Fair Play Division of Fast Company (the parent company) produces wheels for off- road sport vehicles. One-half of Fair Play's output is sold to the Glow Division of Fast; the remainder is sold to outside customers. Fair Play's estimated operating profit for the year is: Sales Internal Sales $ 300,000 200,000 External Sales $ 400,000 200,000 60,000 S 140,000 20,000 Variable costs Fixed costs Operating profits Unit sales 60,000 $ 40,000 20,000 Unless otherwise stated assume the fixed costs given above are unavoidable. Glow Division has an opportunity to purchase 20,000 wheels of the same quality from an outside supplier on a continuing basis for $12.50 per wheel. Required: This problem involves transfer pricing. Transfer pricing involves the determination of the price used to transfer a product from one division of a company that is used as an input in another division of the company. This is a topic we did not cover in the lecture (it is covered in the text, so you can read about it there). It does, however, rely upon the same type of analysis we used for other problems from chapter 4. Often the key elements in transfer pricing problems are 1) the existence of a market price for the item being transfered and 2) the level of capacity utilization in the transfering division. The Fair Play Division of Fast Company (the parent company) produces wheels for off- road sport vehicles. One-half of Fair Play's output is sold to the Glow Division of Fast; the remainder is sold to outside customers. Fair Play's estimated operating profit for the year is: Sales Internal Sales $ 300,000 200,000 External Sales $ 400,000 200,000 60,000 S 140,000 20,000 Variable costs Fixed costs Operating profits Unit sales 60,000 $ 40,000 20,000 Unless otherwise stated assume the fixed costs given above are unavoidable. Glow Division has an opportunity to purchase 20,000 wheels of the same quality from an outside supplier on a continuing basis for $12.50 per wheel. Required: This problem involves transfer pricing. Transfer pricing involves the determination of the price used to transfer a product from one division of a company that is used as an input in another division of the company. This is a topic we did not cover in the lecture (it is covered in the text, so you can read about it there). It does, however, rely upon the same type of analysis we used for other problems from chapter 4. Often the key elements in transfer pricing problems are 1) the existence of a market price for the item being transfered and 2) the level of capacity utilization in the transfering division. The Fair Play Division of Fast Company (the parent company) produces wheels for off- road sport vehicles. One-half of Fair Play's output is sold to the Glow Division of Fast; the remainder is sold to outside customers. Fair Play's estimated operating profit for the year is: Sales Internal Sales $ 300,000 200,000 External Sales $ 400,000 200,000 60,000 S 140,000 20,000 Variable costs Fixed costs Operating profits Unit sales 60,000 $ 40,000 20,000 Unless otherwise stated assume the fixed costs given above are unavoidable. Glow Division has an opportunity to purchase 20,000 wheels of the same quality from an outside supplier on a continuing basis for $12.50 per wheel. Required
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


