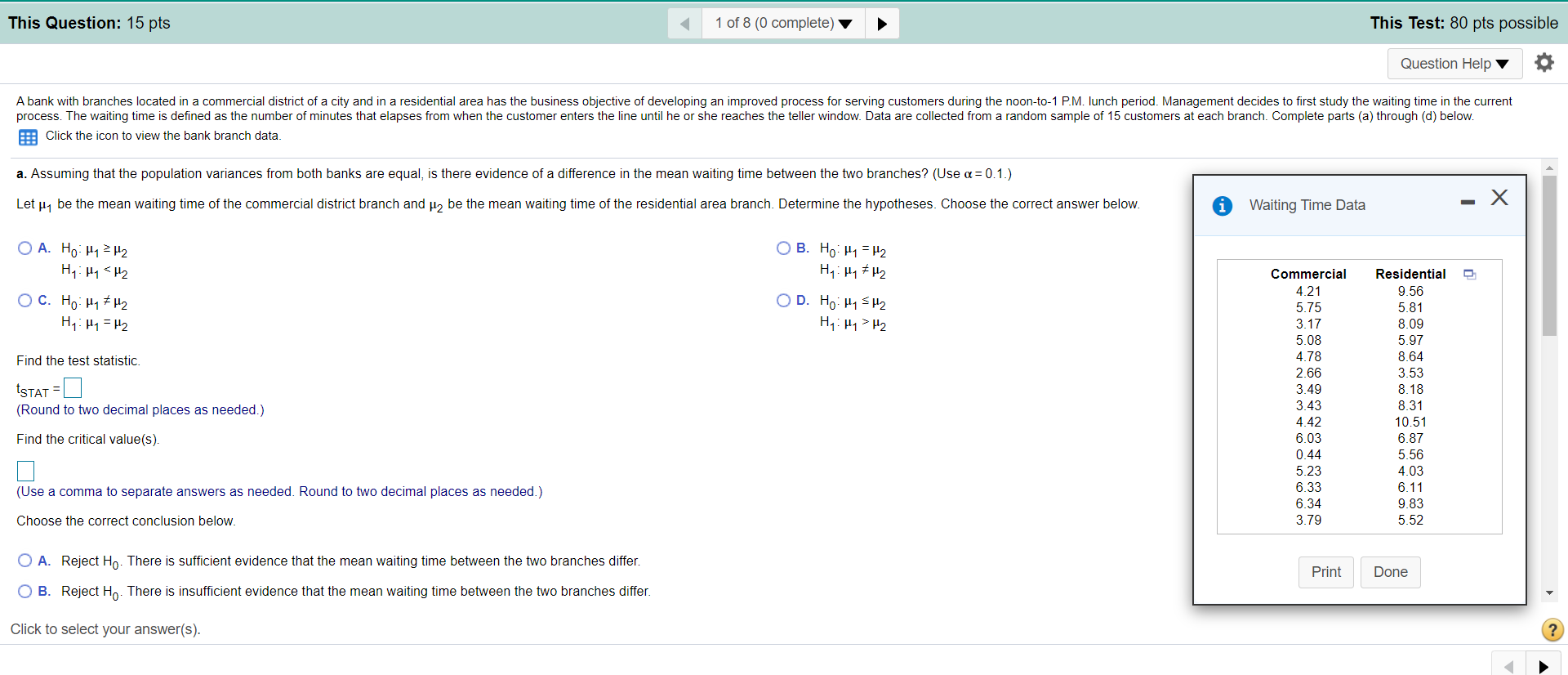
This Question: 15 pts 1 of 8 (0 complete) This Test: 80 pts possible Question Help A bank with branches located in a commercial district of a city and in a residential area has the business objective of developing an improved process for serving customers during the noon-to-1 P.M. lunch period. Management decides to first study the waiting time in the current process. The waiting time is defined as the number of minutes that elapses from when the customer enters the line until he or she reaches the teller window. Data are collected from a random sample of 15 customers at each branch. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. Click the icon to view the bank branch data. a. Assuming that the population variances from both banks are equal, is there evidence of a difference in the mean waiting time between the two branches? (Use H2 3.17 8.09 5.08 5.97 4.78 8.64 Find the test statistic. 2.66 3.53 ISTAT = 3.49 8.18 3.43 8.31 (Round to two decimal places as needed.) 4.42 10.51 Find the critical value(s). 6.03 6.87 0.44 5.56 5.23 4.03 (Use a comma to separate answers as needed. Round to two decimal places as needed.) 6.33 6.11 6.34 9.83 Choose the correct conclusion below. 3.79 5.52 O A. Reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence that the mean waiting time between the two branches differ. Print Done O B. Reject Ho. There is insufficient evidence that the mean waiting time between the two branches differ. Click to select your answer(s). ?Question Help A bank with branches located in a commercial district of a city and in a residential area has the business objective of developing an improved process for serving customers during the noon-to-1 P.M. lunch period. Management decides to first study the waiting time in the current process. The waiting time is defined as the number of minutes that elapses from when the customer enters the line until he or she reaches the teller window. Data are collected from a random sample of 15 customers at each branch. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. Click the icon to view the bank branch data. A. Reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence that the mean waiting time between the two branches differ. O B. Reject Ho. There is insufficient evidence that the mean waiting time between the two branches differ. O C. Do not reject Ho. There is insufficient evidence that the mean waiting time between the two branches differ. O D. Do not reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence that the mean waiting time between the two branches differ. b. Determine the p-value in (a) and interpret its meaning. p-value = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Interpret the p-value. Choose the correct answer below. O A. It is the probability of obtaining a sample that yields a t-test statistic farther away from 0 in the positive direction than the computed test statistic if there is no difference in the mean waiting time between commercial and residential banks. B. It is the probability the two banks have different population mean waiting times. C. It is the probability of obtaining a sample that yields a t-test statistic farther away from 0 in the negative direction than the computed test statistic if there is no difference in the mean waiting time between commercial and residential banks. O D. It is the probability of obtaining a sample that yields a t-test statistic farther away from 0 in either direction than the computed test statistic if there is no difference in the mean waiting time between commercial and residential banks. c. In addition to equal variances, what other assumption is necessary in (a)? O A. The sample sizes must be equal. O B. The samples are specifically chosen and not independently sampled. Click to select your answer(s).Question Help A bank with branches located in a commercial district of a city and in a residential area has the business objective of developing an improved process for serving customers during the noon-to-1 P.M. lunch period. Management decides to first study the waiting time in the current process. The waiting time is defined as the number of minutes that elapses from when the customer enters the line until he or she reaches the teller window. Data are collected from a random sample of 15 customers at each branch. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. Click the icon to view the bank branch data. C. It is the probability of obtaining a sample that yields a t-test statistic farther away from 0 in the negative direction than the computed test statistic if there is no difference in the mean waiting time between commercial and residential banks. O D. It is the probability of obtaining a sample that yields a t-test statistic farther away from 0 in either direction than the computed test statistic if there is no difference in the mean waiting time between commercial and residential banks. c. In addition to equal variances, what other assumption is necessary in (a)? A. The sample sizes must be equal. O B. The samples are specifically chosen and not independently sampled. O C. Both sampled populations are approximately normal. O D. Both sampled populations are not approximately normal. d. Construct and interpret a 90% confidence interval estimate of the difference between the population means between the two branches. The 90% confidence interval is |=1 - 12 = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Interpret the confidence interval. Choose the correct answer below. A. With 10% confidence, the difference between the population mean waiting time between the two banks falls below the lower confidence interval limit. O B. With 90% confidence, the difference between the population mean waiting time between the two banks falls outside this interval. O C. With 10% confidence, the difference between the population mean waiting time between the two banks falls above the upper confidence interval limit. O D. With 90% confidence, the difference between the population mean waiting time between the two banks falls in this interval. Click to select your answer(s)