Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
This time i put them as separate images. Hopefully they are legible now! Situation: Table 1, below, shows the viscosity of aqueous solutions of sucrose
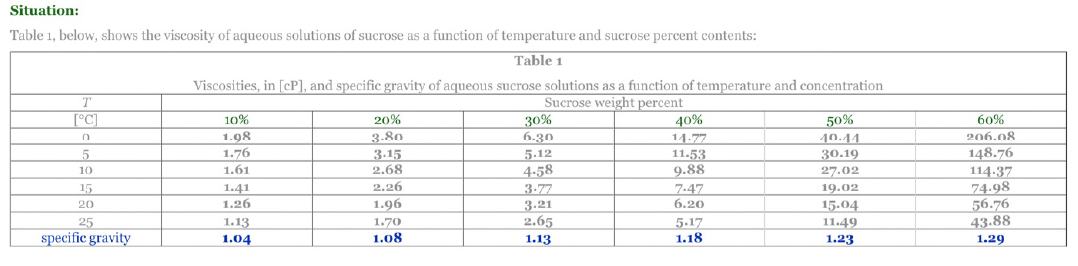

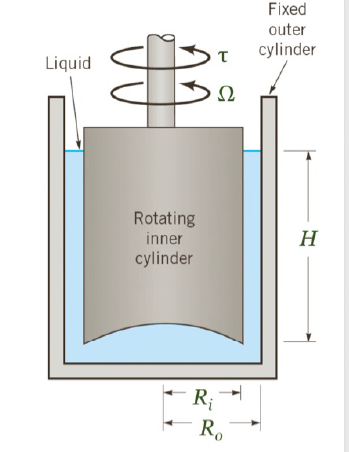

This time i put them as separate images. Hopefully they are legible now!
Situation: Table 1, below, shows the viscosity of aqueous solutions of sucrose as a function of temperature and sucrose percent contents: a Table 1 Viscosities, in (CP), and specific gravity of aqueous sucrose solutions as a function of temperature and concentration Sucrose weight percent [C] 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 6.30 14.77 40.44 5 1.76 3.15 11.53 30.19 10 1.61 2.68 9.88 27.02 15 1.41 2.26 3.77 7.47 19.02 20 1.26 1.96 3.21 6.20 15.04 25 1.13 1.70 2.65 5.17 11.49 specific gravity 1.04 1.08 1.13 1.18 1.23 1.98 3.80 5.12 4.58 6096 206.08 148.76 114.37 74.98 56.76 43.88 1.29 Last row shows the specific gravities as a function of sucrose weight percent. It is assumed that the variation with temperature is small. Assume that the viscosity of pure water is 1 [g/cm3) This problem deals with calculations involving concentric-cylinders viscometers also called rotating cylinder viscometers or Couette viscometers. The attached schematic shows how they work. In this device the outer cylinder is fixed, and the inner cylinder rotates with an angular velocity, 2. The torque required to develop 2 is measured and the viscosity is calculated from these two measurements. Assume that in a given case, H = 6 [cm], Ri= 4.0 [cm], and Ro = 4.2 [cm], and that the rotational speed of the inner cylinder is 50 [RPM). Fixed outer cylinder Liquid 12 Rotating inner cylinder H Ri R (C) Neglecting variations in the vertical direction and the curvature of the gap... ... the linear velocity of the outer surface of the inner cylinder is: X (m/s) ... the velocity gradient in the liquid gap is: x (1/5) (d) Assuming that the liquid is Newtonian ... ... the total frictional force exerted on the outer surface of the inner cylinder is: * [N] (absolute value) ... the torque needed to be applied to the inner cylinder is: X [Nm] Situation: Table 1, below, shows the viscosity of aqueous solutions of sucrose as a function of temperature and sucrose percent contents: a Table 1 Viscosities, in (CP), and specific gravity of aqueous sucrose solutions as a function of temperature and concentration Sucrose weight percent [C] 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 6.30 14.77 40.44 5 1.76 3.15 11.53 30.19 10 1.61 2.68 9.88 27.02 15 1.41 2.26 3.77 7.47 19.02 20 1.26 1.96 3.21 6.20 15.04 25 1.13 1.70 2.65 5.17 11.49 specific gravity 1.04 1.08 1.13 1.18 1.23 1.98 3.80 5.12 4.58 6096 206.08 148.76 114.37 74.98 56.76 43.88 1.29 Last row shows the specific gravities as a function of sucrose weight percent. It is assumed that the variation with temperature is small. Assume that the viscosity of pure water is 1 [g/cm3) This problem deals with calculations involving concentric-cylinders viscometers also called rotating cylinder viscometers or Couette viscometers. The attached schematic shows how they work. In this device the outer cylinder is fixed, and the inner cylinder rotates with an angular velocity, 2. The torque required to develop 2 is measured and the viscosity is calculated from these two measurements. Assume that in a given case, H = 6 [cm], Ri= 4.0 [cm], and Ro = 4.2 [cm], and that the rotational speed of the inner cylinder is 50 [RPM). Fixed outer cylinder Liquid 12 Rotating inner cylinder H Ri R (C) Neglecting variations in the vertical direction and the curvature of the gap... ... the linear velocity of the outer surface of the inner cylinder is: X (m/s) ... the velocity gradient in the liquid gap is: x (1/5) (d) Assuming that the liquid is Newtonian ... ... the total frictional force exerted on the outer surface of the inner cylinder is: * [N] (absolute value) ... the torque needed to be applied to the inner cylinder is: X [Nm]Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


