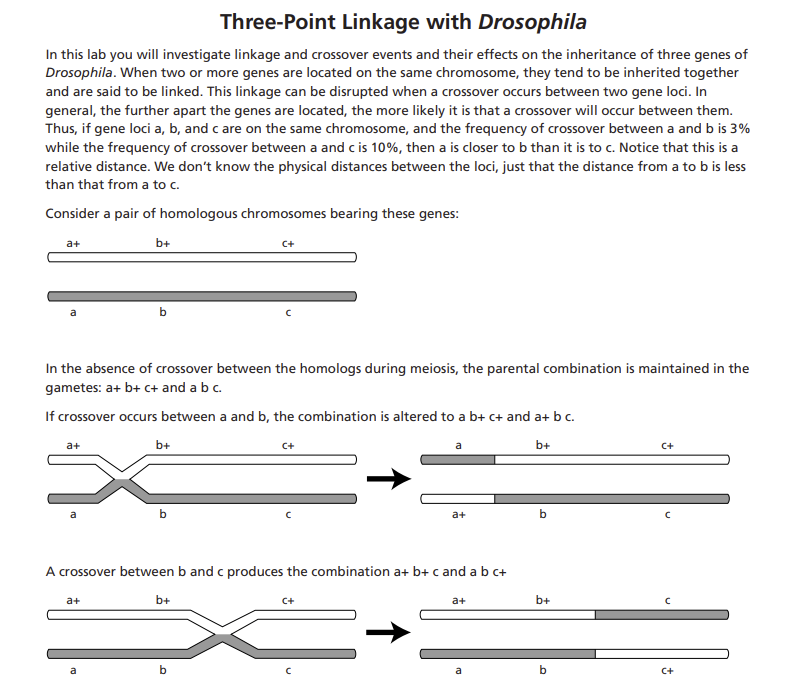
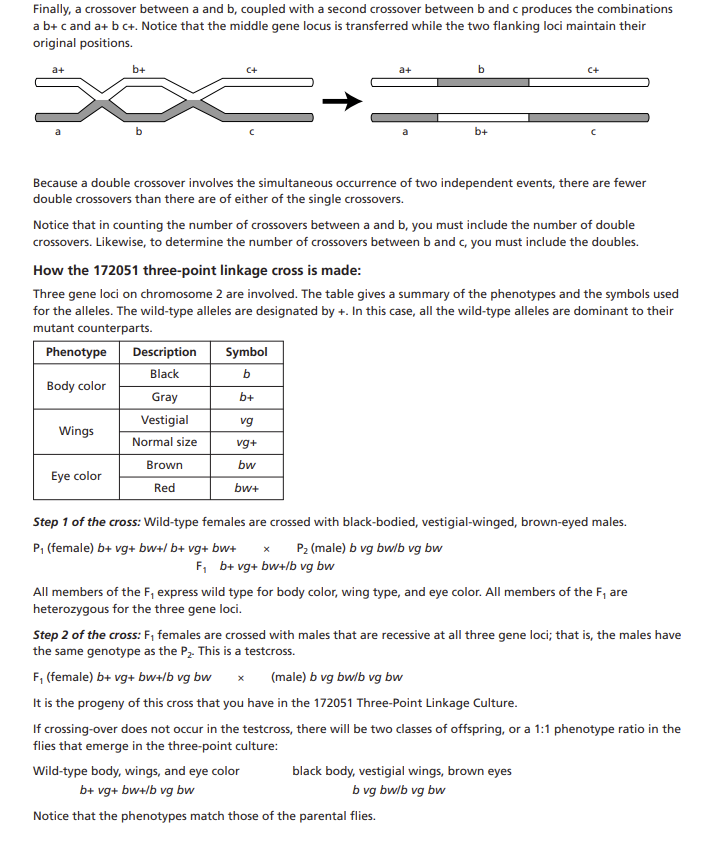
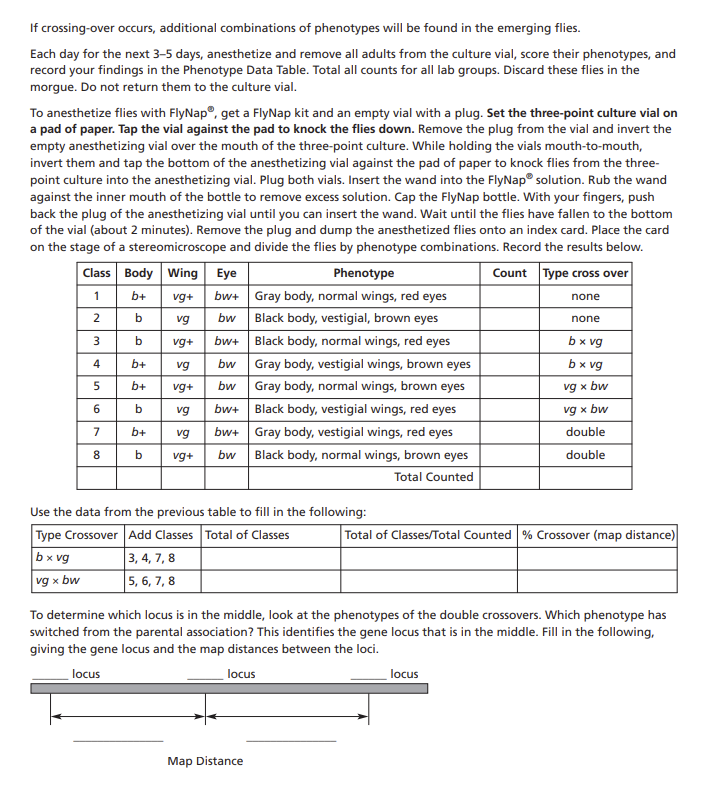
Three-Point Linkage with Drosophila In this lab you will investigate linkage and crossover events and their effects on the inheritance of three genes of Drosophila. When two or more genes are located on the same chromosome, they tend to be inherited together and are said to be linked. This linkage can be disrupted when a crossover occurs between two gene loci. In general, the further apart the genes are located, the more likely it is that a crossover will occur between them. Thus, if gene loci a,b, and c are on the same chromosome, and the frequency of crossover between a and b is 3% while the frequency of crossover between a and c is 10%, then a is closer to b than it is to c. Notice that this is a relative distance. We don't know the physical distances between the loci, just that the distance from a to b is less than that from a to c. Consider a pair of homologous chromosomes bearing these genes: In the absence of crossover between the homologs during meiosis, the parental combination is maintained in the gametes: a+b+c+ and abc If crossover occurs between a and b, the combination is altered to ab+c+anda+bc. A crossover between b and c produces the combination a+b+c and abc+ Finally, a crossover between a and b, coupled with a second crossover between b and c produces the combinations ab+c and a+bc+. Notice that the middle gene locus is transferred while the two flanking loci maintain their original positions. Because a double crossover involves the simultaneous occurrence of two independent events, there are fewer double crossovers than there are of either of the single crossovers. Notice that in counting the number of crossovers between a and b, you must include the number of double crossovers. Likewise, to determine the number of crossovers between b and c, you must include the doubles. How the 172051 three-point linkage cross is made: Three gene loci on chromosome 2 are involved. The table gives a summary of the phenotypes and the symbols used for the alleles. The wild-type alleles are designated by +. In this case, all the wild-type alleles are dominant to their mutant counterparts. Step 1 of the cross: Wild-type females are crossed with black-bodied, vestigial-winged, brown-eyed males. P1 (female) b+vg+bw+/b+vg+bw+P2 (male) bvgbw/bvgbw F1b+vg+bw+/bvgbw All members of the F1 express wild type for body color, wing type, and eye color. All members of the F1 are heterozygous for the three gene loci. Step 2 of the cross: F1 females are crossed with males that are recessive at all three gene loci; that is, the males have the same genotype as the P2This is a testcross. F1 (female) b+vg+bw+/bvgbw (male) bvgbw/bvgbw It is the progeny of this cross that you have in the 172051 Three-Point Linkage Culture. If crossing-over does not occur in the testcross, there will be two classes of offspring, or a 1:1 phenotype ratio in the flies that emerge in the three-point culture: Wild-type body, wings, and eye color black body, vestigial wings, brown eyes b+vg+bw+/bvgbw bgbw/bgbw Notice that the phenotypes match those of the parental flies. If crossing-over occurs, additional combinations of phenotypes will be found in the emerging flies. Each day for the next 3-5 days, anesthetize and remove all adults from the culture vial, score their phenotypes, and record your findings in the Phenotype Data Table. Total all counts for all lab groups. Discard these flies in the morgue. Do not return them to the culture vial. To anesthetize flies with FlyNap get a FlyNap kit and an empty vial with a plug. Set the three-point culture vial on a pad of paper. Tap the vial against the pad to knock the flies down. Remove the plug from the vial and invert the empty anesthetizing vial over the mouth of the three-point culture. While holding the vials mouth-to-mouth, invert them and tap the bottom of the anesthetizing vial against the pad of paper to knock flies from the threepoint culture into the anesthetizing vial. Plug both vials. Insert the wand into the FlyNap solution. Rub the wand against the inner mouth of the bottle to remove excess solution. Cap the FlyNap bottle. With your fingers, push back the plug of the anesthetizing vial until you can insert the wand. Wait until the flies have fallen to the bottom of the vial (about 2 minutes). Remove the plug and dump the anesthetized flies onto an index card. Place the card on the stage of a stereomicroscope and divide the flies by phenotype combinations. Record the results below. Use the data from the previous table to fill in the following: To determine which locus is in the middle, look at the phenotypes of the double crossovers. Which phenotype has switched from the parental association? This identifies the gene locus that is in the middle. Fill in the following, giving the gene locus and the map distances between the loci









