Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Time left 1:23:41 Given the graph G=(V, E), where V = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9), E = {(3,4), (7,1),(1,6),
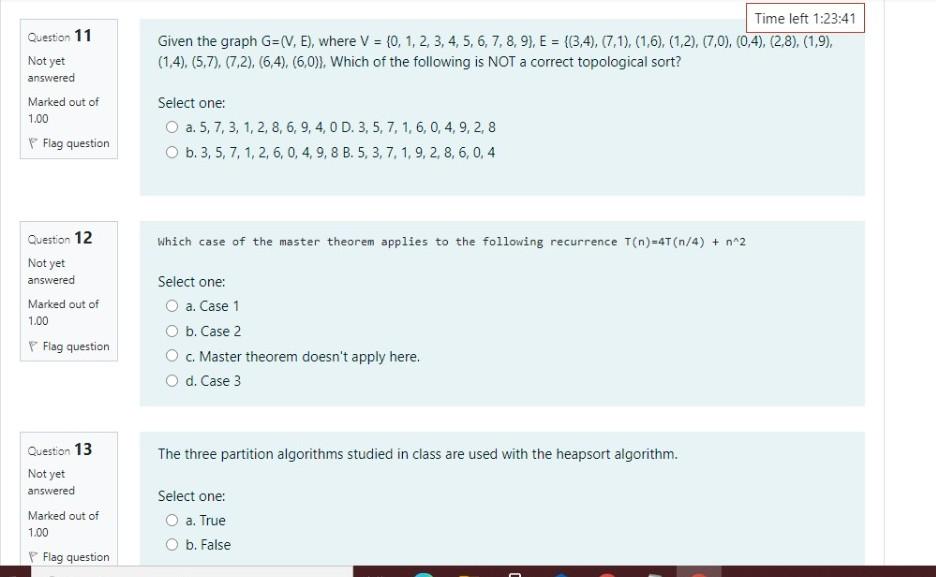
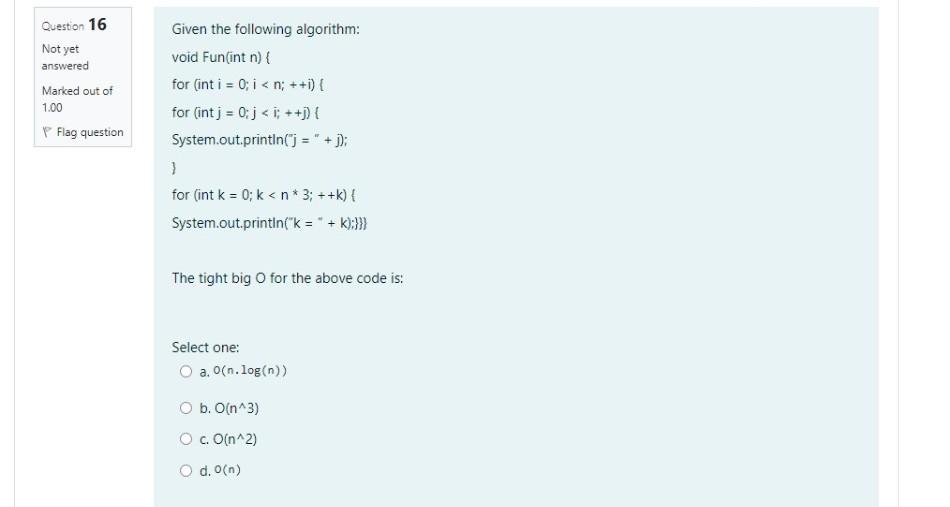
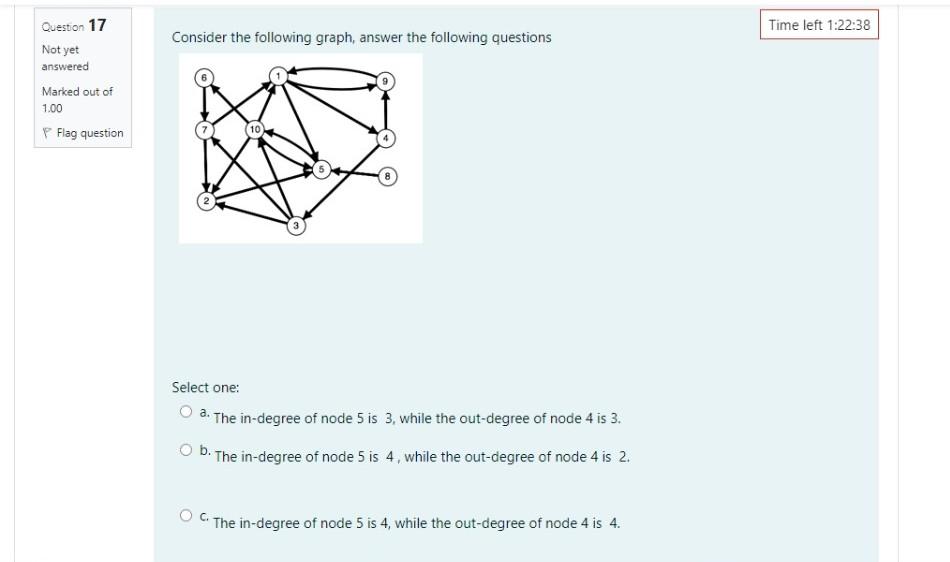
Time left 1:23:41 Given the graph G=(V, E), where V = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9), E = {(3,4), (7,1),(1,6), (1,2), (7,0), (0,4), (2,8), (1,9), (1.4), (5,7), (7,2), (6,4), (6,0)), Which of the following is NOT a correct topological sort? Question 11 Not yet answered Marked out of 1.00 Flag question Select one: O a. 5, 7, 3, 1, 2, 8, 6, 9, 4,0 D. 3, 5, 7, 1,6, 0, 4.9.2,8 O b.3.5, 7, 1, 2, 6, 0, 4, 9,8 B. 5, 3.7.1.9, 2, 8, 6, 0,4 Question 12 Which case of the master theorem applies to the following recurrence T(n)-4T(n/4) + n2 Not yet answered Marked out of 1.00 Flag question Select one: O a. Case 1 O b. Case 2 O c. Master theorem doesn't apply here. O d. Case 3 The three partition algorithms studied in class are used with the heapsort algorithm. Question 13 Not yet answered Marked out of 1.00 Select one: a. True b. False Flag question Question 14 Which statement of the following is false? Not yet answered Marked out of 1.00 Select one: O a. Heap sort is stable sort b. Heap sort is a comparison-based sorting algorithm O c. Heap sort has O(nlogn) average case time complexity Od. Heap sort is an in-place algorithm Flag question Question 15 In a heap with n distinct elements and height h, the second largest element has a height of. Not yet answered Marked out of 1.00 Flag question Select one: O a. 1-2 Obh O c. h-1 O d. 0 Question 16 Not yet answered Marked out of 1.00 Flag question Given the following algorithm: void Fun(int n) { for (int i = 0; i
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


