Question
To find the key AKL, we would first check at index 7, then at 6, and 5, where we are successful. Searching for JFK, on
To find the key AKL, we would first check at index 7, then at 6, and 5, where we are successful. Searching for JFK, on the other hand, we would start with its proper position, given by the hash function value 8, so we would check indices 8, 7, 6, . . . , 1, 0, 10 in that order until we find an empty space which tells us that JFK is, in fact, not present at all. This looks pretty bad at first sight, but bear in mind that we said that we will aim towards keeping the load factor at around 50 percent, so there would be many more empty slots which effectively stop any further search. But this idea brings another problem with it. Suppose we now delete GCM from the table and then search for AKL again. We would find the array empty at index 6 and stop searching, and therefore wrongly conclude that AKL is not present. This is clearly not acceptable, but equally, we do not wish to have to search through the entire array to be sure that an entry is not there. The solution is that we reserve another key to mean that a position is empty, but that it did hold a key at some point.. This calculation ought not be quadratic in N, however being quadratic in M is allowed. You ought to see N as being of the request for 20,000 and M as being of the request for 1,000.
(c) Describe an effective calculation to track down the middle of a bunch of 106 whole numbers where it is realized that there are less than 100 particular numbers in the set. [6 marks] 6 Computer Design (a) Why does pipelining present information risks? [4 marks] (b) What system might be utilized to eliminate a few dards? [4 marks] (c) Why is it unrealistic to eliminate all information dangers? [4 marks] (d) What equipment is expected to forestall information risks from encroaching the developer's model of guidance execution? [4 marks] (e) What is the contrast between an information danger and a control risk? [4 marks] 5 [TURN OVER CST.2001.3.6 7 Operating System Functions (a) What are the central questions with planning for shared-memory multiprocessors? [3 marks] (b) Processor partiality, take booking and group planning are three strategies utilized inside multiprocessor working frameworks. (I) Briefly depict the activity of each. [6 marks] (ii) Which issue does the processor partiality method look to survive? [2 marks] (iii) What issue does the processor liking strategy experience the ill effects of, and how might this issue at any point be survived? [2 marks] (iv) In which conditions is a posse planning approach generally fitting? [2 marks] (c) What unexpected issues does the virtual memory the board framework need to address while managing shared-memory multiprocessor frameworks?
Five housemates run a "status" server on their home organization. The server stores the current status of every housemate as a line of text. For instance, housemate Eva could set her status to "Gone to the test corridor." Messages are passed among clients and the server as message strings sent over TCP. The new line character is utilized solely as the last person in each message. On association with the server, a client can possibly (I) question the situation with a client by sending the client's name to the server as a string (and the server answers with the current status message), or (ii) set the situation with a client by sending the client's name followed by a colon and the new status message. For instance, "Eva:Gone to the test corridor." sets the status message for Eva. (a) Implement a status server in Java. The server ought to run endlessly, answering to client demands. When a client demand has been satisfied, the server ought to close the association. You might accept current status messages are lost if the server is restarted and you don't have to deal with exemptions. [8 marks] (b) One housemate proposes the server and client ought to impart by serializing Java protests instead of sending messages as message. (I) Describe in words the progressions you would make to your server execution to send messages as serialized Java objects. [3 marks] (ii) List two benefits and two detriments of an execution in light of serialized Java objects as opposed to sending messages as message. [4 marks] (c) Another housemate proposes that the server shouldn't close the client's association in the wake of noting the solicitation. Rather the association ought to remain open until the client sends another solicitation or shuts the association. Depict in words what transforms you would have to make to your execution to some degree (a) to accomplish this and remark on the benefits and hindrances of this thought.
(a) Describe the primary illustrations gained from the report into the breakdown of the London Rescue vehicle Service. [12 marks] (b) To what degree have the improvements in programming devices and the board practices of the most recent twenty years advanced the circumstance, and which of the examples do we actually need to watch out for now?
N. Wirth's reading material Algorithms + information structures = programs (1976) contains the following story. I wedded a widow (call her W) who has an adult girl (D). My dad (F), who visited us regularly, became hopelessly enamored with my step-little girl and wedded her. Henceforth my dad turned into my child in-regulation what's more, my progression little girl turned into my mom. A few months after the fact, my significant other brought forth a child (S1), who turned into the brother by marriage of my dad, as well as my uncle. The spouse of my dad - that is, my progression little girl - likewise had a child (S2). Utilizing Prolog, make a rundown of realities that addresses what is happening in the above story. [5 marks] Add rules characterizing the family connections (like father by marriage) depicted in the story. [5 marks] Show how a Prolog framework would utilize your program to demonstrate the objective "I'm my own granddad". [10 marks] 8 Databases Make sense of the ANSI/SPARC engineering for Data Base Management Systems, and show how it upholds information freedom. [5 marks] Portray the social model of information presented by E.F. Codd in 1970. [4 marks] What are its assets and shortcomings? [7 marks] What variables have prompted its prevailing situation in the commercial center today?
(a) Write C capacity revbits() which takes a solitary 8-digit burn boundary and returns a roast outcome by turning around the request for the pieces in the scorch. [4 marks] (b) Write C capacity revbytes() taking two boundaries and returning no outcome. The primary boundary is a pointer to memory containing n coterminous bytes (each of type singe), and the second is the quantity of bytes. The capacity ought to have the result of turning around the request for the pieces in the n bordering bytes, seen as a bitstring of length 8n. For instance, the primary piece of the principal burn ought to be traded with last piece of the last roast. [6 marks] (c) You have been allocated the accompanying apparently working C code, which processes documents controlling the way of behaving of a framework. That's what you see, subsequent to acquiring a few ERR_MALFORMED mistakes, resulting calls to fopen bomb due to an excessive number of documents being open: int process_file(char *name) { Record *p = fopen(name, "r"); in the event that (p == NULL) return ERR_NOTFOUND; while (...) { ... if (...) return ERR_MALFORMED; process_one_option(); ... } fclose(p); bring SUCCESS back; }The class must have private data members to include the following information: a) the nationality of an Army, b) the number of units in an Army, and e) the power of an Army.
Declare one C++ constant, namely MAX_NAME_LEN and set it to 50.
Declare three private data members. [1:20 PM, 7/14/2022] Mumbi Gichobi: Declare an array to hold the nationality of an Army, not exceeding MAX_NAME_LEN characters. Declare an integer variable for the number of units in an Army. Declare a double variable for the power of an Army. Store your class definition in a header file named Army.h and your member function definitions in an implementation file named Army.cpp.
Public Member functions
Declare and implement the following member functions.
setEmpty:
void setEmpty();
This member function initializes the Army object to a safe empty state. An Army is in an empty state when it has an empty nationality and no units.
createArmy:
void createArmy(const char* country, double pow, int troops);
It uses three input parameters to initialize an Army object. It receives the nationality...This function returns true if the Army has more power than the incoming Army, and returns false otherwise.
Global (stand-alone) functionsbattle:
void battle( Army& arm1, Army& arm2);
This function will force both armies to fight. If both armies are valid, the losing Army will lose 50% of their unit count PS: - you might want to use the isStrongerThan function to check which Army will win - you might want to use the updateUnits function to update the losing country. Passed value needs to be casted to an int
display:
void displayDetails(const Army* armies, int size);
This function sends the information about an Army array to standard output in the following format if the object holds valid data values.
Armies reporting to battle:
Each Army in the array will be printed in the following format.
Nationality: XXXXXXXXXXX, Units Count: XXXX, Power left:
Testing Program
main.cpp
#include
using namespace std;
#include "Army.h"
using namespace sdds;
int main() {
Army armies[6]{};
armies[0].createArmy("Atlantis", 500.5, 1000);
armies[1].createArmy("", 100.0, 100);
armies[2].createArmy("Ambrosia", 215.0, 520);
armies[3].createArmy("United States of Auradon", 220.5, 751);
armies[4].createArmy("Azmenistan", 250.0, 750);
armies[5].createArmy(nullptr, 250.5, 750);
//Test 1
cout << "----------------------------------------" << endl;
cout << "1. Testing the validation logic." << endl;
cout << "(only 4 armies should be valid (0,2,3,4) )" << endl;
cout << "----------------------------------------" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
cout << "armies[" << i << "]: "
<< (armies[i].isEmpty() ? "not valid" : "valid") << endl;
}
cout << "----------------------------------------" << endl << endl;
//Test 2
cout << "----------------------------------------" << endl;
cout << "2. Testing the display function." << endl;
cout << "----------------------------------------" << endl;
displayDetails(armies, 6);
cout << "----------------------------------------" << endl << endl;
// Test 3
cout << "----------------------------------------" << endl;
cout << "3. Testing the member functions without the update." << endl;
cout << "----------------------------------------" << endl;
Army backup;
backup.createArmy("Foreigners", 100, 100);
cout << backup.checkNationality()
<< ','
<< backup.checkCapacity()
<< ','
<< backup.checkPower() << endl;
cout << "----------------------------------------" << endl << endl;
// Test 4
cout << "----------------------------------------" << endl;
cout << "4. Testing the member functions with the update." << endl;
cout << "----------------------------------------" << endl;
backup.updateUnits(100);
cout << backup.checkNationality()
<< ','
<< backup.checkCapacity()
<< ','
<< backup.checkPower() << endl;
cout << "----------------------------------------" << endl << endl;
// Test 5
cout << "----------------------------------------" << endl;
cout << "5. Testing the battle function." << endl;
cout << "----------------------------------------" << endl;
battle(armies[0],armies[2]);
battle(armies[3], armies[4]);
displayDetails(armies, 6);
cout << "----------------------------------------" << endl << endl;
return 0;
}
Sample Output
----------------------------------------
1. Testing the validation logic.
(only 4 armies should be valid (0,2,3,4) )
----------------------------------------
armies[0]: valid
armies[1]: not valid
armies[2]: valid
armies[3]: valid
armies[4]: valid
armies[5]: not valid
----------------------------------------
----------------------------------------
2. Testing the display function.
----------------------------------------
Armies reporting to battle:
Nationality: Atlantis, Units Count: 1000, Power left: 500.5
Nationality: Ambrosia, Units Count: 520, Power left: 215.0
Nationality: United States of Auradon, Units Count: 751, Power left: 220.5
Nationality: Azmenistan, Units Count: 750, Power left: 250.0
----------------------------------------
----------------------------------------
3. Testing the member functions without the update.
----------------------------------------
Foreigners,100,100.0
----------------------------------------
----------------------------------------
4. Testing the member functions with the update.
----------------------------------------
Foreigners,200,125.0
----------------------------------------
----------------------------------------
5. Testing the battle function.
----------------------------------------
In battle of Atlantis and Ambrosia, Atlantis is victorious!
In battle of United States of Auradon and Azmenistan, Azmenistan is victorious!
Armies reporting to battle:
Nationality: Atlantis, Units Count: 1000, Power left: 500.5
Nationality: Ambrosia, Units Count: 260, Power left: 150.0
Nationality: United States of Auradon, Units Count: 376, Power left: 126.8
Nationality: Azmenistan, Units Count: 750, Power left: 250.0
----------------------------------------
(I) Explain how to fix the program involving offices in C. [2 marks] (ii) Now guess the capacity above was essential for a framework written in C++ (yet as yet utilizing the C record handling orders, for example, fopen and fclose), and that process_one_option() could raise at least one special cases. Utilizing a class with a destructor, tell the best way to fix the "such a large number of documents open" bug above
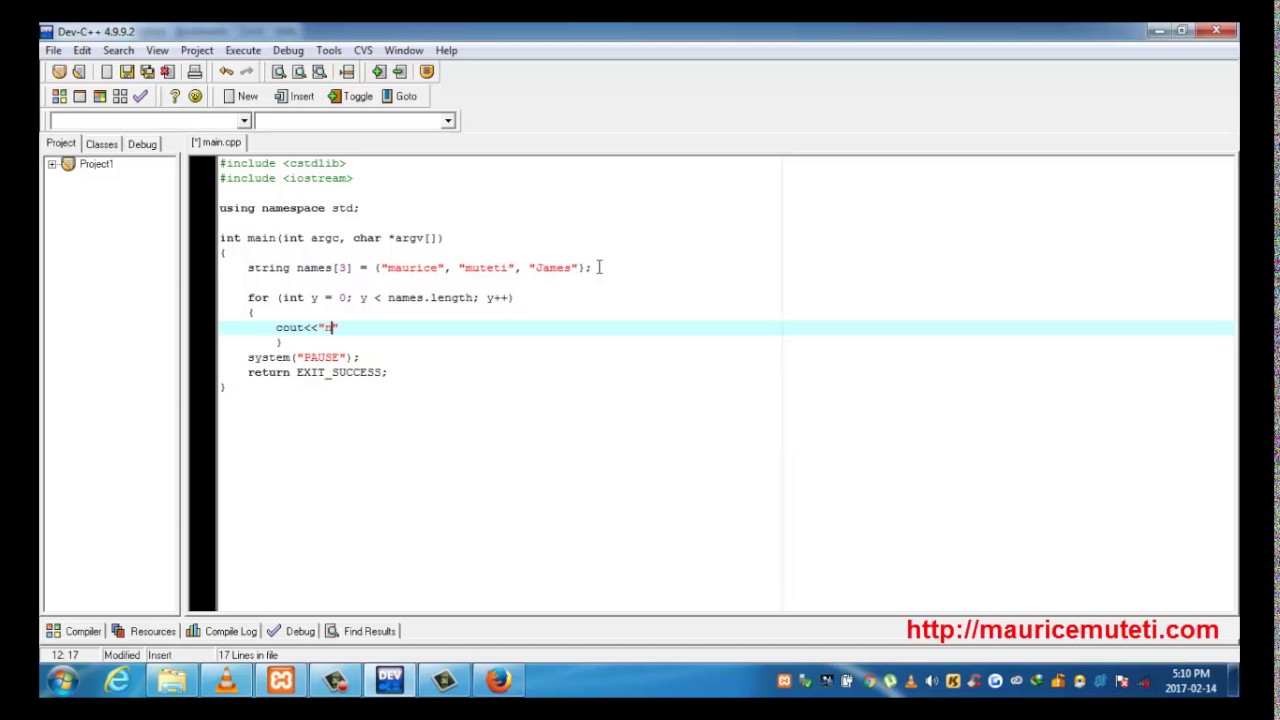
Dev-C++ 4.9.9.2 File Edit Search View Project Execute Debug Tools CVS Window Help New Insert Toggle Goto Project Classes Debug| Project1 main.cpp #include #include using namespace std; int main(int argc, char *argv[]) string names [3] ("maurice", "muteti", "James"); I for (int y 0; y < names.length; y++) cout
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
The passage describes a hash table collision resolution technique called linear probing In this tech...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


