Topic: Asymmetric Information, Risk, and Financial Markets
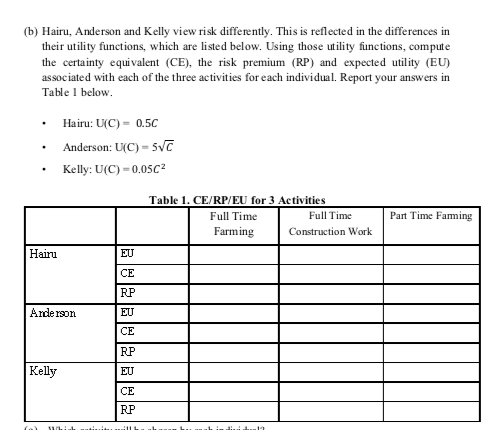
Linda is an insurance agent who offers conventional crop insurance contracts only to full time farmers. He is not interested in offering insurance to part time farmers. The contracts are straightforward. At the beginning of the season, farmers pay a premium of $65. At the end of the season, Linda pays farmers an indemnity payment of $125 if the farmer had a BAD harvest. If the farmer had a GOOD harvest, Linda doesn't pay the farmer anything. For questions e-f, assume that Linda has perfect information about the farmer's activity choice. In other words, he can write and enforce a contract that requires the farmer to choose full time farming. (e) What is Linda's expected profit from this contract? (Linda's profit is just the premium he collects from the farmer minus the indemnity payment he makes to the farmer). (f) What is the expected consumption for an individual who chooses full-time farming with Linda's insurance contract? (g) What is the expected utility associated with full-time farming with an insurance contract for Hairu, Anderson and Kelly?(h) Now assume that each individual can choose between the four available activities; Full Time Farming without Insurance (Activity I above), Full time construction work (Activity 2 above), Part Time Farming without insurance (Activity 3 above) and Full Time Farming with Daniel's insurance contract (Activity 4). Which activity will each individual choose? A. Hairu: B. Anderson: C. Kelly:Question 1 Hairu, Anderson and Kelly are sunflower farmers in the village of Girasol. They each have zero wealth, so their consumption is equal to the income they earn from their economic activity. Each of them must choose one (and only one) of the following three activities: . Activity : Full time farming. Sunflower farming is risky because of a combination of weather and pests. Under full time farming, the farmer works 7 days per week on their farm. There is a 60% probability of having a GOOD harvest and a 40%% chance of having a BAD harvest. If the harvest is GOOD, the farmer earns an income of $200. If the harvest is BAD, the farmer earns an income of only $20. Activity 2: Full time construction work. This activity has no risk. An individual who decides to work full time in construction earns $65 with certainty. Activity 3: Part-time farming, In this third activity, the farmer works during the week as a sunflower farmer and works in construction during the weekend. Since she is not able to work full time on the farm, the probability of having a GOOD harvest and earning $200 drops to 35%, and the probability of having a BAD harvest and earning only $20 increases to 65%. The individual also cams $30 with certainty as a construction worker (the person earns this $30 from construction in addition to her farm income under both a GOOD and BAD harvest).(b) Hairu, Anderson and Kelly view risk differently. This is reflected in the differences in their utility functions, which are listed below. Using those utility functions, compute the certainty equivalent (CE), the risk premium (RP) and expected utility (EU) associated with each of the three activities for each individual. Report your answers in Table I below. . Hairu: U(C) - 0.5C Anderson: U(C) - 5VC Kelly: U(C) =0.05Cz Table 1. CE/RP/EU for 3 Activities Full Time Full Time Part Time Farming Farming Construction Work Hairu EU CE RP Arcde reon ETT CE RP Kelly EU CE RP