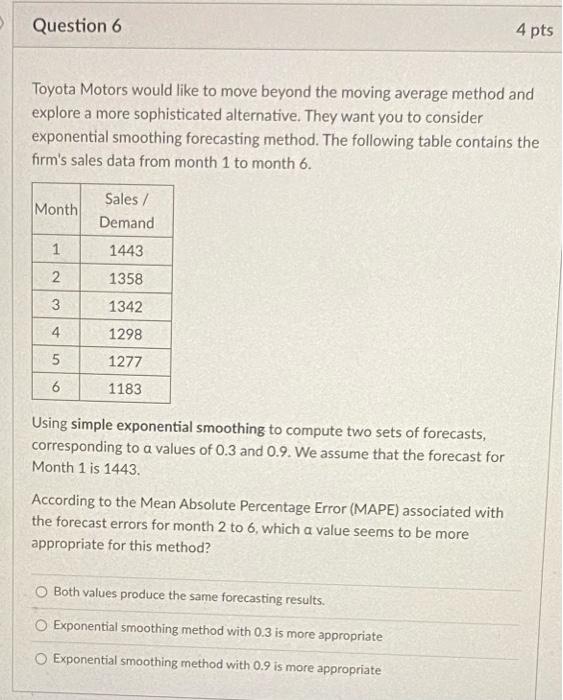
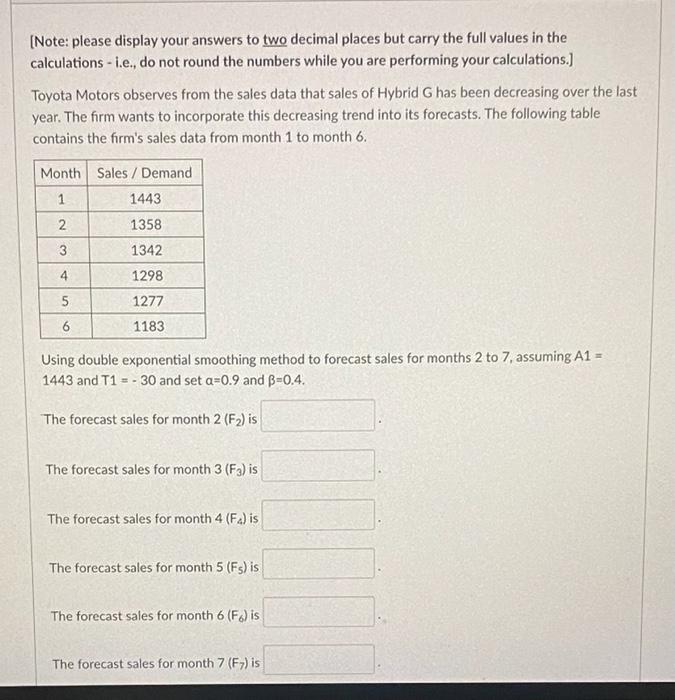
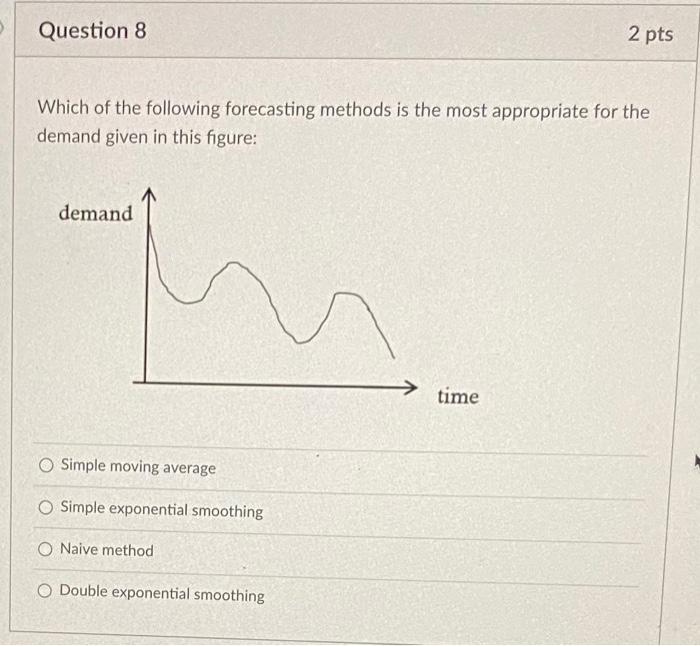
Toyota Motors would like to move beyond the moving average method and explore a more sophisticated alternative. They want you to consider exponential smoothing forecasting method. The following table contains the firm's sales data from month 1 to month 6. Using simple exponential smoothing to compute two sets of forecasts, corresponding to a values of 0.3 and 0.9 . We assume that the forecast for Month 1 is 1443. According to the Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) associated with the forecast errors for month 2 to 6 , which a value seems to be more appropriate for this method? Both values produce the same forecasting results. Exponential smoothing method with 0.3 is more appropriate Exponential smoothing method with 0.9 is more appropriate [Note: please display your answers to two decimal places but carry the full values in the calculations - i.e., do not round the numbers while you are performing your calculations.] Toyota Motors observes from the sales data that sales of Hybrid G has been decreasing over the last year. The firm wants to incorporate this decreasing trend into its forecasts. The following table contains the firm's sales data from month 1 to month 6. Using double exponential smoothing method to forecast sales for months 2 to 7 , assuming A1= 1443 and T1=30 and set =0.9 and =0.4. The forecast sales for month 2(F2) is The forecast sales for month 3(F3) is The forecast sales for month 4(F4) is The forecast sales for month 5(Fs5) is The forecast sales for month 6(F6) is The forecast sales for month 7(F7) is Which of the following forecasting methods is the most appropriate for the demand given in this figure: Simple moving average Simple exponential smoothing Naive method Double exponential smoothing Facility planning entails asking crucial questions, including all of the following EXCEPT How much capacity does the competition have? When is the capacity needed? How much total capacity is needed? Where should facilities be located? Which of the following fits with a preemptive facilities strategy? Reduce risk by allowing capacity to lag the market by a small amount. Wait and see what competitors do, then seek to match or exceed their capacity. Create a positive capacity cushion to stimulate the market