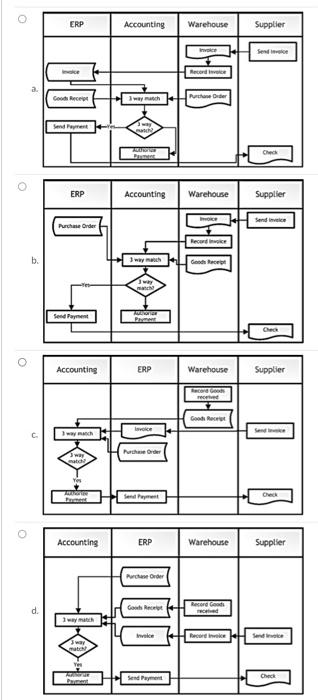
Question 1 2 pts Mini-Scenario: For purchasing goods from a supplier, a local firm's (ABC company) accounting department generates a purchase order (P.O.). Upon receipt of the P.O., the supplier ships goods on time, which is received by ABC's Warehouse employee. Assume the following additional ERP-based seven-step business process: 1. A copy of the 'Purchase Order' is saved in ABC's ERP system. 2. An employee at ABC's Warehouse records the goods received (i.e., 'Goods Receipt") in ABC's ERP system. 3. The Supplier sends a billing 'invoice, which the Warehouse employee records in ABC's ERP system. 4. The Accounting department conducts a three way match by comparing different data items among the Purchase Order, the Goods Receipt, and the Invoice. 5. If the three items match, ABC's accounting department authorizes a 'check' for payment to the Supplier 6. ABC's ERP system automatically sends the payment to the supplier. 7. The supplier prints and stores a hard copy image of the payment check in order to record or file the electronic payment made by ABC Company, Which of the following activity diagrams best models the above process? (Note: The answer choices are NOT a complete illustration of the scenario. In order to keep all four diagrams concise, assume that we allow for upward arrows. Also, we don't illustrate some key steps such as creating and saving P.O., sending alerts, supplier receiving P.O., supplier shipping goods, ERP creating e-checks, and supplier printing the check. Hence, all choices in this question have some errors such as those mentioned in this note. Ignore such errors and select the best choice that best depicts the mini-scenario mentioned above). ERP Accounting Warehouse Supplier Record a Good Recipe way | Purchase Order Son Payment Che ERP Accounting Warehouse Supplier Sendvice Purchase Order Record b. way Good wy Accounting ERP Warehouse Supplier Record God Purchase Order Yo Accounting ERP Warehouse Supplier d. Goals Recept Recorded Sand way Yee Check Question 2 2 pts Process time la component of cycle time): a refers to the time between the start and end of a business process. b. refers to the time spent waiting in a queue. c. is often considered to be value-added time to the customer. d. is always the smallest part of cycle time. Question 3 2 pts The time between a customer ordering coffee and the customer leaving the store with the coffee is referred to as: a. Wait time. b. Cycle time. c. Process time. d. Queue time. Question 4 2 pts One process is more efficient than another if: a. It results in fewer defects and failures. b. It better supports quality control verification. c. It uses fewer resources to accomplish the task. Question 5 2 pts Identify the correct statement O a. A deterministic process always has several possible outcomes. Ob. Determining the outcome of a coin toss as 'heads' or 'tails is an example of a deterministic process. c. For a given system behavior and a given starting (ie, initial) state, a stochastic process has at least two possible outcomes. Question 6 2 pts While some companies have had great success with ERP, some companies have had ERP failures. As per BA270 class discussions, which is one of the most important causes of these failures? a. Some companies had ERP failures due to lack of well-trained programmers. b. Some companies had ERP failures due to lack of good project managers. c. Some companies had ERP failures because top management did not have a clear understanding of the business implications of ERP, and the ERP logic conflicted with the business logic. d. Some companies were just too old to be successful ERP companies. Question 7 3 pts The probability distributions typically associated with patient arrival rate and service time at a hospital are: a. Exponential distribution and normal distribution respectively (le, in that order). b. Exponential distributions for both arrival rate and service time. c. Exponential distribution and Poisson distribution respectively (i.e.. in that order) d. Poisson distribution and exponential distribution respectively (ie, in that order), e. Normal distribution and uniform distribution respectively (ie, in that order)