Question: UCM-Gravity 1. A space probe is launched into space from Earth's surface. Which graph represents the relationship between the magnitude of the gravitational force exerted
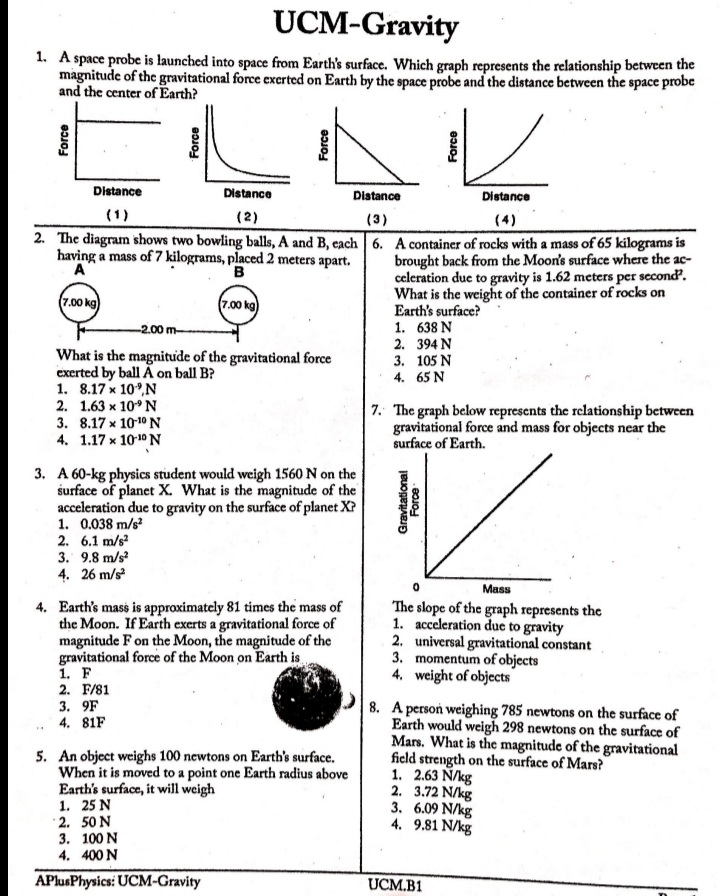

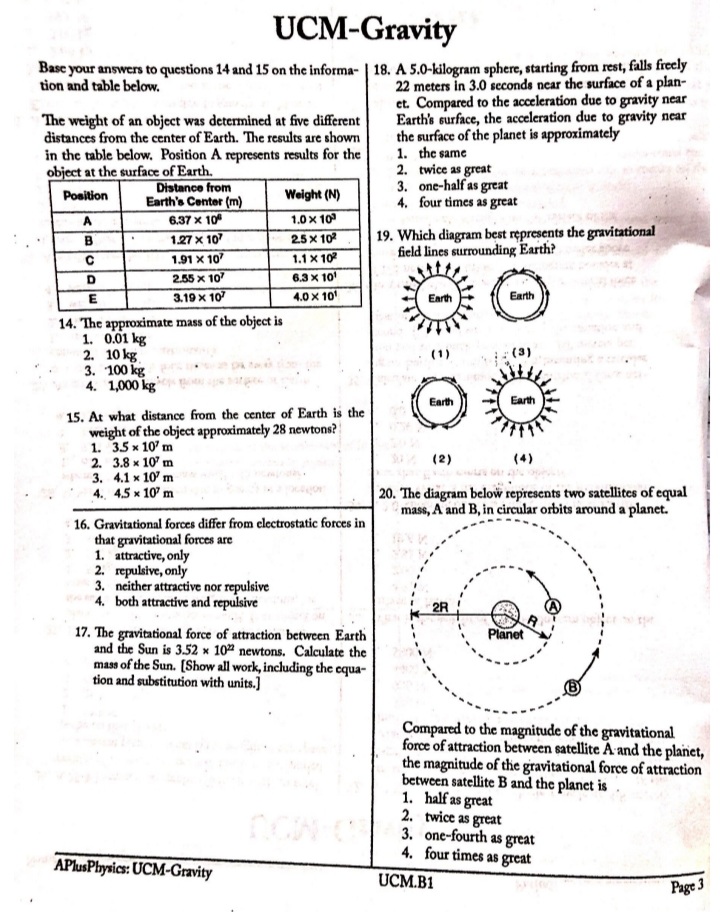


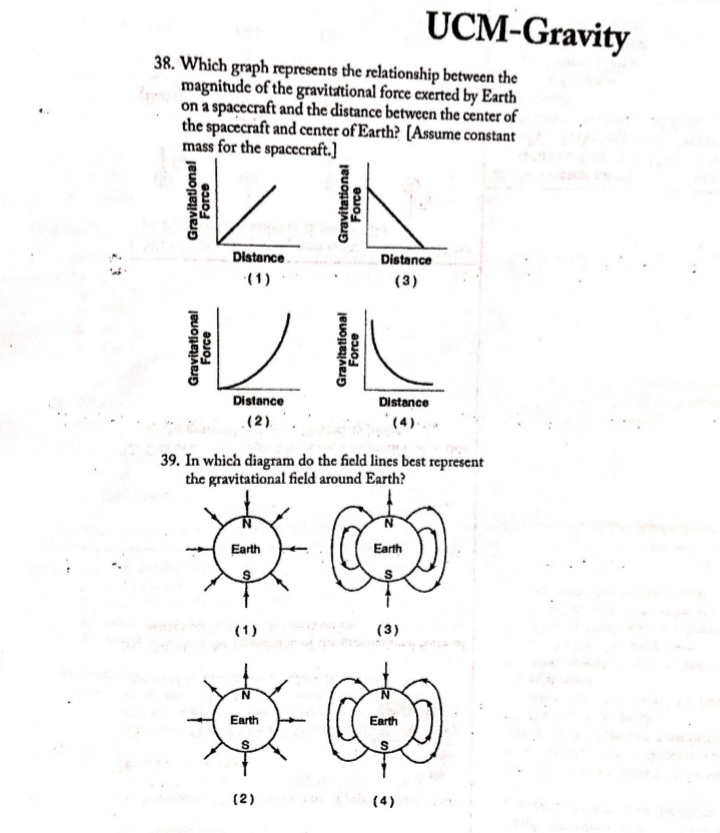
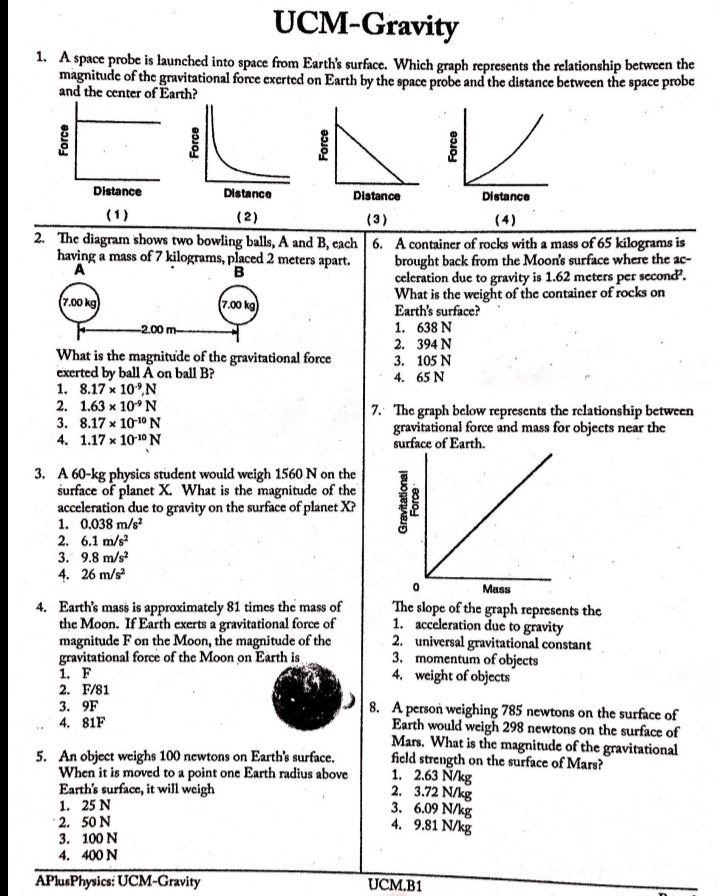

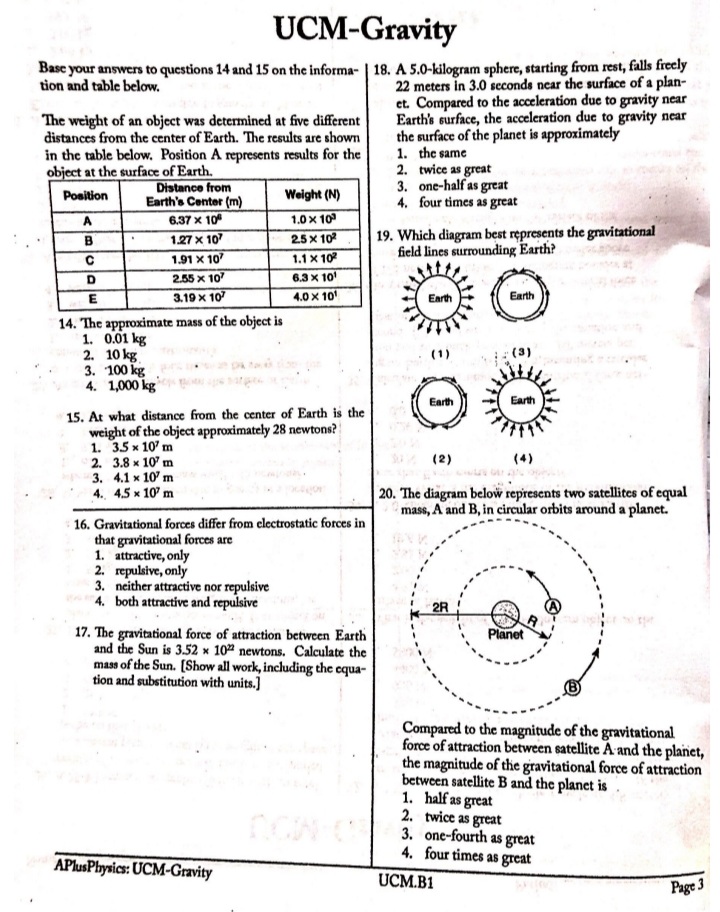


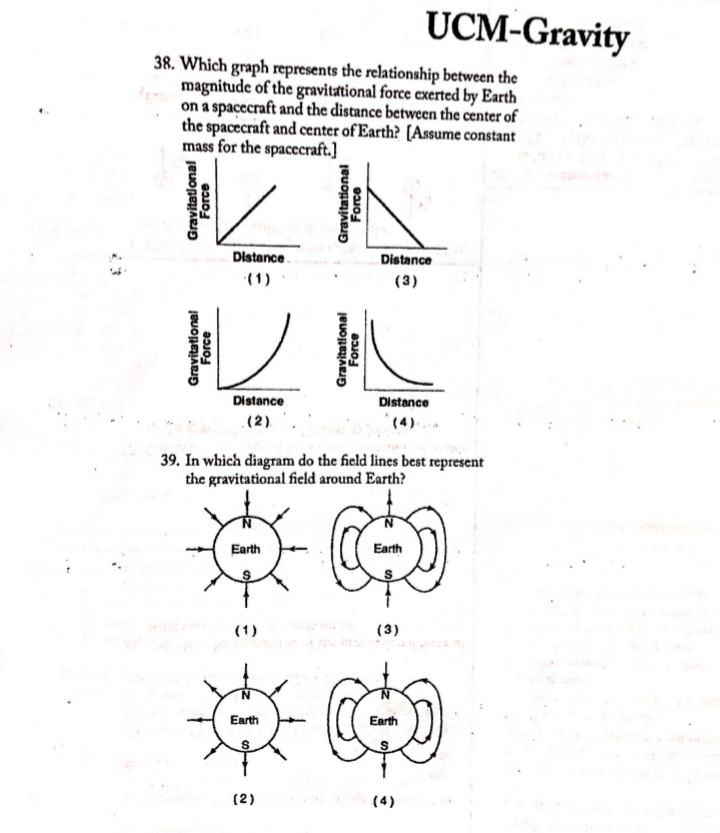
UCM-Gravity 1. A space probe is launched into space from Earth's surface. Which graph represents the relationship between the magnitude of the gravitational force exerted on Earth by the space probe and the distance between the space probe and the center of Earth? Force Force Force Force Distance Distance Distance Distance (1) (2) (3) (4) 2. The diagram shows two bowling balls, A and B, each | 6. A container of rocks with a mass of 65 kilograms is having a mass of 7 kilograms, placed 2 meters apart. brought back from the Moon's surface where the ac- A B celeration due to gravity is 1.62 meters per second'. What is the weight of the container of rocks on 7.00 kg 7.00 kg Earth's surface? -2.00 m- 1. 638 N 2. 394 N What is the magnitude of the gravitational force 3. 105 N exerted by ball A on ball B? 4. 65 N 1. 8.17 x 10",N 2. 1.63 x 109 N 7. The graph below represents the relationship between 3. 8.17 x 10-10 N gravitational force and mass for objects near the 4. 1.17 x 10-10 N surface of Earth. 3. A 60-kg physics student would weigh 1560 N on the surface of planet X. What is the magnitude of the Gravitational Force acceleration due to gravity on the surface of planet X? 1. 0.038 m/s' 2. 6.1 m/s2 3. 9.8 m/s 4. 26 m/s Mass 4. Earth's mass is approximately 81 times the mass of The slope of the graph represents the the Moon. If Earth exerts a gravitational force of 1. acceleration due to gravity magnitude F on the Moon, the magnitude of the 2. universal gravitational constant gravitational force of the Moon on Earth is 3. momentum of objects 1. F 4. weight of objects 2. F/81 3. 9F 8. A person weighing 785 newtons on the surface of 4. 81F Earth would weigh 298 newtons on the surface of Mars. What is the magnitude of the gravitational 5. An object weighs 100 newtons on Earth's surface. field strength on the surface of Mars? When it is moved to a point one Earth radius above 1. 2.63 N/kg Earth's surface, it will weigh 2. 3.72 N/kg 1. 25 N 3. 6.09 N/kg 2. 50 N 4. 9.81 N/kg 3. 100 N 4. 400 N APlusPhysics: UCM-Gravity UCM.B1UCM-Gravity Base your answers to questions 9 through 11 on the passage and data table below. The net force on a planet is due primarily to the other planets and the Sun. By taking into account all the forces acting on a planet, investigators calculated the orbit of each planet. A small discrepancy between the calculated orbit and the observed orbit of the planet Uranus was noted. It ap- peared that the sum of the forces on Uranus did not equal its mass times its acceleration, unless there was another force on the planet that was not included in the calculation. Assuming that this force was exerted by an unobserved planet, two scientists working independently calculated where this unknown planet must be in order to account for the dis- crepancy. Astronomers pointed their telescopes in the predicted direction and found the planet we now call Neptune. Data Table Mass of the Sun 1.99 x 1030 kg Mass of Uranus 8.73 x 1025 kg Mass of Neptune 1.03 x 10 kg Mean distance of Uranus to the Sun 2.87 x 1012 m Mean distance of Neptune to the Sun 4.50 x 1012 m 9. What fundamental force is the author referring to in this passage as a force between planets? 10. The diagram at right represents Neptune, Uranus, and the Sun in a Sun straight line. Neptune is 1.63 x 1012 meters from Uranus. Uranus Neptune Calculate the magnitude of the interplanetary force of attraction between Uranus and Neptune at this point. [Show all work, in- cluding the equation and substitution with units.] 1.63 x10um ; ( Not drawn to scale ) 11. The magnitude of the force the Sun exerts on Uranus is 1.41 x 10" newtons. Explain how it is possible for the Sun to exert a greater force on Uranus than Neptune exerts on Uranus. 12. When Earth and the Moon are separated by a dis- 13. An astronaut weighs 8.00 x 10" newtons on the sur- tance of 3.84 x 10" meters, the magnitude of the grav- face of Earth. What is the weight of the astronaut itational force of attraction between them is 2.0 x 1020 6.37 * 10" meters above the surface of Earth? newtons. What would be the magnitude of this grave 1. 0.00 N itational force of attraction if Earth and the Moon 2. 2.00 * 10' N were separated by a distance of 1.92 x 10" meters? 1.60 x 10' N 1. 5.0 x 10" N 4. 3.20 x 10' N 2. 2.0 * 1020 N 3. 4.0 x 10 N 4. 8.0 x 10" N APhisPhysics: UCM-Gravity UCM.B1 Page 2UCM-Gravity Base your answers to questions 14 and 15 on the informa- | 18. A 5.0-kilogram sphere, starting from rest, falls freely tion and table below. 22 meters in 3.0 seconds near the surface of a plan- et. Compared to the acceleration due to gravity near The weight of an object was determined at five different Earth's surface, the acceleration due to gravity near distances from the center of Earth. The results are shown the surface of the planet is approximately in the table below. Position A represents results for the 1. the same object at the surface of Earth. 2. twice as great Position Distance from Earth's Center (m) Weight (N) 3. one-half as great 4. four times as great A 6.37 x 10" 1.0 * 103 B 1.27 x 10 25 x 10 19. Which diagram best represents the gravitational C 1.91 x 10 1.1 X 10 field lines surrounding Earth? D 2.55 x 10 3.3 x 10 3.19 x 10 4.0 X 101 Earth 14. The approximate mass of the object is 1. 0.01 kg 2. 10 kg (1) (3) 3. 100 kg 4. 1,000 kgags margate Earth Earth 15. At what distance from the center of Earth is the weight of the object approximately 28 newtons? 1. 35 x 10' m 2. 3.8 x 10' m (2) (4) 3. 4.1 x 10' m 4.5 x 10' m 20. The diagram below represents two satellites of equal mass, A and B, in circular orbits around a planet. 16. Gravitational forces differ from electrostatic forces in that gravitational forces are 1. attractive, only 2. repulsive, only 3. neither attractive nor repulsive 4. both attractive and repulsive 2R 17. The gravitational force of attraction between Earth Planet and the Sun is 3.52 x 10% newtons. Calculate the mass of the Sun. [Show all work, including the equa- tion and substitution with units.] Compared to the magnitude of the gravitational force of attraction between satellite A and the planet, the magnitude of the gravitational force of attraction between satellite B and the planet is 1. half as great 2. twice as great 3. one-fourth as great 4. four times as great APlusPhysics: UCM-Gravity UCM.B1 Page 3UCM-Gravity Base your answers to questions 21 and 22 on the informa- | 24. Two physics students have been selected by NASA to accompany astronauts on a future mission to the tion below. [Show all work, including the equation and Moon. The students are to design and carry out a substitution with units.] simple experiment to measure the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the Moon. Io (pronounced "EYE oh") is one of Jupiter's moons dis- covered by Galileo. Io is slightly larger can Describe an experiment that the students could con- than Earth's Moon. duct to measure the acceleration due to gravity on the The mass of Jo is 8.93 x 10# kilograms Moon. Your description must include: and the mass of Jupiter is 1.90 x 10#7 the equipment needed kilograms. The distance between the what quantities would be measured using the centers of Io and Jupiter is 4.22 x 10" meters. equipment what procedure the students should follow in 21. Calculate the magnitude of the gravitational force of conducting their experiment attraction that Jupiter exerts on Io. what equations and/or calculations the students would need to do to arrive at a value for the ac- celeration due to gravity on the Moon. 22. Calculate the magnitude of the acceleration of Io due to the gravitational force exerted by Jupiter. 23. Which diagram best represents the gravitational fore- es, F_, between a satellite, S, and Earth? Fo F S Fo 25. As a meteor moves from a distance of 16 Earth radii to a distance of 2 Earth radii from the center Earth Earth Earth of Earth, the magnitude of the gravitational force Earth between the meteor and Earth Fa becomes (1) (2) 1. 1/8 as great (3) (4) 2. 8 times as great 3. 64 times as great APlusPhysics: UCM-Gravity 4. 4 times as great UCM.B1UCM-Gravity 26. A 25-kilogram space probe fell freely with an accel- 32. A 1200-kilogram space vehicle travels at 4.8 meters eration of 2 meters per second? just before it landed per second along the level surface of Mars. If the on a distant planet. What is the weight of the space magnitude of the gravitational field strength on the probe on that planet? surface of Mars is 3.7 newtons per kilogram, the mag- 1. 12.5 N nitude of the normal force acting on the vehicle is 1. 320 N 2. 25 N 2. 930 N 3. 50 N 3. 4400 N 4. 250 N 4. 5800 N 27. The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of planet X is 19.6 meters per second'. If an object on 33. What is the weight of a 2.00-kilogram object on the the surface of this planet weighs 980 newtons, the surface of Earth? mass of the object is 1. 4.91 N 1. 50 kg 2. 2.00 N 2. 100 kg . 9.81 N 490 N 4. 19.6 N 4. 908 N 34. A 2.0-kilogram object is falling freely near Earth's 28. What is the acceleration due to gravity at a location surface. What is the magnitude of the gravitational where a 15-kilogram mass weighs 45 newtons? force that Earth exerts on the object? 1. 675 m/s' 1. 20 N 2. 9.81 m/s' 2. 2.0 N 3. 3.00 m/s 3. 0.20 N 4. 0.333 m/s 4. 0.0 N 29. As an astronaut travels from the surface of Earth 35. Calculate the magnitude of the centripetal force act- to a position that is four times as far away from the ing on Earth as it orbits the Sun, assuming a circular center of Earth, the astronaut's orbit and an orbital speed of 3.00 x 10" meters per 1. mass decreases second. [Show all work, including the equation and 2. mass remains the same substitution with units.] 3. weight increases 4. weight remains the same 36. On a small planet, an astronaut uses a vertical force of 175 newtons to lift an 87.5-kilogram boulder at 30. A satellite weighs 200 newtons on the surface of constant velocity to a height of 0.350 meter above Earth. What is its weight at a distance of one Earth the planet's surface. What is the magnitude of the radius above the surface of Earth? 1. 50 N gravitational field strength on the surface of the 2. 100 N planet 3. 400 N 1. 0.500 N/kg 4. 800 N 2. 2.00 N/kg 3. 9.81 N/kg 31. A 2.00-kilogram object weighs 19.6 newtons on 4. 61.3 N/kg Earth. If the acceleration due to gravity on Mars is 37. Calculate the magnitude of the average gravitational Mars? 3.71 meters per second', what is the object's mass on force between Earth and Moon. [Show all work, 1. 2.64 kg including the equation and substitution with units.] 2. 2.00 kg 3. 19.6 N 4. 7.42 N APlusPhysics: UCM-Gravity UCM.B1 Page 5UCM-Gravity 38. Which graph represents the relationship between the magnitude of the gravitational force exerted by Earth on a spacecraft and the distance between the center of the spacecraft and center of Earth? [Assume constant mass for the spacecraft.] Gravitational Gravitational Force Force Distance. Distance (1) (3) Gravitational Gravitational Force Force Distance Distance . (2) (4). 39. In which diagram do the field lines best represent the gravitational field around Earth? Earth Earth (1 ) (3) Earth Earth (2) (4)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


