
 undefin
undefin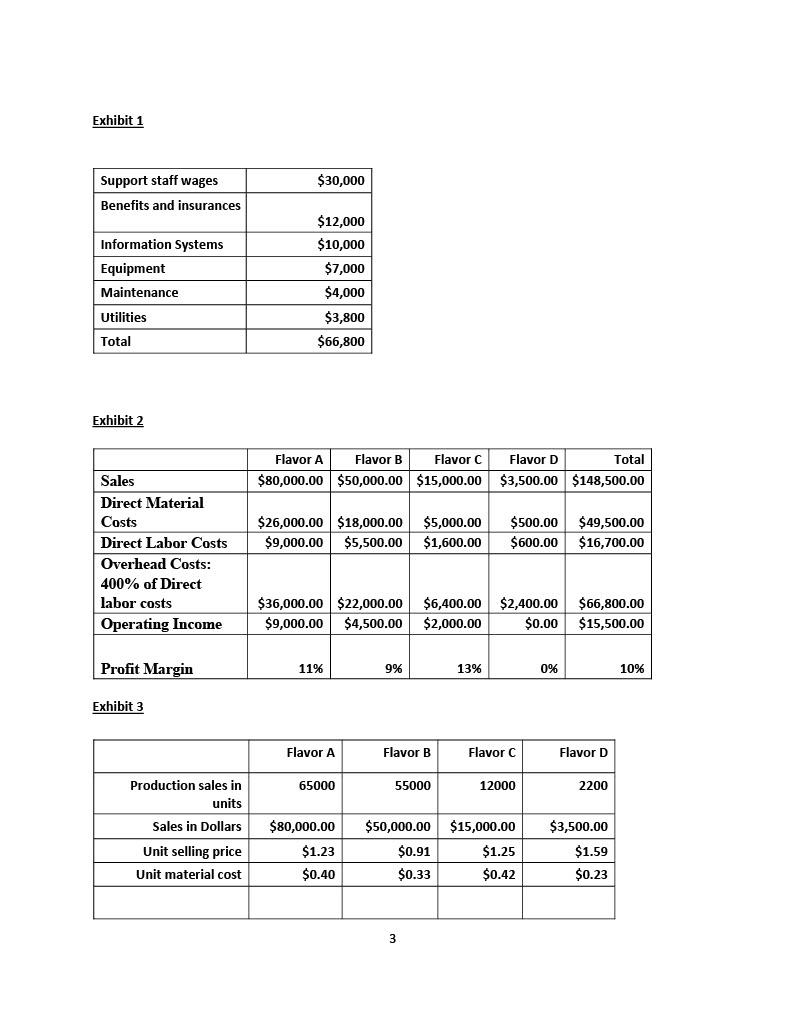
 ed
ed
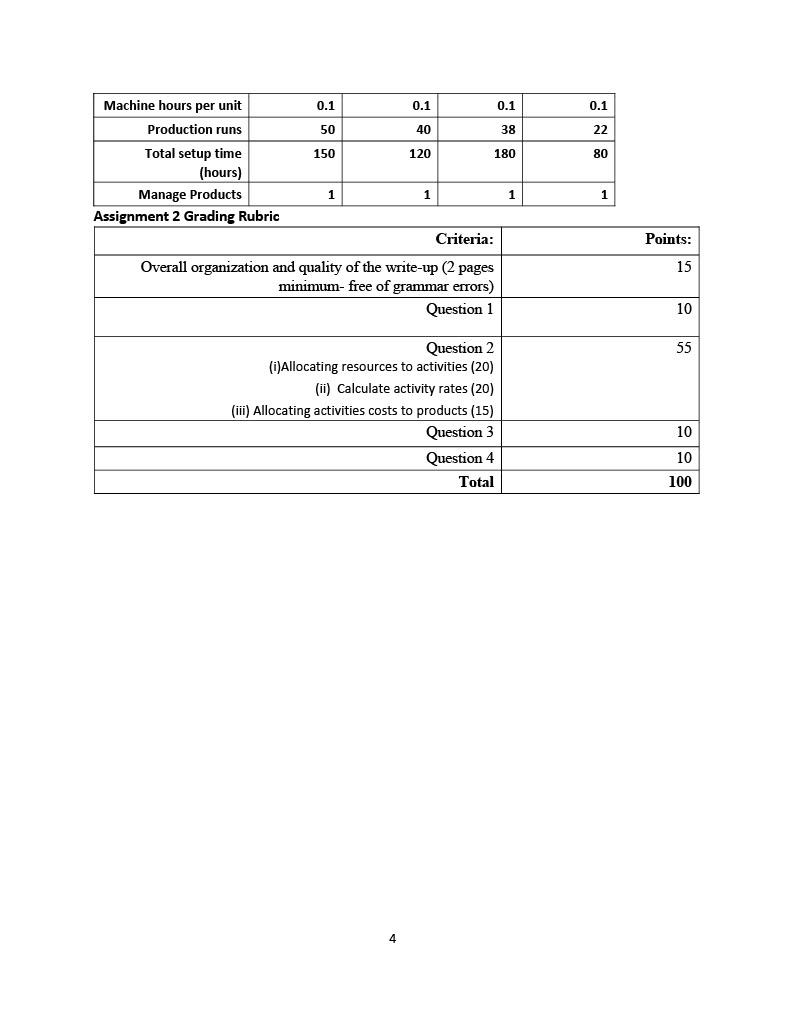
Implementation of Activity-Based Costing (ABC) The case of a Juice Company John Orland, controller of the Juice Company, has been concerned over the erosion of the recent financial results especially for the standard flavors (A and B) which used to earn a hefty 20 per cent of profit margin. Recently, Dan Brun, the sales manager has expanded the lines of products to encompass new flavors (B & C) which were in high demand by customers who were willing to pay 5 to 10 % premium. Richard Dunn, the manufacturing manager, was also excited to introduce the new flavors since they were expected to generate higher margins while using the same technology as standard flavors. However, he noticed that the introduction of new flavors added some technical complexities to the production process. For instance, unlike Flavors A & B, which were produced in huge volume and in long production runs, difficulties started to arise with the new flavors which were produced in smaller batches but required more changeovers and more production runs (see Exhibit 3). The Juice Company produced the different flavors in the same factory. Each flavor had a bill of materials that determines the quantity and cost of direct materials used for the production of each flavor. Additionally, a cost sheet was used to track the direct labor expenses incurred at each operating step for each of the four flavors. All overhead costs were grouped at the plant level and allocated to each flavor on the basis of direct labor cost. The rate was set at 400 % of direct labor costs (see Exhibit 2). John was intrigued by the behavior of their main competitors who were more interested in competing in, what appears according to the company's current costing system, to be low profit margin flavors (A and B) than in high profit margins (Flavors C&D). Such behavior has led the controller to question the accuracy of that costing system and to conclude that the current method of allocation of indirect costs is distorting their product costs thereby causing inappropriate pricing. To remedy the distortions caused by the traditional method of costing based on one single cost pool of indirect costs, John decided to implement Activity-based costing (ABC) method which focuses on the activities, how they are performed, and the resources they consumed and to assign activities costs to products based on how much demand each of these products puts on these activities. After careful analysis of the company's operations, the controller identified four main activities: process production 1 run, set up equipment, manage products, and run machines. The demand on these activities by different flavors is illustrated in Exhibit 3. He began by identifying the resources that were being consumed by the activities. These resources were grouped in six categories as shown in Exhibit 1. After interviewing the department heads in charge of support staff wages and benefits and insurance, he found out that their services are used by three activities: process production run (35%), set up (35%), and the remaining 30 % consumed to manage products. Next, the controller tackled the information system item and determines, after interview with the head of the information system department, that process production runs accounts for 40% of their services while 60 % are used to manage products. The results of his investigations about the usage of the equipment revealed that it was entirely used to run machines. Maintenance services were shared equally between the production run activity and run machine activity. Finally, utility was shared equally by the four activities. Questions 1. Describe the issue the company is facing 2. Calculate the costs for the four favors using ABC, reproduce the income statement, and calculate the new profit margin for each flavor 3. Compare the assigned overhead cost of each flavor (per unit) under both methods. Analyze why has ABC changed the total cost assigned to each flavor? provide tangible examples from the case to support your analysis. Which flavors are mispriced? 4. What actions may management consider in addressing the problems the company is facing? 2 Exhibit 1 $30,000 Support staff wages Benefits and insurances Information Systems Equipment Maintenance $12,000 $10,000 $7,000 $4,000 Utilities $3,800 $66,800 Total Exhibit 2 Flavor A Flavor B Flavor C $80,000.00 $50,000.00 $15,000.00 Flavor D Total $3,500.00 $148,500.00 $26,000.00 $18,000.00 $9,000.00 $5,500.00 $5,000.00 $1,600.00 $500.00 $600.00 $49,500.00 $ 16,700.00 Sales Direct Material Costs Direct Labor Costs Overhead Costs: 400% of Direct labor costs Operating Income $36,000.00 $22,000.00 $9,000.00 $4,500.00 $6,400.00 $2,000.00 $2,400.00 $0.00 $66,800.00 $15,500.00 Profit Margin 11% 9% 13% 0% 10% Exhibit 3 Flavor A Flavor B Flavor C Flavor D 65000 55000 12000 2200 Production sales in units Sales in Dollars Unit selling price Unit material cost $80,000.00 $1.23 $0.40 $50,000.00 $0.91 $0.33 $15,000.00 $1.25 $0.42 $3,500.00 $1.59 $0.23 3 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 50 40 38 22 150 120 180 80 Machine hours per unit Production runs Total setup time (hours) Manage Products Assignment 2 Grading Rubric 1 1 1 1 Criteria: Points: 15 Overall organization and quality of the write-up (2 pages minimum- free of grammar errors) Question 1 10 55 Question 2 (i)Allocating resources to activities (20) (ii) Calculate activity rates (20) (iii) Allocating activities costs to products (15) Question 3 Question 4 Total 10 10 100 Implementation of Activity-Based Costing (ABC) The case of a Juice Company John Orland, controller of the Juice Company, has been concerned over the erosion of the recent financial results especially for the standard flavors (A and B) which used to earn a hefty 20 per cent of profit margin. Recently, Dan Brun, the sales manager has expanded the lines of products to encompass new flavors (B & C) which were in high demand by customers who were willing to pay 5 to 10 % premium. Richard Dunn, the manufacturing manager, was also excited to introduce the new flavors since they were expected to generate higher margins while using the same technology as standard flavors. However, he noticed that the introduction of new flavors added some technical complexities to the production process. For instance, unlike Flavors A & B, which were produced in huge volume and in long production runs, difficulties started to arise with the new flavors which were produced in smaller batches but required more changeovers and more production runs (see Exhibit 3). The Juice Company produced the different flavors in the same factory. Each flavor had a bill of materials that determines the quantity and cost of direct materials used for the production of each flavor. Additionally, a cost sheet was used to track the direct labor expenses incurred at each operating step for each of the four flavors. All overhead costs were grouped at the plant level and allocated to each flavor on the basis of direct labor cost. The rate was set at 400 % of direct labor costs (see Exhibit 2). John was intrigued by the behavior of their main competitors who were more interested in competing in, what appears according to the company's current costing system, to be low profit margin flavors (A and B) than in high profit margins (Flavors C&D). Such behavior has led the controller to question the accuracy of that costing system and to conclude that the current method of allocation of indirect costs is distorting their product costs thereby causing inappropriate pricing. To remedy the distortions caused by the traditional method of costing based on one single cost pool of indirect costs, John decided to implement Activity-based costing (ABC) method which focuses on the activities, how they are performed, and the resources they consumed and to assign activities costs to products based on how much demand each of these products puts on these activities. After careful analysis of the company's operations, the controller identified four main activities: process production 1 run, set up equipment, manage products, and run machines. The demand on these activities by different flavors is illustrated in Exhibit 3. He began by identifying the resources that were being consumed by the activities. These resources were grouped in six categories as shown in Exhibit 1. After interviewing the department heads in charge of support staff wages and benefits and insurance, he found out that their services are used by three activities: process production run (35%), set up (35%), and the remaining 30 % consumed to manage products. Next, the controller tackled the information system item and determines, after interview with the head of the information system department, that process production runs accounts for 40% of their services while 60 % are used to manage products. The results of his investigations about the usage of the equipment revealed that it was entirely used to run machines. Maintenance services were shared equally between the production run activity and run machine activity. Finally, utility was shared equally by the four activities. Questions 1. Describe the issue the company is facing 2. Calculate the costs for the four favors using ABC, reproduce the income statement, and calculate the new profit margin for each flavor 3. Compare the assigned overhead cost of each flavor (per unit) under both methods. Analyze why has ABC changed the total cost assigned to each flavor? provide tangible examples from the case to support your analysis. Which flavors are mispriced? 4. What actions may management consider in addressing the problems the company is facing? 2 Exhibit 1 $30,000 Support staff wages Benefits and insurances Information Systems Equipment Maintenance $12,000 $10,000 $7,000 $4,000 Utilities $3,800 $66,800 Total Exhibit 2 Flavor A Flavor B Flavor C $80,000.00 $50,000.00 $15,000.00 Flavor D Total $3,500.00 $148,500.00 $26,000.00 $18,000.00 $9,000.00 $5,500.00 $5,000.00 $1,600.00 $500.00 $600.00 $49,500.00 $ 16,700.00 Sales Direct Material Costs Direct Labor Costs Overhead Costs: 400% of Direct labor costs Operating Income $36,000.00 $22,000.00 $9,000.00 $4,500.00 $6,400.00 $2,000.00 $2,400.00 $0.00 $66,800.00 $15,500.00 Profit Margin 11% 9% 13% 0% 10% Exhibit 3 Flavor A Flavor B Flavor C Flavor D 65000 55000 12000 2200 Production sales in units Sales in Dollars Unit selling price Unit material cost $80,000.00 $1.23 $0.40 $50,000.00 $0.91 $0.33 $15,000.00 $1.25 $0.42 $3,500.00 $1.59 $0.23 3 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 50 40 38 22 150 120 180 80 Machine hours per unit Production runs Total setup time (hours) Manage Products Assignment 2 Grading Rubric 1 1 1 1 Criteria: Points: 15 Overall organization and quality of the write-up (2 pages minimum- free of grammar errors) Question 1 10 55 Question 2 (i)Allocating resources to activities (20) (ii) Calculate activity rates (20) (iii) Allocating activities costs to products (15) Question 3 Question 4 Total 10 10 100

 undefin
undefin
 ed
ed





