Question
Under the normal conditions, noble gases are monoatomic and have closed shell electronic configuration. Lighter noble gases have low boiling points due to weak dispersion
Under the normal conditions, noble gases are monoatomic and have closed shell electronic configuration. Lighter noble gases have low boiling points due to weak dispersion forces between the atoms and the absence of other interatomic interactions. Xenon, one of the important noble gas, forms a series of compounds with fluorine with oxidation number +2, +4 and +6. All xenon fluorides are strong oxidising agents. XeF4reacts violently with water to give XeO3. The geometry of xenon compounds can be deduced by considering the total number of electron pairs in their valence shell. (i) Among noble gases (from He to Xe) only xenon reacts with fluorine to form stable xenon fluorides because xenon
| (a) has the largest size |
| (b) has the lowest ionisation enthalpy |
| (c) has the highest heat of vapourisation |
| (d) is the most readily available noble gas. |
(ii)The structure of XeO3is
| (a) square planar | (b) pyramidal | (c) linear | (d) T-shaped. |
(iii) In the preparation of compound of xenon, Bartlett had takenO+2PtF6O2+PtF6as a basecompound. This is because
| (a) both O2and Xe have same size |
| (b) both Xe and O2have same electron gain enthalpy |
| (c) both have almost same ionisation enthalpy |
| (d) both Xe and O2are gases. |
(iv) The oxidation state of xenon in XeO3is
| (a) +4 | (b) +2 | (c) +8 | (d) +6 |
5
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions : Interhalogen compounds are formed when halogen group elements react with each other. These are the compounds which consist of two or more different elements of group - 17. A halogen with large size and low electronegativity reacts with an element of group - 17with small size and high electronegativity. As the ratio of radius of larger and smaller halogen increases, the number of atoms in a molecule also increases. The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer : (i) The stability of interhalogen compounds follows the order
| (a) IF3> BrF3> ClF3 | (b) ClF3> BrF3> IF3 |
| (c) BrF3> IF3> ClF3 | (d) ClF3> IF3> BrF3 |
(ii) Identify the correct match from the following.
| (a) [ICl2]--bent | (b) IF7- pentagonal bipyramidal |
| (c) ClF3- trigonal planar | (d)[BrF4r]--square pyramidal |
(iii) In XA5,the central atom has (both X and A are halogens)
| (a) 5 bond pairs and no lone pairs | (b) 5 bond pairs and one lone pair |
| (c) 6 bond pairs and no lone pairs | (d) 4 bond pairs and one lone pair. |
(iv) In the known interhalogen compounds, the maximum number of atoms are
| (a) 4 | (b) 5 |
| (c) 8 | (d) 7 |
5
Noble gases are inert gases with general electronic configuration of ns2np6. These are mono atomic, colourless, odourless and tasteless gases. The first compound of noble gases was obtained by the reaction of Xe with PtF6. A large number of compounds of Xe and fluorine have been prepared till now. The structure of these compounds can be explained on the basis of VSEPR theory as well as concept of hybridisation. The compounds of krypton are fewer. Only the difluoride of krypton (KrF2) has been studied in detail. Compounds of radon have not isolated but only identified by radio tracer technique. However, no true compounds of helium, neon or argon are yet known. (i) The formula of the compound when Xe and PtF6are mixed, is
| (a) XeF6 | (b) XeF4 | (c) Xe2PtF6 | (d) Xe+[PtF6]- |
(ii) Which of the following is not formed by Xe?
| (a) XeFs | (b) XeF | (c) XeF3 | (d) All of these |
(iii) The number of lone pairs and bond pairs of electrons around Xe in XeOF4respectively are
| (a) O and 5 | (b) 1 and 5 | (c) 1 and 4 | (d) 2 and 3 |
(iv) Which of the following compounds has more than one lone pair of electrons around central atom?
| (a) XeO3 | (b) XeF2 | (c) XeOF4 | (d) XeO2F2 |
5
All the elements of group 16 have ns2np4configuration in their outermost shell. Therefore, the atoms of these elements try to gain or share two electrons to achieve noble gas configuration. Sulphur and other elements of group 16 are less electronegative than oxygen, so, they cannot accept electrons easily. By sharing of two electrons with other elements, these elements acquire ns2np6configuration and exhibit +2 oxidation state. Except oxygen, group 16 elements have vacant d-orbitals in their valence shell to which electrons can be promoted from p- and s-orbitals of the same shell. As a result, they can show +4 and +6 oxidation states also. (i) Oxygen shows +2 oxidation state in
| (a) OF2 | (b) H2O | (c) Cl2O | (d) H2O2 |
(ii) Like sulphur, oxygen is not able to show +4 and +6 oxidation states because
| (a) oxygen is a gas while sulphur is a solid |
| (b) sulphur has high ionisation enthalpy as compared to oxygen |
| (c) oxygen has no d-orbitals in its valence shell |
| (d) oxygen has high electron affinity as compared to sulphur. |
(iii) Oxidation state of sulphur inNa2S4O6
| (a) 7/2 | (b) 5/2 | (c) | (d) 3/2 |
(iv) The oxidation states of sulphur in S8'SO3and H2S are respectively
| (a) 0, +6 and -2 | (b) +6,0 and -2 | (c) -2,0 and +6 | (d) +2, +6 and -2 |
5
Nitric acid reacts with most of the metals (except noble metals like gold and platinum) and non-metals. Towards its reaction with metals, HNO3acts as an acid as well as an oxidising agent. Like other acids, HNO3liberate nascent hydrogen from metals which further reduces the nitric acid into number of products like NO, NO2, N2O or NH3. The different stages of reduction of nitric acid are: HNO3+eNO2+4+2eNO+2NaOHN+12O+4eNH33HNO3+eNO2+4+2eNO+2NaOHN+12O+4eNH33 The product of the reduction of HNO3depends upon the nature of the metal, concentration of nitric acid and temperature. (i) Which of the following reactions Is used to prepare laughing gas?
| (a)Pb+dil.HNO3Pb+dil.HNO3 | (b)Hg+dil.HNO3Hg+dil.HNO3 |
| (c)Zn+dil.HNO2Zn+dil.HNO2 | (d)Cu+dil.HNO3Cu+dil.HNO3 |
(ii) Gold and platinum does not dissolve in HN03 but soluble in 1 : 3 mixture of HNO3and HCI due to theformation of respectively
| (a) Au(NO3)2'[Pt(NO3)2] | (b) H[AuCI4], H2[PtCI6] |
| (c) [AuCI6]2-, [PtCI2]2- | (d) [Au(NO3)4]+,[Pt(NO3)6]2- |
(iii) Identify B in the following reaction. Cu+HNO3(conc.)(A)+(B)+H2OCu+HNO3(conc.)(A)+(B)+H2O Deep blue colour Gas
| (a) NO2 | (b) N2 | (c) NO | (d) N2O |
(iv) In which of the following reactions HN03 will not act as an oxidising agent?
| (a)HNO3+H2SO4HNO3+H2SO4 | (b)HNO3+FeSO4+H2SO4HNO3+FeSO4+H2SO4 |
| (c)KI+HNO3KI+HNO3 | (d)Au+HNO3Au+HNO3 |
5 Ozone is an unstable, dark blue diamagnetic gas. It absorbs the UV radiation strongly, thus protecting the people on earth from the harmful UV-radiation from the sun. The use of chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) in aerosol and refrigerators and their subsequent escape into the atmosphere, is blamed for making holes in the ozone layer over the Antarctica. Ozone acts as a strong oxidising agent in acidic and alkaline medium. For this property, ozone is used as a germicide and disinfectant for sterilizing water. It is also used in laboratory for the ozonolysis of organic compounds and in industry for the manufacture of potassium permanganate, artificialsilk, etc The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer : (i) Which of the following statements is not correct for ozone?
| (a) It oxidises lead sulphide | (b) It oxidises potassium iodide |
| (c) It oxidises mercury. | (d) It cannot act as bleaching agent in dry state. |
(ii) Ozone reacts with moist iodine gives
| (a) HI | (b) HIO3 | (c) I2O5 | (d) I2O4 |
(iii) Ozone acts as an oxidising agent due to
| (a) liberation of nascent oxygen | (b) liberation of oxygen gas |
| (c) both (a) and (b) | (d) none of these |
(iv) The colour of ozone molecule is
| (a) white | (b) blue | (c) pale green | (d) pale yellow. |
5
Chlorine is a greenish yellow gas with pungent and suffocating odour. With dry slaked lime, it gives bleaching powder. Bleaching powder is a mixture of calcium hypochlorite and basic calcium chloride : [Ca(OCI)2.CaCl2Ca(OH)2 2 H2O]. The amount of chlorine obtained from a sample of bleaching powder by the treatment with excess of dilute acids or CO2is called available chlorine. Chlorine is a powerful bleaching agent. Bleaching effect of chlorine ispermanent. (i) Chlorine gas reacts with_____to form bleaching powder
| (a) Ca(OH)2 | (b) CaCl2 |
| (c) CaSO4 | (d) dry CaO |
(ii) Chlorine reacts with cold and dilute alkali to form
| (a) chloride | (b) hypochlorite | (c) chlorate | (d) both (a) and (b) |
(iii) Chlorine is used as a bleaching agent. The bleaching action is due to
| (a) oxidation | (b) chlorination | (c) hydrogenation | (d) reduction |
(iv) Bleaching powder contains a salt of an oxoacid as one of its components. The anhydride of that oxoacid is
| (a) Cl20 | (b) Cl2O7 | (c) CIO2 | (d) Cl2O6 |
5
The halogen elements show great resemblances to one another in their chemical behaviour and properties of their compounds with other elements. There is, however, a progressive change in properties from F through Cl, Br, and I to At. F is most reactive among the halogens and infact, from all other elements and it has certain other properties that set it apart from the other halogens. In these questions (i-iv), a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
| (a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion. |
| (b) Assertiqn and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion. |
| (c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement |
| (d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement. |
(i)Assertion: F2has high reactivity. Reason: F2has low bond dissociation enthalpy (ii)Assertion:The bond between F - F is weaker than between Cl - Cl. Reason :Atomic size of F is smaller than that of Cl. (iii)Assertion:F atom has less negative electron affinity than Cl atom. Reason:Additional electrons are repelled more effectively by 3p- electrons in Cl than by 2p- electrons in F atom. (iv)Assertion :Fluorine is strongest oxidising agent in halogens. Reason :It displaces other halogens from its aqueous solution.
5
All the elements of group 16 form hydrides : H2O, H2S, H2Se, H2Te and H2Po. All these hydrides have angular structure which involves sp3 hybridisation of the central atom. All hydrides are volatile. The volatility increases from H2O to H2S and then decreases. All hydrides are weakly acidic in character. The increase in acidic characterfrom H2O to H2Te is a result of the decrease in the 1 H- E (where E = 0, S, Se, Te, Po) bond dissociation enthalpy from H2O to H2Te. All the hydrides except water are reducing agents. The reducing property of these hydrides increases from H2S to H2Te. In these questions (i-iv), a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices. (a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion. (b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion. (c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement. (d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement (i) Assertion:Water has high boiling -point. Reason:Water molecules are associated with hydrogen bonding. (ii) Assertion:H2Te has less acidic character than H2S. Reason:Bond dissociation enthalpy of H - Te is less than H - S. (iii) Assertion:Reducing nature of hydrides of group-16 elements increases as the atomic number of central atom increases. Reason :Due to strong force of attraction of H - E bond. (iv) Assertion:H2Ois the only hydrides of the chalcogens which is liquid. Reason :In ice each a-atom is surrounded by 4H -atoms.
5
Group 15 elements consist of N, P, As, Sb, Bi and Mc (Moscovium) with general electronic configuration ns2np3and oxidation states +3 and +5. Nitrogen differs from rest of the elements. Phosphorus show allotropy and is more reactive than Nitrogen. Hydrides of group 15 elements show variation in bond angle, boiling point, basic character, stability and reducing character. Oxides of group 15 elements show decrease in acidic character and more increase in basic character. Nitrogen forms large number of oxides. Halides of group 15 elements are mostly covalent. Nitrogen and phosphorus form oxoacids along with As. Nitric acid is manufactured by Ostwald process and useful for nitration and as oxidising agent. NH3is used in manufacture of fertilisers. HNO3reacts with metals and non-metals to give different products under different conditions. Phosphorus reacts with oxygen, halogens, nitric acid, NaOH to form different products. (a) Why does reducing character increases from NH3to BiH3? (b) Draw the structure of oxides of nitrogen in which oxidation state of nitrogen is +5. (c) What happens when white phosphorus reacts with NaOH in inert atmosphere? Write the reaction involved. (d) Which one out ofPCl+4andPCl4PCl4+andPCl4is not likely to exist, why? (e) Write the formula of the compound of phosphorus which is obtained when HNO3(conc.) oxidises phosphorus. (f) Why does PCI3fumes in moist air? (g) What happen when copper sulphate reacts with phosphine gas? Give chemical equation.
5
Group 16 elements are called chalcogens i.e., ore forming elements (oxygen, sulphur, selenium etc.) because most of the ores are oxides and sulphides. Oxygen is gas where as other elements of group 16 are solids. Oxygen shows anomalous behaviour. Oxygen is diatomic where is sulphur exists as S8 which has crown shaped structure. It shows allotropy. Sulphur is present in onion and garlic that is why they have pungent smell. Sulphur is used for manufacture of sulphuric acid which is called 'King of chemicals', used in fertilizer, detergents, dyes and drugs. (a) Name the most abundant element in the earth crust. (b) A gas 'X' is obtained from roasting of sulphide ore. It turns lime water milky. Identify the gas and write the chemical reaction involved. (c) What happens when SO2gas is reacted with o, in presence of V2O5at 770K temperature and high pressure? Write the chemical reaction involved. (d) What happens when SO3is passed through sulphuric acid? Write chemical equation for the reaction (e) Why is SO3not directly absorbed in water to get sulphuric acid?
5
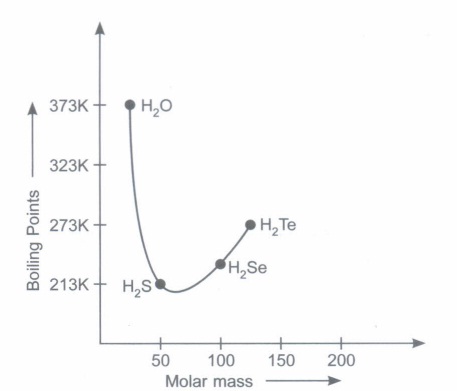
Observe the graph shown in the diagram and answer the questions that follow. The graph is plotted between molar mass of hydrides of group 16 Vs boiling points of hydrides of group 16.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


