Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Understanding Variation/Managing Chaos Compute Average Moving Range, Natural Process Limits,Upper Range Limit Please help with ONLY questions 9 and 10. I believe that the answer
Understanding Variation/Managing Chaos
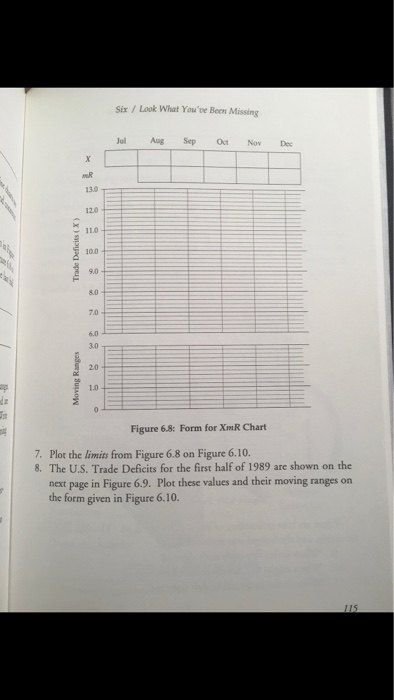
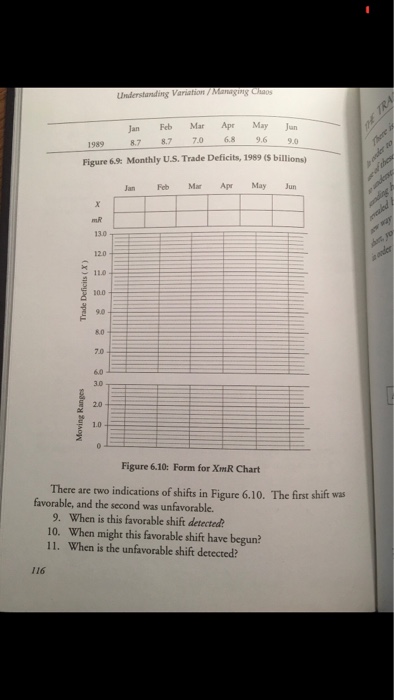
Compute Average Moving Range, Natural Process Limits,Upper Range Limit
Please help with ONLY questions 9 and 10. I believe that the answer can either be that the favorable shift begins during April when the negative trend slows down dramatically OR in May when it begins a steep positive trend. Thanks! Please explain to me how this is an honor code violation?



Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


