Question
Undertake elements of the Strategic Outline Case (using the HMT 5-case model methodology) for a new superfast broadband network in the UK referred to as
Undertake elements of the Strategic Outline Case (using the HMT 5-case model methodology) for a new superfast broadband network in the UK referred to as the “Express Broadband Programme UK” or EBPUK.
The underlying intent of the EBPUK Programme is to progress towards achieving 100% broadband coverage for the UK utilising wire/fibre, wireless and satellite communications networks by 2023, with the deployment of superfast broadband where affordable. This will lead to the ongoing incremental further evolution of improvements to superfast broadband capability beyond this date.
In particular, implementation of the programme aims to achieve investment to provide a consistent network broadband experience across the whole of the UK comparable to that experienced in urban areas. Intervention by government is required to cover the investment gap in order to achieve such equality across the UK; the justification is that this strategic intervention is the only way such improvements can be achieved.
EBPUK currently has five primary goals:
• To support economic growth in the UK, including in rural areas which are currently poorly served and designated Enterprise Zones (Figure 1).
• To ensure this country has the best Superfast Broadband in Europe by the end of 2023.
• To ensure delivery of Standard Broadband to virtually all communities in the UK within the lifetime of this parliament (2023)
• To ensure the efficient use of funding to deliver Superfast Broadband and Standard Broadband including the leveraging of private funding
• To assist other Government initiatives which are dependent upon customers ability to access Broadband based services.
EBPUK’s vision for broadband is driven by two key IT policy goals:
• The target set by the Secretary of State for Culture, Media and Sport: to have the best Superfast Broadband network in Europe by 2023; and
• The European Union aspiration to have 30Mbps available to all and for 50% access to 100Mbps by 2028.
Three potential project delivery options have been identified in response to the above spending objectives as follows:
Option 1: Centrally led delivery via a single EBPUK Megaproject:
EBPUK contracts for and directs the provision of services centrally through subsidised national contract(s) directly with suppliers to deliver improved infrastructure.
Option 2: Locally led delivery via multiple local schemes:
Locally delivered subsidised local contracts with suppliers to deliver improved infrastructure, where services are provided at a local authority level (boroughs and councils). EBPUK funding is provided as a contribution to projects when a local body produces a satisfactory Local Broadband Plan and undertakes a competition to select a supplier.
Option 3: Customer led delivery:
Subsidised individual householder and small business contracts with suppliers to deliver increased demand for services to stimulate improved infrastructure, where consumers make the delivery decision and the market provides the subscriptions, products and services.
Broader policy contexts and challenges:
Government departments have 100 major IT projects underway with a total value of £35 billion. However, over the recent past IT difficulties have affected many of theseprojects, not least in the management of large IT companies, leading to the Government seeking new delivery models as an alternative to major projects.
Government is pursuing a policy of ‘Localism’ and ‘Big Society’ which seeks to put citizens at the heart of public services. The future of local government is being shaped by two forces: a
drive towards localism; the need to cut spending and achieve efficiencies.
Local authorities vary considerably in their experience of rolling out broadband schemes and funds available to support such projects.
There is a lack of diversity in broadband providers operating in the UK market, and customers tend to be poorly consulted during IT initiatives and poorly informed regarding key broadband performance metrics.
Many people in the UK do not enjoy the full benefits of the internet, either because the speeds they can receive do not support more data-rich services such as video-streaming, or indeed they cannot get fixed- line or mobile broadband service at all. The business case for broadband is often weaker in rural areas, and in some cases non-existent as the cost of deployment rises considerably.
Question:
1. Evaluate the current project spending objectives for the EBPUK against the HMT SMART objectives framework.
2. Undertake a swot analysis for each of the three delivery options (Options 1, 2 and 3) to identify associated benefits, risks, constraints and dependencies for each option. Use dimensions of the 5 case model to help focus your analysis.
3. The time scale for the construction of the programme is 1 year (2022), the subsequent operational life (2023 onwards) of the project is set as 4 years. Use the data outlined in table 1, 2 and this project option based on its economic return.
4. Considering your responses to questions above, advise the DCMS of the possible limitations to using CBA to determine the viability of Option 1.
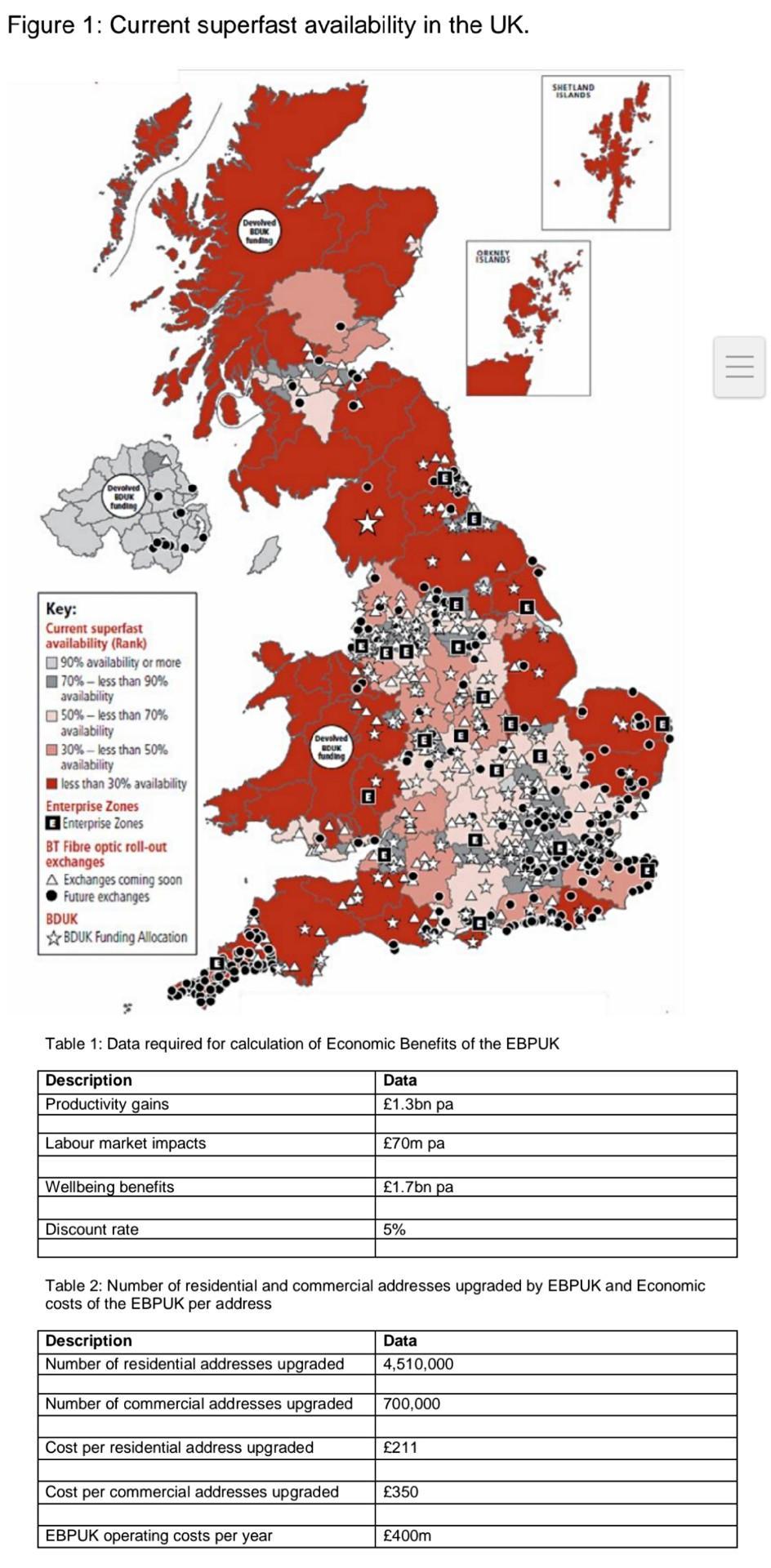
Figure 1: Current superfast availability in the UK. Devolved BOUK funding Key: Current superfast availability (Rank) 90% availability or more 70%-less than 90% availability 50%-less than 70% availability 30%-less than 50% availability less than 30% availability Enterprise Zones Enterprise Zones BT Fibre optic roll-out exchanges A Exchanges coming soon Future exchanges BDUK BDUK Funding Allocation Wellbeing benefits Devolved BOUK funding Discount rate Devolved BOUK funding Table 1: Data required for calculation of Economic Benefits of the EBPUK Description Productivity gains Labour market impacts Description Number of residential addresses upgraded Number of commercial addresses upgraded Cost per residential address upgraded Data 1.3bn pa Cost per commercial addresses upgraded EBPUK operating costs per year 70m pa 1.7bn pa 5% Table 2: Number of residential and commercial addresses upgraded by EBPUK and Economic costs of the EBPUK per address Data 4,510,000 700,000 211 ORKNEY ISLANDS 350 SHETLAND ISLANDS 400m
Step by Step Solution
3.51 Rating (154 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Answer 1 Evaluation of the Current Project Spending Objectives for the EBPUK against the HMT SMART Objectives Framework The Government of the United Kingdom has set spending objectives for the EBPUK E...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


