
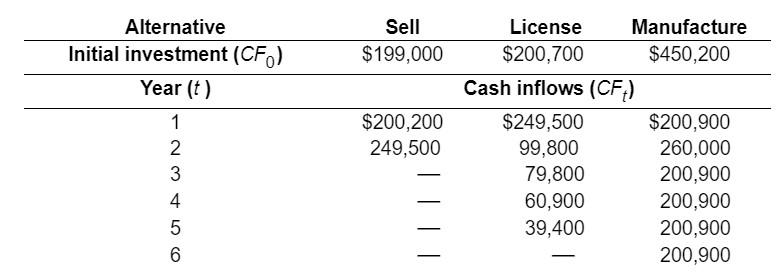


Unequal livesANPV approach JBL Co. has designed a new conveyor system. Management must choose among three alternative courses of action: (1) The firm can sell the design outright to another corporation with payment over 2 years. (2) It can license the design to another manufacturer for a period of 5 years, its likely product life. (3) It can manufacture and market the system itself; this alternative will result in 6 years of cash inflows. The company has a cost of capital of 12.9%. Cash flows associated with each alternative are as shown in the following table. (Click on the icon here in order to copy the contents of the data table below into a spreadsheet.) Sell $199,000 Alternative Initial investment (CF) Year (t) 1 2 3 4 5 6 $200,200 249,500 License Manufacture $200,700 $450,200 Cash inflows (CF) $249,500 $200,900 99,800 260,000 79,800 200,900 60,900 200,900 39,400 200,900 200,900 a. Calculate the net present value of each alternative and rank the alternatives on the basis of NPV. b. Calculate the annualized net present value (ANPV) of each alternative and rank them accordingly. c. Why is ANPV preferred over NPV when ranking projects with unequal lives? a. The net present value for the option to sell is $ (Round to the nearest cent.) The net present value for the option to license is $ . (Round to the nearest cent.) ) The net present value for the option to manufacture is $ (Round to the nearest cent.) Rank the projects below. (Select from the drop-down menus.) First Option to Second: Option to Third: Option to b. The ANPV for the option to sell is $ (Round to the nearest cent.) The ANPV for the option to license is $ (Round to the nearest cent.) The ANPV for the option to manufacture is $ (Round to the nearest cent.) Rank the projects below. (Select from the drop-down menus.) First: Option to Second: Option to Third Option to c. Why is ANPV preferred over NPV when ranking projects with unequal lives? (Select all that apply.) A. Comparing the NPVs of projects with unequal lives gives an advantage to those projects that generate cash flows over the longer period. B. Both the NPV method and the ANPV technique always give the same result as long as the project's IRR is positive. C. The ANPV technique implicitly assumes that all projects can be selected again at their conclusion an infinite number of times. D. ANPV adjusts for the differences in the length of the projects and allows selection of the optimal project. Unequal livesANPV approach JBL Co. has designed a new conveyor system. Management must choose among three alternative courses of action: (1) The firm can sell the design outright to another corporation with payment over 2 years. (2) It can license the design to another manufacturer for a period of 5 years, its likely product life. (3) It can manufacture and market the system itself; this alternative will result in 6 years of cash inflows. The company has a cost of capital of 12.9%. Cash flows associated with each alternative are as shown in the following table. (Click on the icon here in order to copy the contents of the data table below into a spreadsheet.) Sell $199,000 Alternative Initial investment (CF) Year (t) 1 2 3 4 5 6 $200,200 249,500 License Manufacture $200,700 $450,200 Cash inflows (CF) $249,500 $200,900 99,800 260,000 79,800 200,900 60,900 200,900 39,400 200,900 200,900 a. Calculate the net present value of each alternative and rank the alternatives on the basis of NPV. b. Calculate the annualized net present value (ANPV) of each alternative and rank them accordingly. c. Why is ANPV preferred over NPV when ranking projects with unequal lives? a. The net present value for the option to sell is $ (Round to the nearest cent.) The net present value for the option to license is $ . (Round to the nearest cent.) ) The net present value for the option to manufacture is $ (Round to the nearest cent.) Rank the projects below. (Select from the drop-down menus.) First Option to Second: Option to Third: Option to b. The ANPV for the option to sell is $ (Round to the nearest cent.) The ANPV for the option to license is $ (Round to the nearest cent.) The ANPV for the option to manufacture is $ (Round to the nearest cent.) Rank the projects below. (Select from the drop-down menus.) First: Option to Second: Option to Third Option to c. Why is ANPV preferred over NPV when ranking projects with unequal lives? (Select all that apply.) A. Comparing the NPVs of projects with unequal lives gives an advantage to those projects that generate cash flows over the longer period. B. Both the NPV method and the ANPV technique always give the same result as long as the project's IRR is positive. C. The ANPV technique implicitly assumes that all projects can be selected again at their conclusion an infinite number of times. D. ANPV adjusts for the differences in the length of the projects and allows selection of the optimal project












