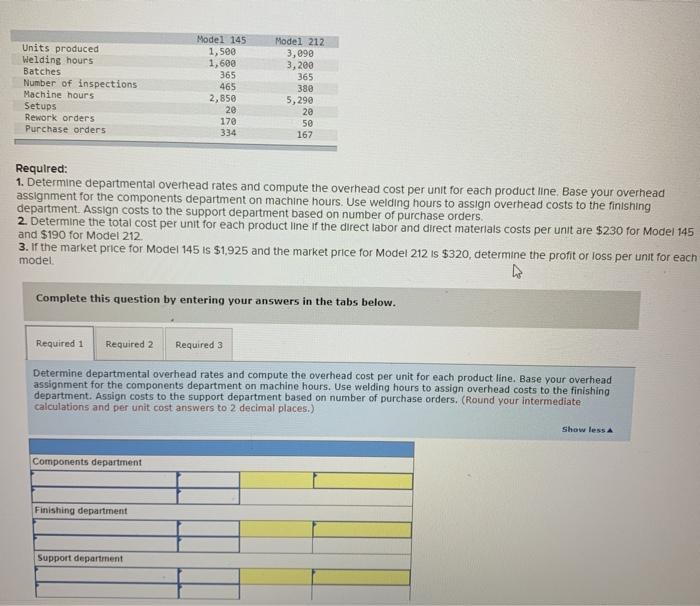
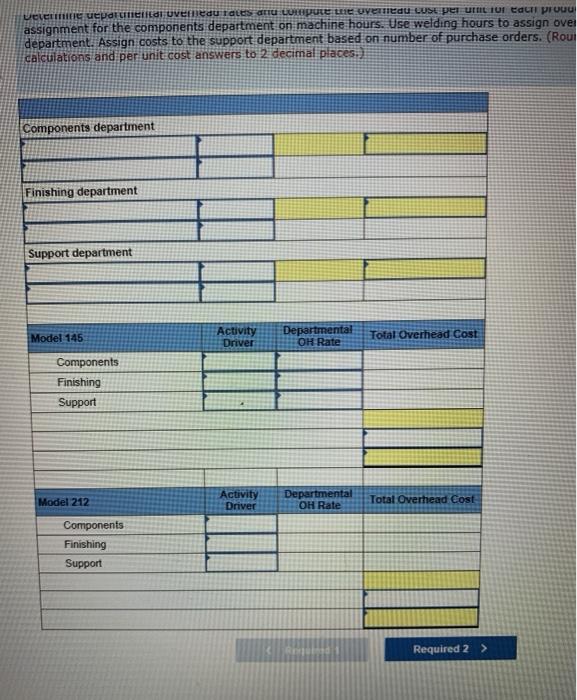
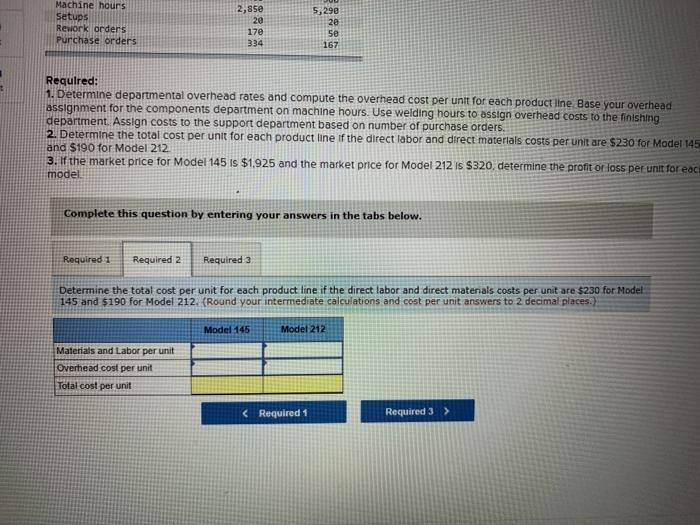
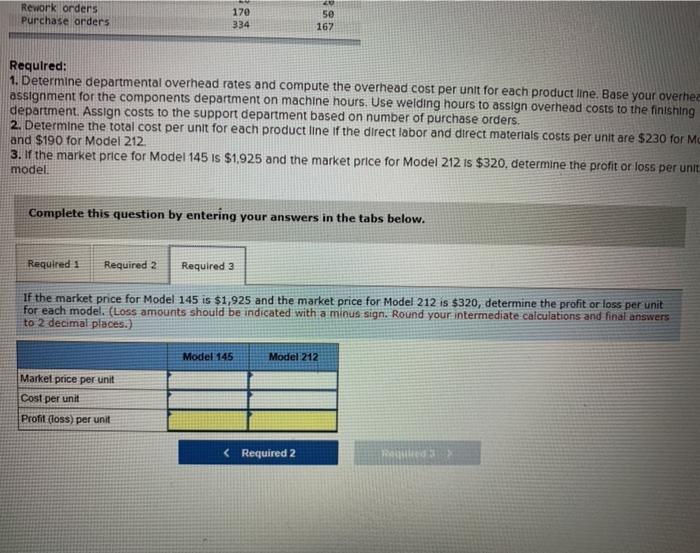
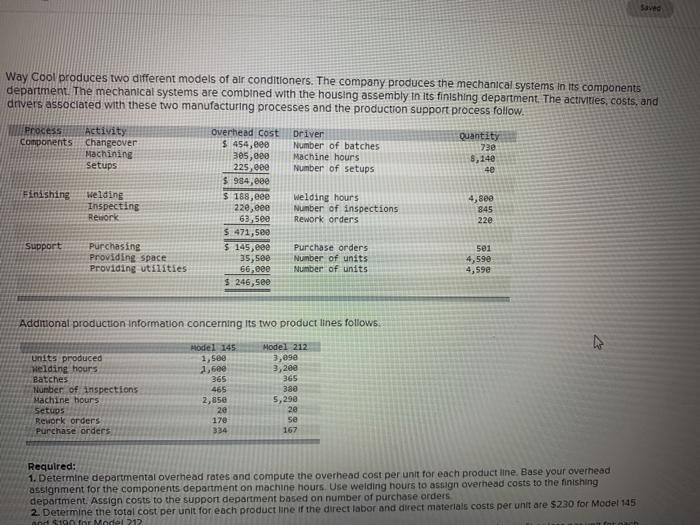
Units produced Welding hours Batches Number of inspections Machine hours Setups Rework orders Purchase orders Model 145 1,500 1,600 365 465 2,850 20 170 334 Model 212 3,090 3,200 365 380 5,290 20 50 167 Required: 1. Determine departmental overhead rates and compute the overhead cost per unit for each product line. Base your overhead assignment for the components department on machine hours. Use welding hours to assign overhead costs to the finishing department. Assign costs to the support department based on number of purchase orders 2. Determine the total cost per unit for each product line if the direct labor and direct materials costs per unit are $230 for Model 145 and $190 for Model 212. 3. If the market price for Model 145 is $1925 and the market price for Model 212 is $320, determine the profit or loss per unit for each model Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Required 3 Determine departmental overhead rates and compute the overhead cost per unit for each product line. Base your overhead assignment for the components department on machine hours. Use welding hours to assign overhead costs to the finishing department. Assign costs to the support department based on number of purchase orders. (Round your intermediate calculations and per unit cost answers to 2 decimal places.) Show less Components department Finishing department Support department Levente upalunettdi uveneau Tales and compute te uviedu LUSE per unit 10 Calli prouu assignment for the components department on machine hours. Use welding hours to assign ove department. Assign costs to the support department based on number of purchase orders. (Rou calculations and per unit cost answers to 2 decimal places.) Components department Finishing department Support department Model 145 Activity Driver Departmental OH Rate Total Overhead Cost Components Finishing Support Model 212 Activity Driver Departmental OH Rate Total Overhead Cost Components Finishing Support Required 2 > Machine hours Setups Rework orders Purchase orders 2,850 20 17e 334 5,290 2e 5e 167 Required: 1. Determine departmental overhead rates and compute the overhead cost per unit for each product line Base your overhead assignment for the components department on machine hours. Use welding hours to assign overhead costs to the finishing department. Assign costs to the support department based on number of purchase orders. 2. Determine the total cost per unit for each product line of the direct labor and direct materials costs per unit are $230 for Model 145 and $190 for Model 212 3. If the market price for Model 145 is $1.925 and the market price for Model 212 is $320, determine the profit or loss per unit for each model Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Required 3 Determine the total cost per unit for each product line if the direct labor and direct matenals costs per unit are $230 for Model 145 and $190 for Model 212. (Round your intermediate calculations and cost per unit answers to 2 decimal places.) Model 145 Model 212 Materials and Labor per unit Overhead cost per unit Total cost per unit Rework orders Purchase orders 170 334 50 167 Required: 1. Determine departmental overhead rates and compute the overhead cost per unit for each product line. Base your overhee assignment for the components department on machine hours. Use welding hours to assign overhead costs to the finishing department. Assign costs to the support department based on number of purchase orders. 2. Determine the total cost per unit for each product line of the direct labor and direct materials costs per unit are $230 for Me and $190 for Model 212 3. If the market price for Model 145 is $1.925 and the market price for Model 212 is $320. determine the profit or loss per unit model. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Required 3 If the market price for Model 145 is $1,925 and the market price for Model 212 is $320, determine the profit or loss per unit for each model. (Loss amounts should be indicated with a minus sign. Round your intermediate calculations and final answers to 2 decimal places.) Model 145 Model 212 Market price per unit Cost per unit Profit (loss) per unit