Question
Unsupervised Learning 1. The figure below contains twelve points that live in 2-dimensional Euclidean space, and each of the point is named by its (x,
Unsupervised Learning
1. The figure below contains twelve points that live in 2-dimensional Euclidean space, and each of the point is named by its (x, y) coordinates.
Perform hierarchical clustering of the points in figure below.
The distance between two clusters is defined to be the minimum of the distances between any two points, one chosen from each cluster.
You may refer to A , containing the instructions on how to perform this method of clustering, i.e. single link clustering.
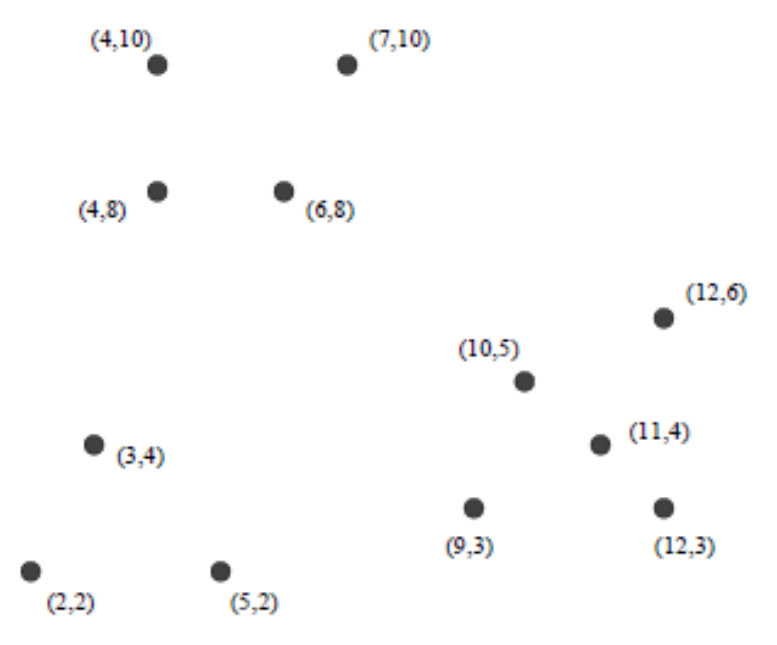
State clearly the steps that you have taken to merge the different clusters, along with the distance matrices.
State the result of the clustering using a tree representation or a dendrogram.
A content:
You are here because, you knew something about Hierarchical clustering and want to know how Single Link clustering works and how to draw a Dendrogram.
Hierarchical Clustering : Its slow :: complicated :: repeatable :: not suited for big data sets.
Lets take a 6 simple Vectors.
6 Vectors
Using Euclidean Distance lets compute the Distance Matrix. Euclidean Distance = sqrt( (x2 -x1)**2 + (y2-y1)**2 )
Example : Distance between A and B sqrt ( (18- 22) ** 2 + (00) ** 2)) sqrt( (16) + 0) sqrt(16)= 4
Distance Matrix
Single Link Clustering: Minimum of two distances. Leads to large more diverse clusters.
Distance Matrix: Diagonals will be 0 and values will be symmetric.
Step 0
Step a: The shortest distance in the matrix is 1 and the vectors associated with that are C & D
So the first cluster is C D
Distance between other vectors and CD
A to CD = min(A->C, A->D) = min(25,24) = 24 B to CD = min(B-
and similarly find for E & F
Step b : Now 2 is the shortest distance and the vectors associated with that are E & F
Second cluster is E F
A to EF = min(A->E, A->F) = min(9,7) = 7 CD to EF = min(CD->E, CD->F) = min(15,17) = 15
Step c : Next shortest is 3, and the associated vectors are B & EF
Third cluster is B EF
A to BEF = min(A->B, A->EF) = min(4,7) = 4 CD to BEF = min(CD->B, CD->EF) = min(20,15) = 15
Step d : Next shortest is 4, and the associated vectors are A& BEF
Fourth cluster is A BEF
CD to ABEF = min(CD->A, CD->BEF) = min(24,15) = 15
Step e : Last cluster is CD ABEF
Lets looks at the Dendrogram for the single link cluster.
Single Link Dendrogram
Simple Python 3 script for achieving the same.
import numpy as npfrom scipy.cluster.hierarchy import dendrogram, linkage from scipy.spatial.distance import squareformimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt#skipping the distance calculation part and directly using the Distance Matrixmat = np.array([[0,4,25,24,9,7], [4,0,21,20,5,3], [25,21,0,1,16,18], [24,20,1,0,15,17], [9,5,16,15,0,2], [7,3,18,17,2,0] ])dists = squareform(mat)#This step is where we mention its "Single Link" Clusterlinkage_matrix = linkage(dists, "single")dendrogram(linkage_matrix, labels=["A","B","C","D","E","F"])plt.title("Single Link")plt.show() (4.10 7.10) 4.8) (6.8) (12.0 10.5] (11.4) 3.4] 19.3) (12.3) 2.2) 6.2) (4.10 7.10) 4.8) (6.8) (12.0 10.5] (11.4) 3.4] 19.3) (12.3) 2.2) 6.2) Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


