Question
Update the code to support tree-structure parallelism with an efficient barrier mechanism. convert the serial code into POSIX threads using C language code is givern
Update the code to support tree-structure parallelism with an efficient barrier mechanism.
convert the serial code into POSIX threads using C language
code is givern below at end.
Pi () is one of the most important and fascinating numbers in mathematics. Roughly 3.14, it is a constant that is used to calculate the circumference of a circle from that circle's radius or diameter. It is also an irrational number, which means that it can be calculated to an infinite number of decimal places without ever slipping into a repeating pattern. This makes it difficult, but not impossible, to calculate precisely. Let us use the calculation of the number pi answer these above-mentioned questions via POSIX Threads shared-memory approach.
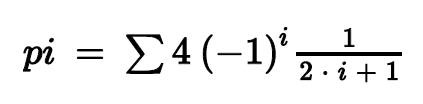 Please download the .c code which implements its serial algorithm of computing the pi. In terminal, run gcc -o computingPi CCalPi.c Then 1. Copy CCalPi.c as CCalPi_pthreads.c 2. Update the CCalPi_pthreads.c to support tree-structure parallelism with an efficient barrier mechanism.Including the pseudo code
Please download the .c code which implements its serial algorithm of computing the pi. In terminal, run gcc -o computingPi CCalPi.c Then 1. Copy CCalPi.c as CCalPi_pthreads.c 2. Update the CCalPi_pthreads.c to support tree-structure parallelism with an efficient barrier mechanism.Including the pseudo code
CODE:
#include #include
double computingPiSerial();
int main(void) { double sum = computingPiSerial(); printf("Pi is equal to %f ", sum);
return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
double computingPiSerial(){ double sum = 0; double factor; long i, n = 100000;
for (i = 0; i
sum = sum + 4 * factor / (2*i+1); } return sum; }
pi = 4 (-1). pi = 4 (-1)Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


