**Updated Question**
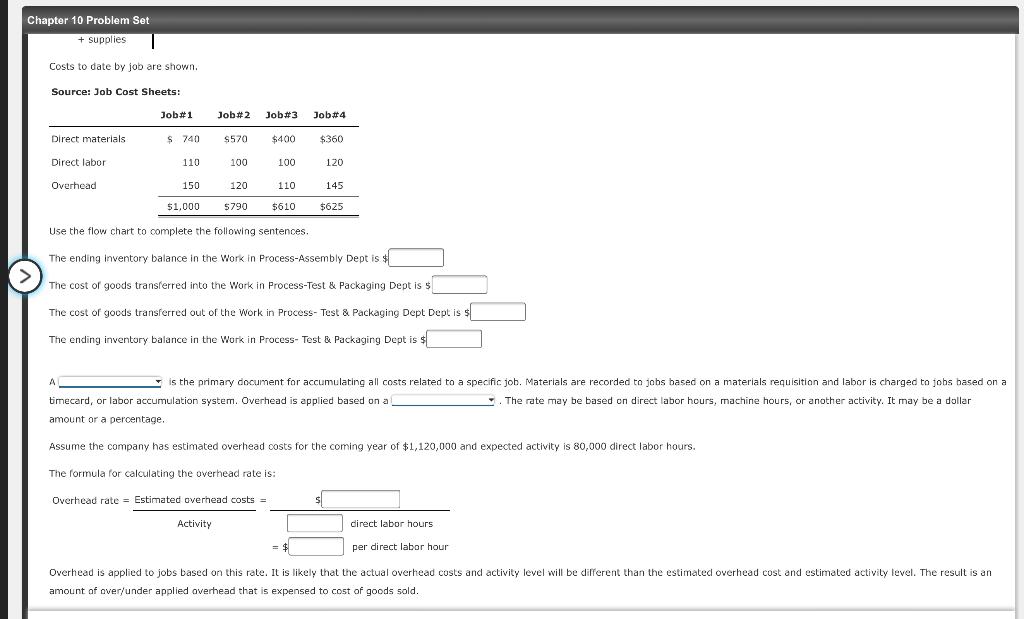
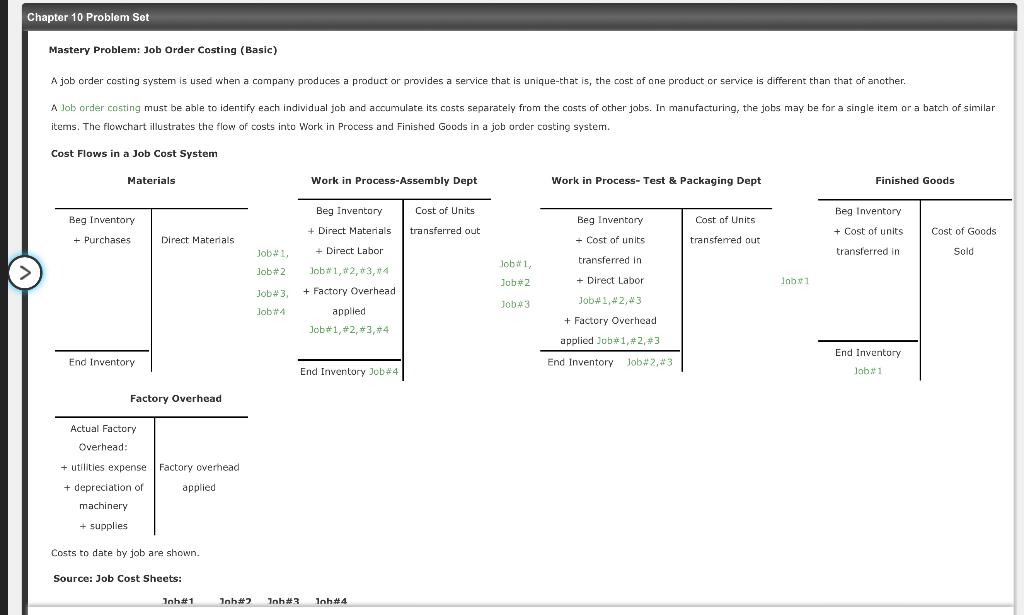
Chapter 10 Problem Set + supplies Costs to date by job are shown. Source: Job Cost Sheets: Job#1 Job#2 Job#3 Job#4 Direct materials S 740 $570 $400 $360 Direct labor 110 100 100 120 Overhead 150 120 110 145 $625 $1,000 5790 $610 Use the flow chart to complete the following sentences. . The ending Inventory balance in the Work in Process-Assembly Dept is The cost of goods transferred into the Work in Process-Test & Packaging Dept is s The cost of goods transferred out of the Work in Process- Test & Packaging Dept Dept is s The ending inventory balance in the Work in Process- Test & Packaging Dept is $ A is the primary document for accumulating all costs related to a specific job. Materials are recorded to jobs based on a materials requisition and labor is charged to jobs based on a timecard, or labor accumulation system. Overhead is applied based on a The rate may be based on direct labor hours, machine hours, or another activity. It may be a dollar amount or a percentage. Assume the company has estimated overhead costs for the coming year of $1,120,000 and expected activity is 80,000 direct labor hours. The formula for calculating the overhead rate is: : Overhead rate = Estimated overhead costs = = Activity direct labor hours = $ per direct labor hour Overhead is applied to jobs based on this rate. It is likely that the actual overhead costs and activity level will be different than the estimated overhead cost and estimated activity level. The result is an amount of over/under applied overhead that is expensed to cost of goods sold. Chapter 10 Problem Set Mastery Problem: Job Order Costing (Basic) A job order costing system is used when a company produces a product or provides a service that is unique-that is, the cost of one product or service is different than that of another. A Job order costing must be able to identify each individual job and accumulate its costs separately from the costs of other jobs. In manufacturing, the jobs may be for a single item or a batch of similar items. The flowchart illustrates the flow of costs into Work in Process and Finished Goods in a job order costing system. Cost Flows in a Job Cost System Materials Work in Process-Assembly Dept Work in Process-Test & Packaging Dept Finished Goods Cost of Units Beg Inventory Beg Inventory Cost of Units transferred out + Cost of units Cost of Goods + Purchases Direct Materials Beg Inventory + + Cost of units transferred in transferred out Job1, transferred in Sold job#2 Beg Inventory + Direct Materials + Direct Labor Job#1, #2,13,14 #, 2 + Factory Overhead applied job#1, #2,3,4 lob#1 Job*2 + Direct Labor lob Job #3 Job*3 Job#1,42,43 Job4 + Factory Overhead applied Job#1, #2, #3 End Inventory Job#2 #3 #, #3 End Inventory End Inventory lab#1 End Inventory Job#4 Factory Overhead Actual Factory Overhead: + utilities expense Factory overhead + depreciation of applied machinery + supplies Costs to date by job are shown Source: Job Cost Sheets: Joh#1 loh#2 nh43 lnh 4 3 #








