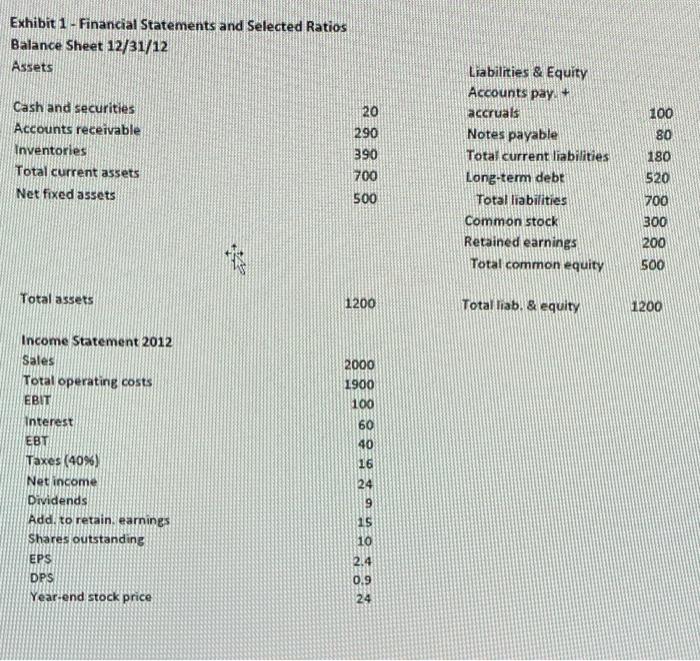
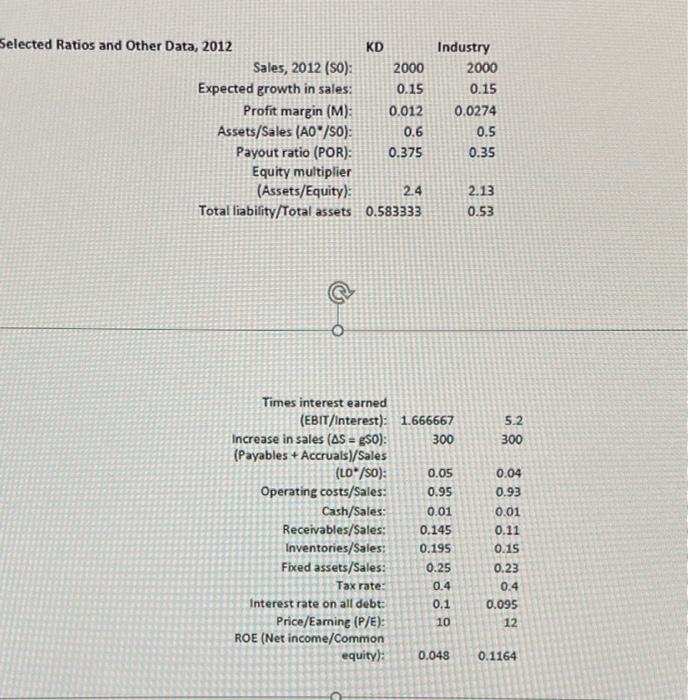
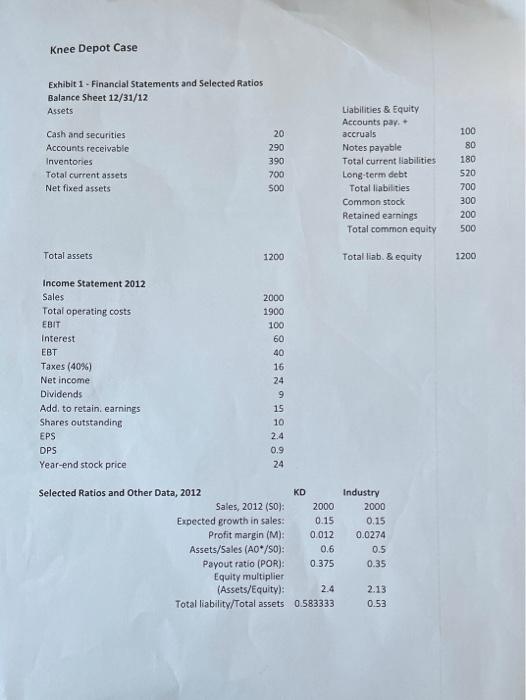
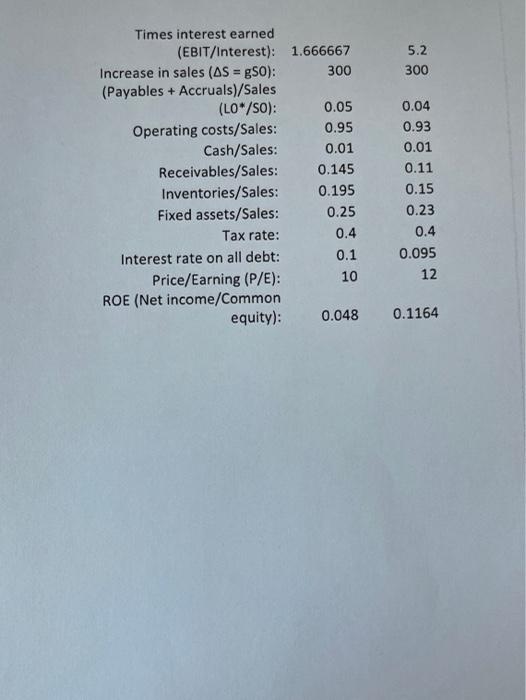
UR SO NO Ford 2010 Che Roshe Op het Naine ON WS ten th year 2011 OM IN M WAIMISIMINIM MER SE COM 1 2 n NE Knee Depot Case IN WI To Te HOME w ch SA Ver Problem Part 1: Knee Depot, a building supplies company, has been lagging the rest of the industry in its performance. So the board has brought in a new CEO, Milo T. Barnsworth to fix things. Since he had a strong financial background, the first item on his to do list was to develop a financial planning section to an overall strategic plan. Barnsworth began by comparing KD's financial ratios to the rest of the industry. Whenever he encountered a substandard ratio, he would meet with the manager responsible to develop a plan to fix it. You have been hired to help Barnsworth finish his analysis of the company so that he can start implementing solutions. To do so, you must answer the following questions based on the financial data provided: Forecast the Balance Sheet and Income Statement for 2013. In this scenario (call it the Steady Scenario) operations are not changed in any way. Calculate the following items: AFN, FCF, ROIC, EPS, DPS and ROE. Use the following assumptions: a. Operating ratios stay the same (use the ratios provided). b. No additional long-term debt or equity is issued c. Interest rate on all debt is 10% d. Any additional funding will be acquired through a line of credit on the last day of the year (thus no interest for 2013) e. Dividends will grow by 15% f. Sales will grow by 15% Exhibit 1 -Financial Statements and Selected Ratios Balance Sheet 12/31/12 Assets 100 80 Cash and securities Accounts receivable Inventories Total current assets Net fixed assets 20 290 390 700 500 Liabilities & Equity Accounts pay. + accruals Notes payable Total current liabilities Long-term debt Total liabilities Common stock Retained earnings Total common equity 180 520 700 300 200 500 Total assets 1200 Total liab. & equity 1200 Income Statement 2012 Sales Total operating costs EBIT 2000 1900 100 60 40 16 24 Interest EBT Taxes (40%) Net income Dividends Add. to retain, earnings Shares outstanding EPS 9 15 10 2.4 DPS Year-end stock price 0.9 24 Selected Ratios and Other Data, 2012 KD Sales, 2012 (50): 2000 Expected growth in sales: 0.15 Profit margin (M): 0.012 Assets/Sales (AO/SO): 0.6 Payout ratio (POR): 0.375 Equity multiplier (Assets/Equity): 2.4 Total liability/Total assets 0.583333 Industry 2000 0.15 0.0274 0.5 0.35 2.13 0.53 5.2 300 Times interest earned (EBIT/Interest): 1.666667 Increase in sales (AS = g50): 300 (Payables + Accruals)/Sales (LO" /so): 0.05 Operating costs/Sales: 0.95 Cash/Sales: 0.01 Receivables/Sales: 0.145 Inventories/Sales: 0.195 Fixed assets/Sales: 0.25 Tax rate: 0.4 Interest rate on all debt: 0.1 Price/Eaming (P/E): 10 ROE (Net income/Common equity): 0.048 0.04 0.93 0.01 0.11 0.15 0.23 0.4 0.095 12 0.1164 Problem Part 1: Knee Depot, a building supplies company, has been lagging the rest of the industry in its performance. So the board has brought in a new CEO, Milo T. Barnsworth to fix things. Since he had a strong financial background, the first item on his to do list was to develop a financial planning section to an overall strategic plan. Barnsworth began by comparing KD's financial ratios to the rest of the industry. Whenever he encountered a substandard ratio, he would meet with the manager responsible to develop a plan to fix it. You have been hired to help Barnsworth finish his analysis of the company so that he can start implementing solutions. To do so, you must answer the following questions based on the financial data provided: Forecast the Balance Sheet and Income Statement for 2013. In this scenario (call it the Steady Scenario) operations are not changed in any way. Calculate the following items: AFN, FCF, ROIC, EPS, DPS and ROE. Use the following assumptions: a. Operating ratios stay the same (use the ratios provided). b. No additional long-term debt or equity is issued c. Interest rate on all debt is 10% d. Any additional funding will be acquired through a line of credit on the last day of the year (thus no interest for 2013) e. Dividends will grow by 15% f. Sales will grow by 15% Knee Depot Case Exhibit 1 - Financial Statements and Selected Ratios Balance Sheet 12/31/12 Assets Cash and securities 20 100 Accounts receivable 290 Liabilities & Equity Accounts pay. accruals Notes payable Total current liabilities Long-term debt Total liabilities 80 390 180 Inventories Total current assets Net fixed assets 700 520 500 700 Common stock 300 200 Retained earnings Total common equity 500 Total assets 1200 Total liab. & equity 1200 Income Statement 2012 2000 Sales Total operating costs 1900 EBIT 100 interest 60 40 16 24 EBT Taxes (40%) Net income Dividends Add to retain, earnings Shares outstanding EPS 9 15 10 2.4 DPS 0.9 Year-end stock price 24 Industry 2000 0.15 0.0274 Selected Ratios and Other Data, 2012 KD Sales, 2012 (50): 2000 Expected growth in sales: 0.15 Profit margin (M): 0.012 Assets/Sales (A0*/50): 0.6 Payout ratio (POR): 0.375 Equity multiplier (Assets/Equity): 2.4 Total liability/Total assets 0.583333 0.5 0.35 2.13 0.53 5.2 300 0.04 0.93 Times interest earned (EBIT/Interest): 1.666667 Increase in sales (AS = g50): 300 (Payables + Accruals)/Sales (LO*/S0): 0.05 Operating costs/Sales: 0.95 Cash/Sales: 0.01 Receivables/Sales: 0.145 Inventories/Sales: 0.195 Fixed assets/Sales: 0.25 Tax rate: 0.4 0.01 0.11 0.15 0.23 0.4 0.1 0.095 Interest rate on all debt: 10 12 Price/Earning (P/E): ROE (Net income/Common equity): 0.048 0.1164 UR SO NO Ford 2010 Che Roshe Op het Naine ON WS ten th year 2011 OM IN M WAIMISIMINIM MER SE COM 1 2 n NE Knee Depot Case IN WI To Te HOME w ch SA Ver Problem Part 1: Knee Depot, a building supplies company, has been lagging the rest of the industry in its performance. So the board has brought in a new CEO, Milo T. Barnsworth to fix things. Since he had a strong financial background, the first item on his to do list was to develop a financial planning section to an overall strategic plan. Barnsworth began by comparing KD's financial ratios to the rest of the industry. Whenever he encountered a substandard ratio, he would meet with the manager responsible to develop a plan to fix it. You have been hired to help Barnsworth finish his analysis of the company so that he can start implementing solutions. To do so, you must answer the following questions based on the financial data provided: Forecast the Balance Sheet and Income Statement for 2013. In this scenario (call it the Steady Scenario) operations are not changed in any way. Calculate the following items: AFN, FCF, ROIC, EPS, DPS and ROE. Use the following assumptions: a. Operating ratios stay the same (use the ratios provided). b. No additional long-term debt or equity is issued c. Interest rate on all debt is 10% d. Any additional funding will be acquired through a line of credit on the last day of the year (thus no interest for 2013) e. Dividends will grow by 15% f. Sales will grow by 15% Exhibit 1 -Financial Statements and Selected Ratios Balance Sheet 12/31/12 Assets 100 80 Cash and securities Accounts receivable Inventories Total current assets Net fixed assets 20 290 390 700 500 Liabilities & Equity Accounts pay. + accruals Notes payable Total current liabilities Long-term debt Total liabilities Common stock Retained earnings Total common equity 180 520 700 300 200 500 Total assets 1200 Total liab. & equity 1200 Income Statement 2012 Sales Total operating costs EBIT 2000 1900 100 60 40 16 24 Interest EBT Taxes (40%) Net income Dividends Add. to retain, earnings Shares outstanding EPS 9 15 10 2.4 DPS Year-end stock price 0.9 24 Selected Ratios and Other Data, 2012 KD Sales, 2012 (50): 2000 Expected growth in sales: 0.15 Profit margin (M): 0.012 Assets/Sales (AO/SO): 0.6 Payout ratio (POR): 0.375 Equity multiplier (Assets/Equity): 2.4 Total liability/Total assets 0.583333 Industry 2000 0.15 0.0274 0.5 0.35 2.13 0.53 5.2 300 Times interest earned (EBIT/Interest): 1.666667 Increase in sales (AS = g50): 300 (Payables + Accruals)/Sales (LO" /so): 0.05 Operating costs/Sales: 0.95 Cash/Sales: 0.01 Receivables/Sales: 0.145 Inventories/Sales: 0.195 Fixed assets/Sales: 0.25 Tax rate: 0.4 Interest rate on all debt: 0.1 Price/Eaming (P/E): 10 ROE (Net income/Common equity): 0.048 0.04 0.93 0.01 0.11 0.15 0.23 0.4 0.095 12 0.1164 Problem Part 1: Knee Depot, a building supplies company, has been lagging the rest of the industry in its performance. So the board has brought in a new CEO, Milo T. Barnsworth to fix things. Since he had a strong financial background, the first item on his to do list was to develop a financial planning section to an overall strategic plan. Barnsworth began by comparing KD's financial ratios to the rest of the industry. Whenever he encountered a substandard ratio, he would meet with the manager responsible to develop a plan to fix it. You have been hired to help Barnsworth finish his analysis of the company so that he can start implementing solutions. To do so, you must answer the following questions based on the financial data provided: Forecast the Balance Sheet and Income Statement for 2013. In this scenario (call it the Steady Scenario) operations are not changed in any way. Calculate the following items: AFN, FCF, ROIC, EPS, DPS and ROE. Use the following assumptions: a. Operating ratios stay the same (use the ratios provided). b. No additional long-term debt or equity is issued c. Interest rate on all debt is 10% d. Any additional funding will be acquired through a line of credit on the last day of the year (thus no interest for 2013) e. Dividends will grow by 15% f. Sales will grow by 15% Knee Depot Case Exhibit 1 - Financial Statements and Selected Ratios Balance Sheet 12/31/12 Assets Cash and securities 20 100 Accounts receivable 290 Liabilities & Equity Accounts pay. accruals Notes payable Total current liabilities Long-term debt Total liabilities 80 390 180 Inventories Total current assets Net fixed assets 700 520 500 700 Common stock 300 200 Retained earnings Total common equity 500 Total assets 1200 Total liab. & equity 1200 Income Statement 2012 2000 Sales Total operating costs 1900 EBIT 100 interest 60 40 16 24 EBT Taxes (40%) Net income Dividends Add to retain, earnings Shares outstanding EPS 9 15 10 2.4 DPS 0.9 Year-end stock price 24 Industry 2000 0.15 0.0274 Selected Ratios and Other Data, 2012 KD Sales, 2012 (50): 2000 Expected growth in sales: 0.15 Profit margin (M): 0.012 Assets/Sales (A0*/50): 0.6 Payout ratio (POR): 0.375 Equity multiplier (Assets/Equity): 2.4 Total liability/Total assets 0.583333 0.5 0.35 2.13 0.53 5.2 300 0.04 0.93 Times interest earned (EBIT/Interest): 1.666667 Increase in sales (AS = g50): 300 (Payables + Accruals)/Sales (LO*/S0): 0.05 Operating costs/Sales: 0.95 Cash/Sales: 0.01 Receivables/Sales: 0.145 Inventories/Sales: 0.195 Fixed assets/Sales: 0.25 Tax rate: 0.4 0.01 0.11 0.15 0.23 0.4 0.1 0.095 Interest rate on all debt: 10 12 Price/Earning (P/E): ROE (Net income/Common equity): 0.048 0.1164