Question
Use Newtons interpolating polynomial to determine ln(x) at x = 2. Compute the finite divided differences as shown in the table presented in class. Show
Use Newtons interpolating polynomial to determine ln(x) at x = 2. Compute the finite divided differences as shown in the table presented in class. Show the coefficients for polynomials of first (f1(x)), second (f2(x)), and third (f3(x)) order. Plot the interpolating polynomials and the function ln(x) in the interval [0, 8]. The data points used in the interpolation are given by x 1 4 6 5 ln(x) 0.000000 1.386294 1.791759 1.609438 In the same plot, represent the data points (x1, ln x1), ...,(x4, ln x4) using markers (circles). Add a legend to your plot. A short report (2 pages max) showing calculations, the code used to create the plot and/or to calculate the polynomial coefficients, and the plot is due in class. USE MATLAB CODE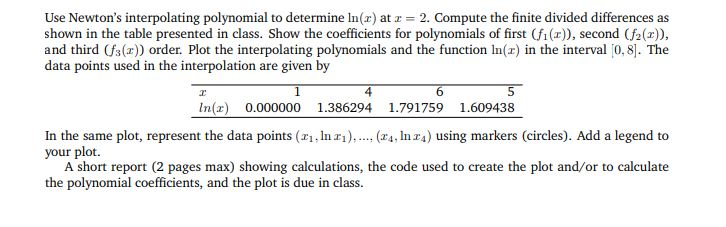
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


