!!!Use Python!!!
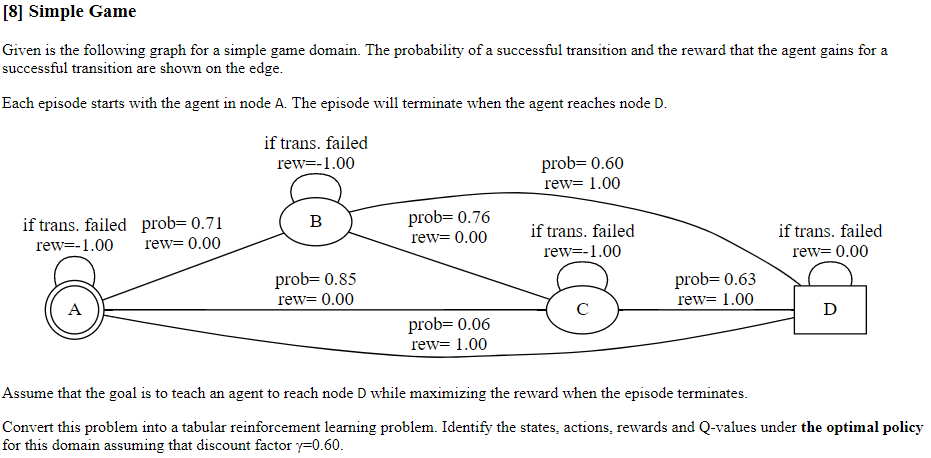

[8] Simple Game Given is the following graph for a simple game domain. The probability of a successful transition and the reward that the agent gains for a successful transition are shown on the edge. Each episode starts with the agent in node A. The episode will terminate when the agent reaches node D. if trans. failed rew=-1.00 prob=0.60 rew= 1.00 B if trans, failed prob=0.71 rew=-1.00 rew= 0.00 prob= 0.76 rew=0.00 if trans, failed rew=-1.00 if trans, failed rew= 0.00 prob=0.85 rew=0.00 prob=0.63 rew= 1.00 A D prob=0.06 rew= 1.00 Assume that the goal is to teach an agent to reach node D while maximizing the reward when the episode terminates. Convert this problem into a tabular reinforcement learning problem. Identify the states, actions, rewards and Q-values under the optimal policy for this domain assuming that discount factor y=0.60. [9] Double Simple Game Domain Given the same domain, convert it into a double simple game problem. In the standard simple game problem, the goal is for the agent to start in A and reach the D. In the double travelling salesman problem, the goal is for the agent to move to node D and then back to A. Convert this problem into a tabular reinforcement learning problem. Identify the states, actions, rewards and Q-values under the optimal policy for this domain assuming that discount factor y=0.9. Remember the Markov assumption for domains in reinforcement learning. [8] Simple Game Given is the following graph for a simple game domain. The probability of a successful transition and the reward that the agent gains for a successful transition are shown on the edge. Each episode starts with the agent in node A. The episode will terminate when the agent reaches node D. if trans. failed rew=-1.00 prob=0.60 rew= 1.00 B if trans, failed prob=0.71 rew=-1.00 rew= 0.00 prob= 0.76 rew=0.00 if trans, failed rew=-1.00 if trans, failed rew= 0.00 prob=0.85 rew=0.00 prob=0.63 rew= 1.00 A D prob=0.06 rew= 1.00 Assume that the goal is to teach an agent to reach node D while maximizing the reward when the episode terminates. Convert this problem into a tabular reinforcement learning problem. Identify the states, actions, rewards and Q-values under the optimal policy for this domain assuming that discount factor y=0.60. [9] Double Simple Game Domain Given the same domain, convert it into a double simple game problem. In the standard simple game problem, the goal is for the agent to start in A and reach the D. In the double travelling salesman problem, the goal is for the agent to move to node D and then back to A. Convert this problem into a tabular reinforcement learning problem. Identify the states, actions, rewards and Q-values under the optimal policy for this domain assuming that discount factor y=0.9. Remember the Markov assumption for domains in reinforcement learning








