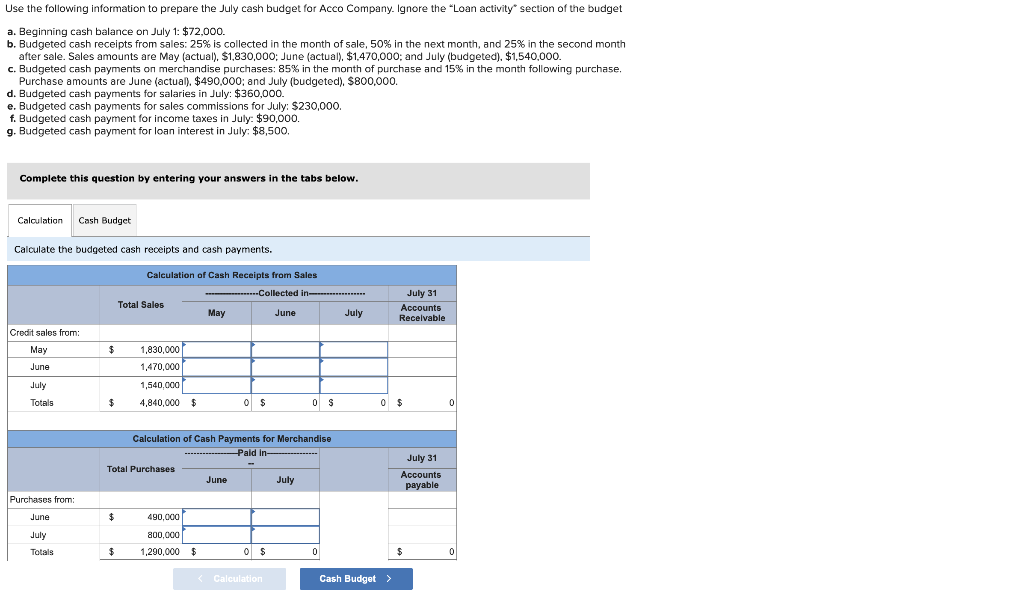
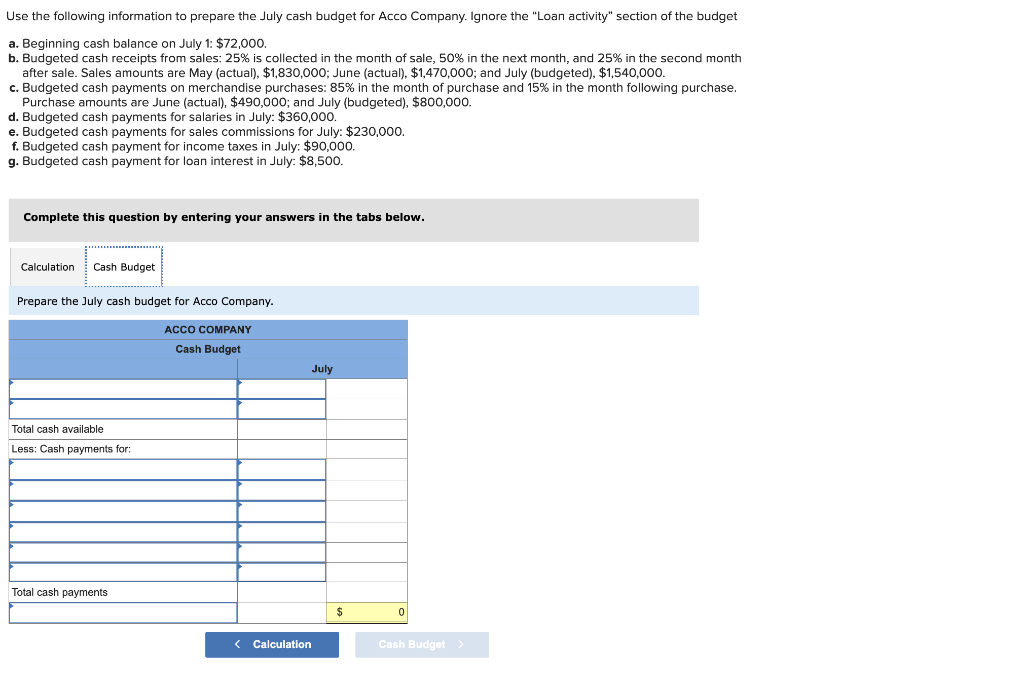
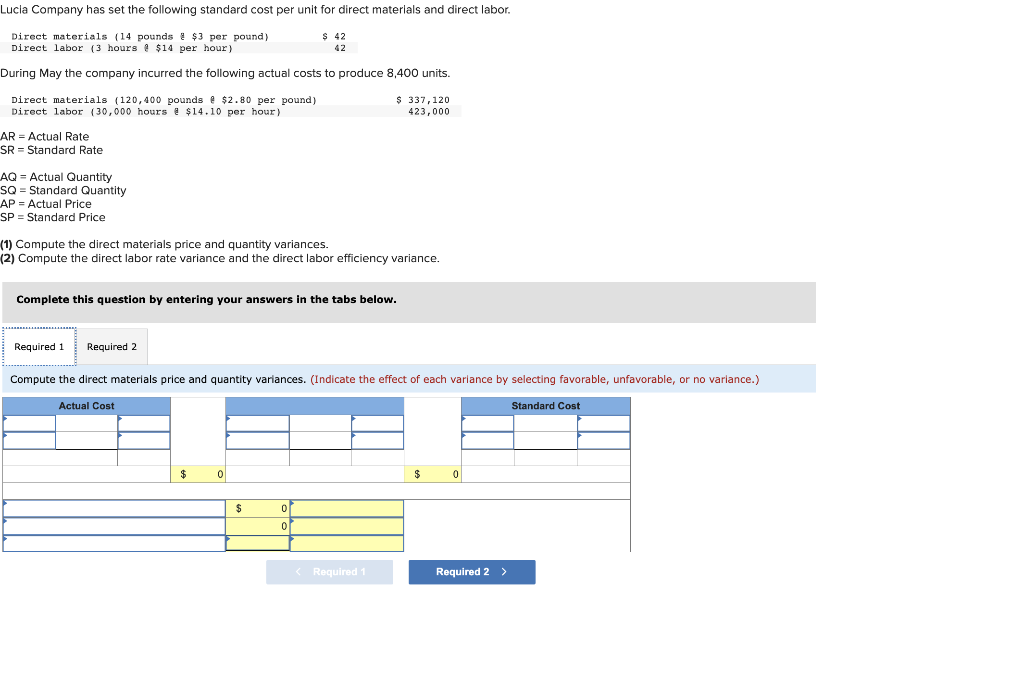
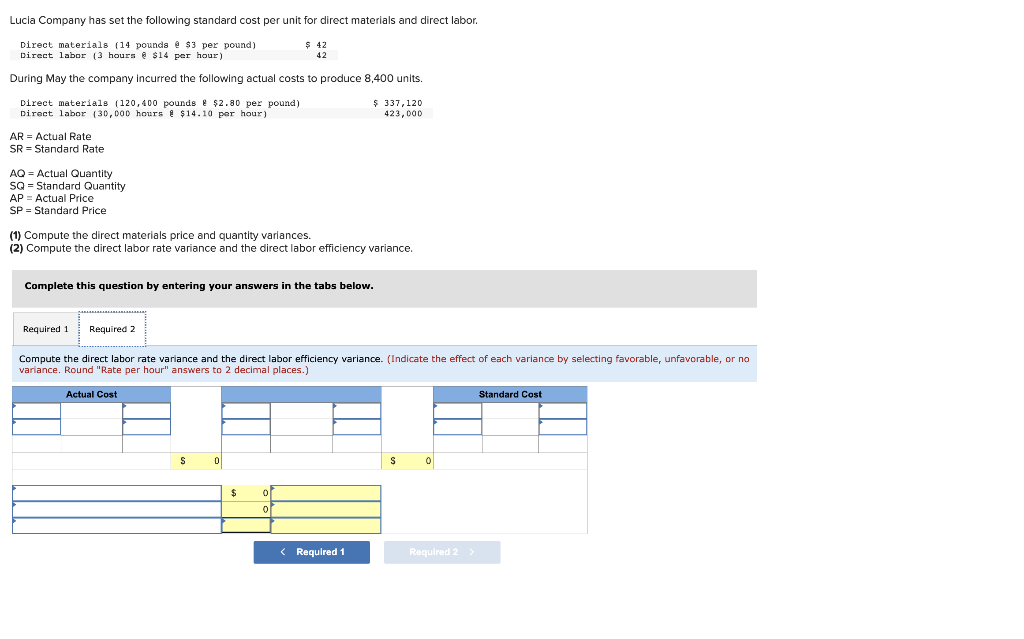
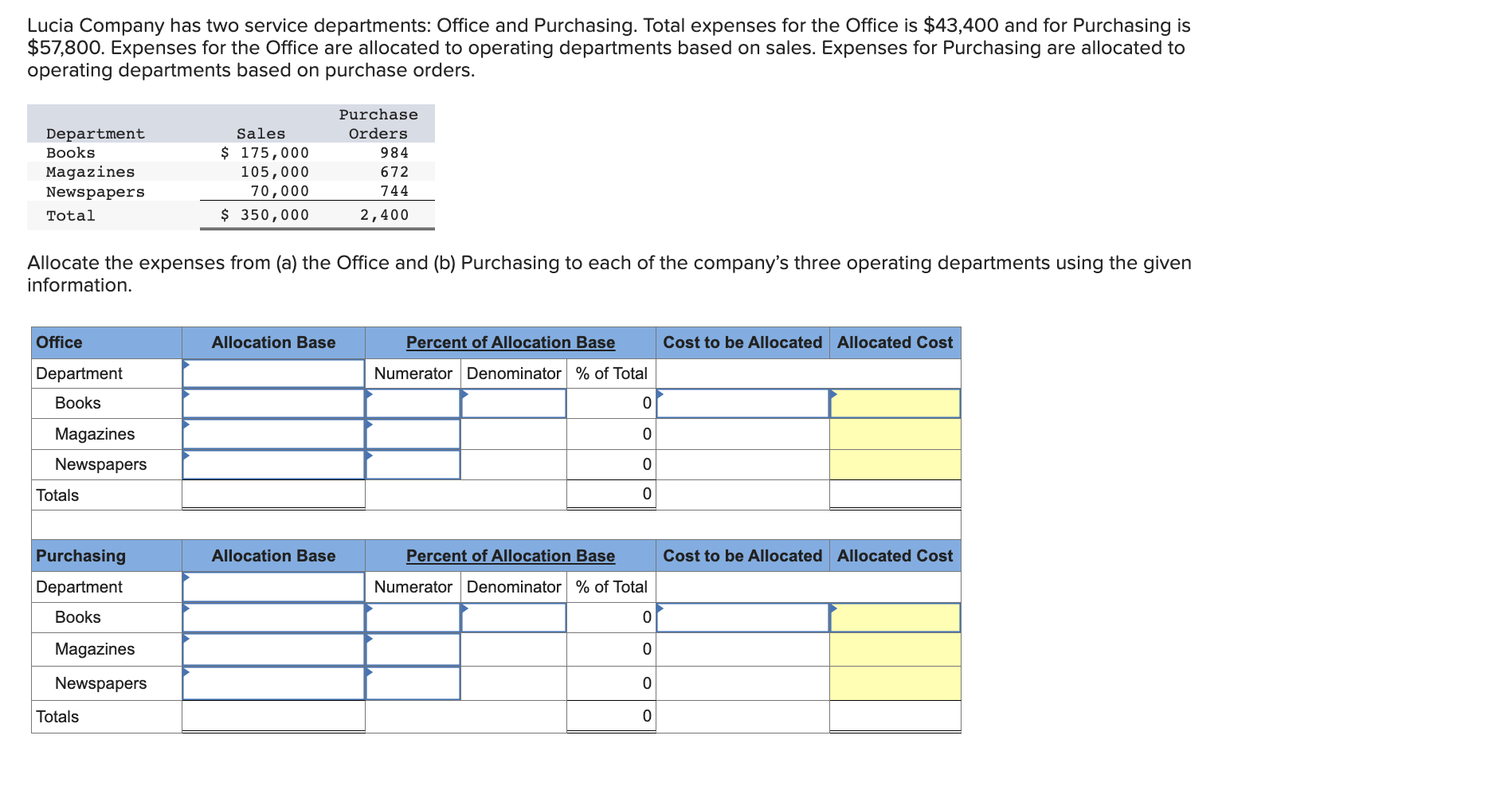

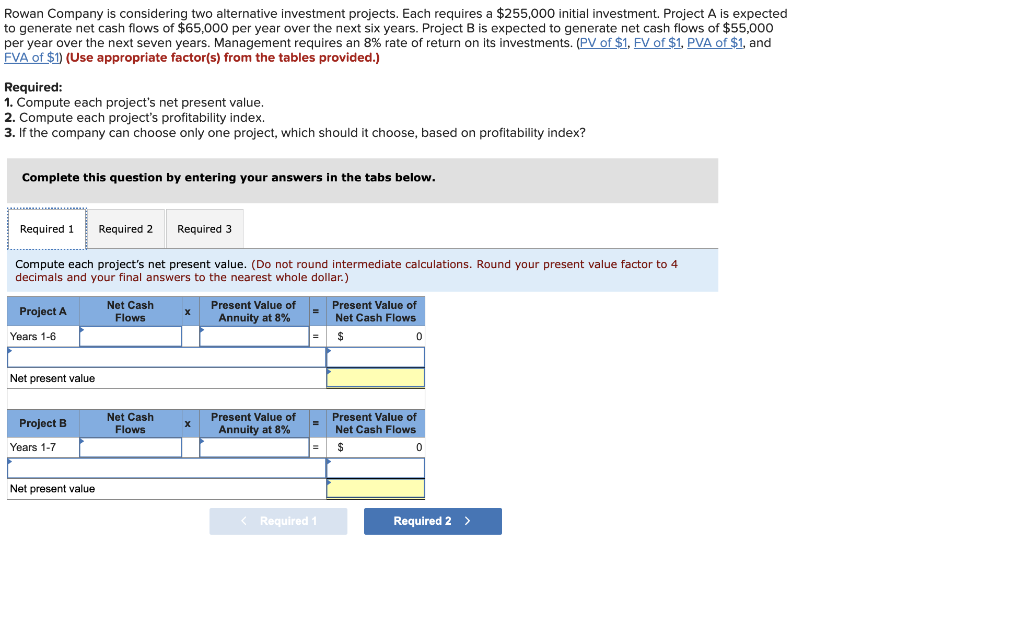
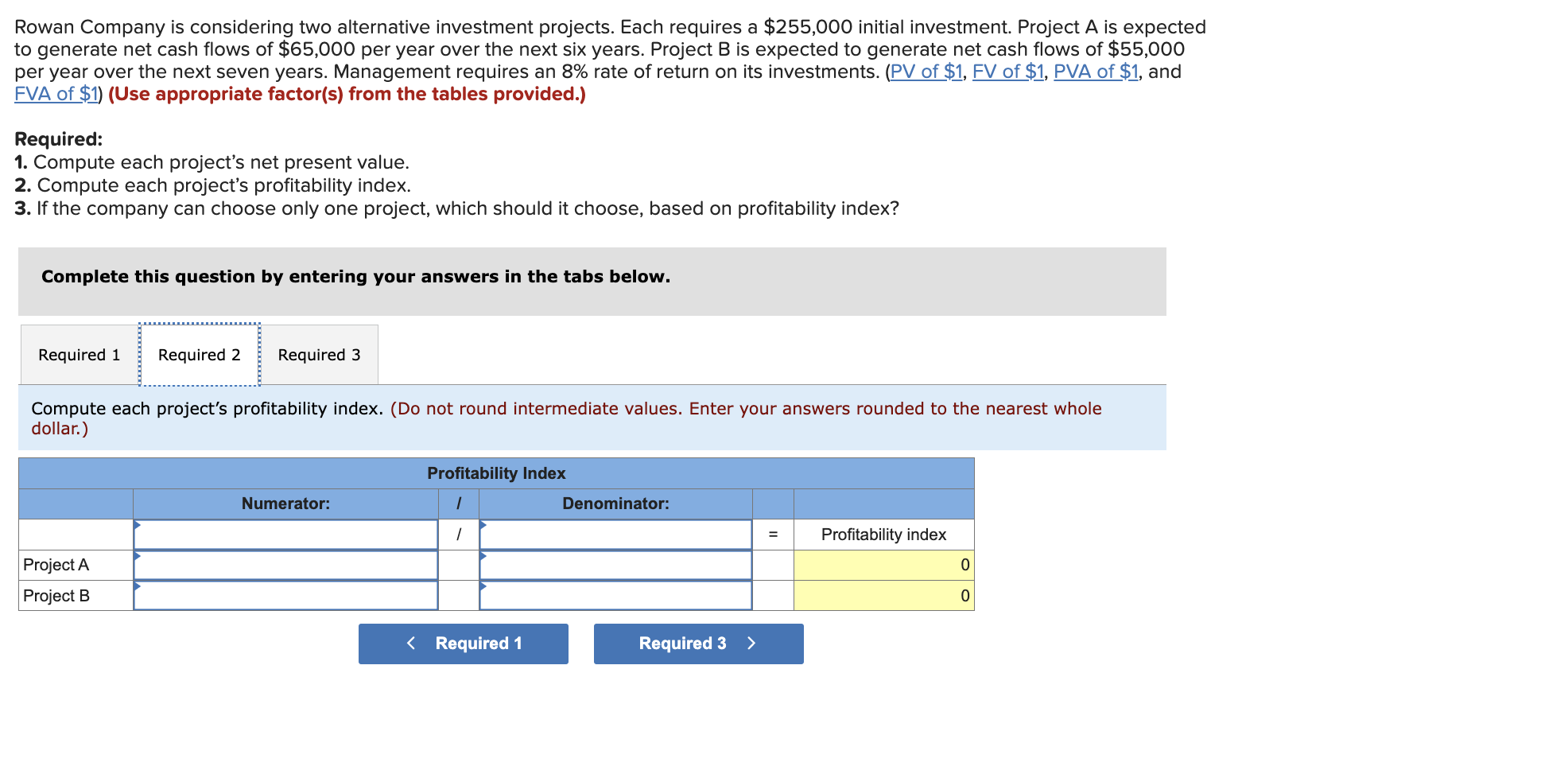
Use the following information to prepare the July cash budget for Acco Company. Ignore the "Loan activity" section of the budget a. Beginning cash balance on July 1: $72,000. b. Budgeted cash receipts from sales: 25% is collected in the month of sale, 50% in the next month, and 25% in the second month after sale. Sales amounts are May (actual), $1,830,000; June (actual), $1,470,000; and July (budgeted), $1,540,000. c. Budgeted cash payments on merchandise purchases: 85% in the month of purchase and 15% in the month following purchase. Purchase amounts are June (actual), $490,000; and July (budgeted), $800,000. d. Budgeted cash payments for salaries in July: $360,000. e. Budgeted cash payments for sales commissions for July: $230,000. f. Budgeted cash payment for income taxes in July: $90,000. g. Budgeted cash payment for loan interest in July: $8,500. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Calculate the budgeted cash receipts and cash payments. Use the following information to prepare the July cash budget for Acco Company. Ignore the "Loan activity" section of the budget a. Beginning cash balance on July 1: $72,000. b. Budgeted cash receipts from sales: 25% is collected in the month of sale, 50% in the next month, and 25% in the second month after sale. Sales amounts are May (actual), $1,830,000; June (actual), $1,470,000; and July (budgeted), $1,540,000. c. Budgeted cash payments on merchandise purchases: 85% in the month of purchase and 15% in the month following purchase. Purchase amounts are June (actual), $490,000; and July (budgeted), $800,000. d. Budgeted cash payments for salaries in July: $360,000. e. Budgeted cash payments for sales commissions for July: $230,000. f. Budgeted cash payment for income taxes in July: $90,000. g. Budgeted cash payment for loan interest in July: $8,500. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Prepare the July cash budget for Acco Company. Direct materials ( 14 pounds a $3 per pound) $42 Direct labor ( 3 hours \& $14 per hour ) During May the company incurred the following actual costs to produce 8,400 units. Directmaterials(120,400pounds&$2.80perpound)Directlabor(30,000hours&$14,10perhour}$337,120423,000 AR= Actual Rate SR= Standard Rate AQ= Actual Quantity SQ= Standard Quantity AP= Actual Price SP= Standard Price (1) Compute the direct materials price and quantity variances. (2) Compute the direct labor rate variance and the direct labor efficiency variance. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Lucla Company has set the following standard cost per unit for direct materials and direct labor. Directmaterials(14pounds$3perDirectlabor(3hours$14perhour)4242 During May the company incurred the following actual costs to produce 8,400 units. Directmaterials(120,400pounds&$2.80perpound)Directlabor(30,000hours&$14.10perhour)$337,120423,000 AR= Actual Rate SR= Standard Rate AQ= Actual Quantity SQ= Standard Quantity AP= Actual Price SP= Standard Price (1) Compute the direct materials price and quantity variances. (2) Compute the direct labor rate variance and the direct labor efficiency variance. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Compute the direct labor rate variance and the direct labor efficiency variance. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting favorable, unfavorable, or no varlance. Round "Rate per hour" answers to 2 decimal places.) Lucia Company has two service departments: Office and Purchasing. Total expenses for the Office is $43,400 and for Purchasing is $57,800. Expenses for the Office are allocated to operating departments based on sales. Expenses for Purchasing are allocated to operating departments based on purchase orders. Allocate the expenses from (a) the Office and (b) Purchasing to each of the company's three operating departments using the given information. A company must decide between scrapping or reworking units that do not pass inspection. The company has 16,000 defective units that have already cost $132,000 to manufacture. The units can be sold as scrap for $46,400 or reworked for $73,600 and then sold for $131,200. (a) Prepare a scrap or rework analysis of income effects. (b) Should the company sell the units as scrap or rework them? Rowan Company is considering two alternative investment projects. Each requires a $255,000 initial investment. Project A is expected to generate net cash flows of $65,000 per year over the next six years. Project B is expected to generate net cash flows of $55,000 per year over the next seven years. Management requires an 8% rate of return on its investments. (PV of $1,FV of $1, PVA of $1, and FVA of $1 ) (Use appropriate factor(s) from the tables provided.) Required: 1. Compute each project's net present value. 2. Compute each project's profitability index. 3. If the company can choose only one project, which should it choose, based on profitability index? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Compute each project's net present value. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your present value factor to 4 decimals and your final answers to the nearest whole dollar.) Rowan Company is considering two alternative investment projects. Each requires a $255,000 initial investment. Project A is expectec to generate net cash flows of $65,000 per year over the next six years. Project B is expected to generate net cash flows of $55,000 per year over the next seven years. Management requires an 8% rate of return on its investments. (PV of $1, FV of $1, P VVA of $1, and FVA of \$1) (Use appropriate factor(s) from the tables provided.) Required: 1. Compute each project's net present value. 2. Compute each project's profitability index. 3. If the company can choose only one project, which should it choose, based on profitability index? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Compute each project's profitability index. (Do not round intermediate values. Enter your answers rounded to the nearest whole dollar.) Rowan Company is considering two alternative investment projects. Each requires a $255,000 initial investment. Project A is expected to generate net cash flows of $65,000 per year over the next six years. Project B is expected to generate net cash flows of $55,000 per year over the next seven years. Management requires an 8% rate of return on its investments. (PV of $1,, FV of $1, PVA of $1, and FVA of $1 ) (Use appropriate factor(s) from the tables provided.) Required: 1. Compute each project's net present value. 2. Compute each project's profitability index. 3. If the company can choose only one project, which should it choose, based on profitability index? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. If the company can choose only one project, which should it choose, based on profitability index? If the company can choose only one project, which should it choose, based on profitability index