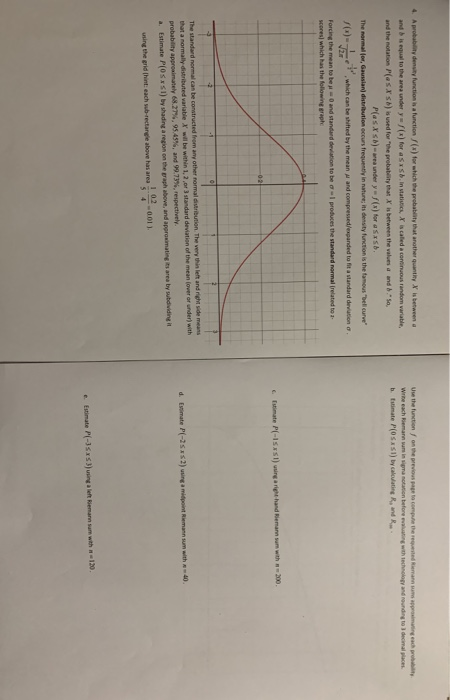
Use the function on the previous page to compute the manum ringer Write each Riemann minnotation before eating with technology and rounding to decimal places b. tatimate P(OSXSI) by calculating R, and R. 4. Aprobability density function is a function f(x) for which the probability that another quanty X is between a and is equal to the area under y = f(x) for a sxs in statistics, X is called a coins random variable, and the notation Plass) used for the probability that is between the values and so PlasX) - under y = f(x) for a sxsb. The normal for, Gaussian distribution occurs frequently in nature; its density function is the famous believe which can be shifted by the mean and compressed/expanded to fit vandard deviation Forcing the mean to be and standard deviation to be produces the standard normal related to scores which has the following graphe imate PC-ISXSI) singarige hand ieman sam with 200 -02 d. imate P(-25*2) using a midpoint Riemann sun with 40. The standard normal can be constructed from any other normal distribution. The very thin left and right side means that a normally distributed variable x' will be within 1. 2. 3 standard deviation of the mean lover or under) with probability approximately 68.27%.95.45%, and 99.73%, respectively. . Estimate POSSI) by shading a region on the graph above and approximating its area by subdividing it I 02 using the grid in each subtectangle above hasarea 001) 54 stimate P(-sxs using a learn som with 120 Use the function on the previous page to compute the manum ringer Write each Riemann minnotation before eating with technology and rounding to decimal places b. tatimate P(OSXSI) by calculating R, and R. 4. Aprobability density function is a function f(x) for which the probability that another quanty X is between a and is equal to the area under y = f(x) for a sxs in statistics, X is called a coins random variable, and the notation Plass) used for the probability that is between the values and so PlasX) - under y = f(x) for a sxsb. The normal for, Gaussian distribution occurs frequently in nature; its density function is the famous believe which can be shifted by the mean and compressed/expanded to fit vandard deviation Forcing the mean to be and standard deviation to be produces the standard normal related to scores which has the following graphe imate PC-ISXSI) singarige hand ieman sam with 200 -02 d. imate P(-25*2) using a midpoint Riemann sun with 40. The standard normal can be constructed from any other normal distribution. The very thin left and right side means that a normally distributed variable x' will be within 1. 2. 3 standard deviation of the mean lover or under) with probability approximately 68.27%.95.45%, and 99.73%, respectively. . Estimate POSSI) by shading a region on the graph above and approximating its area by subdividing it I 02 using the grid in each subtectangle above hasarea 001) 54 stimate P(-sxs using a learn som with 120