Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Use the provided template below for the question: class CircularArrayQueue { private: // private data member public: CircularArrayQueue(); bool isEmpty() const; void enqueue(int x); void

Use the provided template below for the question:
class CircularArrayQueue {
private: // private data member
public: CircularArrayQueue(); bool isEmpty() const; void enqueue(int x); void dequeue(); int peekFront() const; };
CircularArrayQueue::CircularArrayQueue() {
}
bool CircularArrayQueue::isEmpty() const {
}
void CircularArrayQueue::enqueue(int x) {
}
void CircularArrayQueue::dequeue() {
}
int CircularArrayQueue::peekFront() const {
}
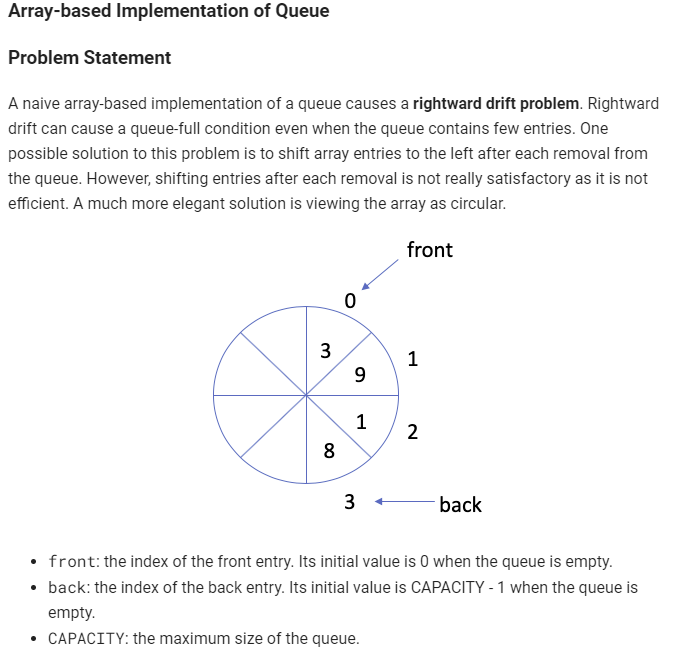
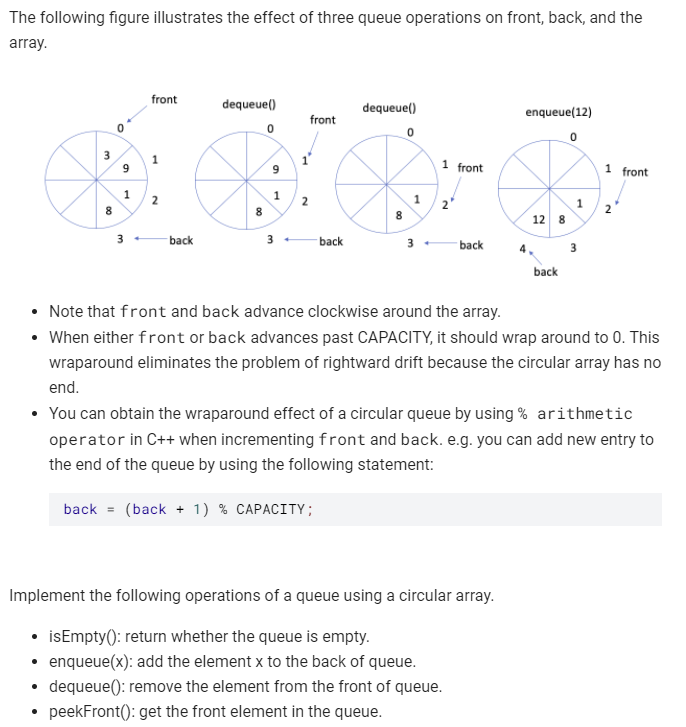
Array-based Implementation of Queue Problem Statement A naive array-based implementation of a queue causes a rightward drift problem. Rightward drift can cause a queue-full condition even when the queue contains few entries. One possible solution to this problem is to shift array entries to the left after each removal from the queue. However, shifting entries after each removal is not really satisfactory as it is not efficient. A much more elegant solution is viewing the array as circular. front 0 3 1 9 1 2 8 3 back front: the index of the front entry. Its initial value is O when the queue is empty. back: the index of the back entry. Its initial value is CAPACITY - 1 when the queue is empty. CAPACITY: the maximum size of the queue. The following figure illustrates the effect of three queue operations on front, back, and the array. front dequeuel) 0 front dequeuel) 0 enqueue(12) 0 9 1 front 1 front 1 2 1 2 8 2' 8 2 8 12 8 back back back 3 back Note that front and back advance clockwise around the array. When either front or back advances past CAPACITY, it should wrap around to 0. This wraparound eliminates the problem of rightward drift because the circular array has no end. You can obtain the wraparound effect of a circular queue by using % arithmetic operator in C++ when incrementing front and back. e.g. you can add new entry to the end of the queue by using the following statement: back = (back + 1) % CAPACITY; Implement the following operations of a queue using a circular array. isEmpty(); return whether the queue is empty. enqueue(x): add the element x to the back of queue. dequeue(): remove the element from the front of queue. peekFront(): get the front element in the queue. Test Cases The first line of the input is the operation we will be calling on your CircularArrayQueue object. The second line of input is the parameters that are passed to the corresponding operation in Line 1. The Output is the return value of the function call to the corresponding operation in Line 1. null in output means the function doesn't return anything. They are of type void. You may assume that all operations are valid (e.g. no dequeue or peekFront operations will be called on an empty queue)Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


