
Use the table below for conversion of data
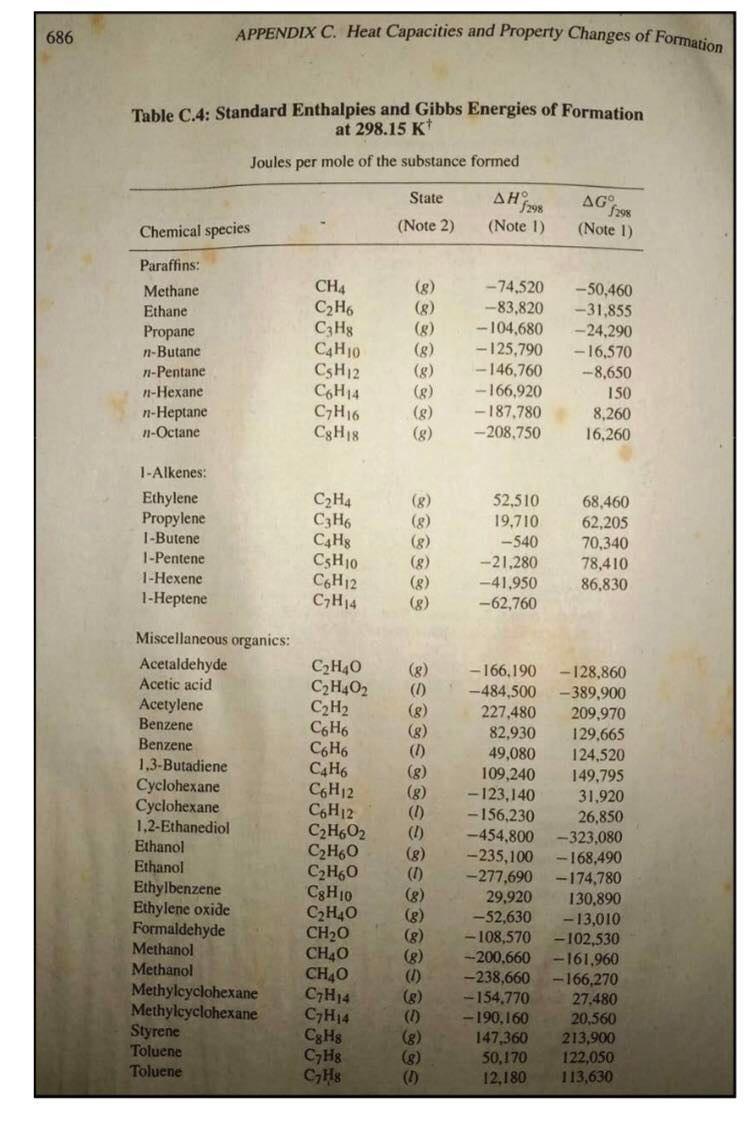
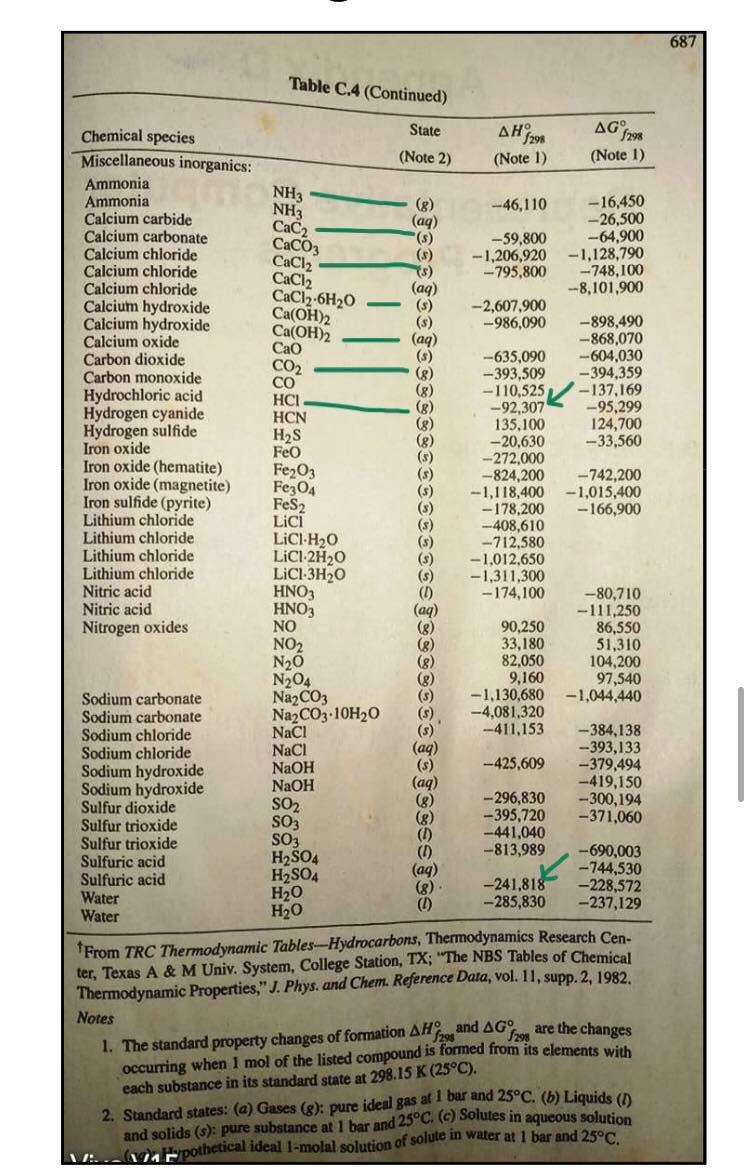


2. An ideal gas initially at 285 Kand 13.8 atm changed pressure to 1.8 atm reversibly. Calculatea, W, AU and AH for the following cases. a. Monoatomic gas, isothermal expansion b. Diatomic gas, constant volume 686 APPENDIX C. Heat Capacities and Property Changes of Formation Table C.4: Standard Enthalpies and Gibbs Energies of Formation at 298.15 K+ Joules per mole of the substance formed State AH7 298 (Note 1) AG f298 (Note 1) Chemical species (Note 2) Paraffins: Methane Ethane Propane n-Butane 71-Pentane n-Hexane n-Heptane 7-Octane CH4 C2H6 CzHg C4Hjo CsH12 C6H14 C7H16 Cg H18 (8) (8) (8) (8) (8) (g) (8) -74,520 -83,820 -104.680 -125,790 - 146,760 -166,920 -187.780 -208,750 -50,460 -31.855 --- 24,290 - 16,570 :-8,650 150 8,260 16,260 1 -Alkenes: Ethylene Propylene 1-Butene 1 -Pentene 1-Hexene 1-Heptene C2H4 C3H6 C4H8 CsH10 C6H12 CH14 (8) (8) (8) (8) (8) (8) 52,510 19,710 -540 -21.280 -41,950 -62,760 68,460 62,205 70,340 78,410 86,830 C2H40 C2H4O2 C2H2 (8) (1) (8) (8) (8) (8) (1) Miscellaneous organics: Acetaldehyde Acetic acid Acetylene Benzene Benzene 1,3-Butadiene Cyclohexane Cyclohexane 1.2-Ethanediol Ethanol Ethanol Ethylbenzene Ethylene oxide Formaldehyde Methanol Methanol Methylcyclohexane Methylcyclohexane Styrene Toluene Toluene C6H6 CoH6 C4H6 C6H12 C6H12 C2H602 C2H60 C2H60 Cg H10 C2H40 CH20 CH40 CHAO C7H14 C7H14 Cg Hg C7H8 CHg (8) (0) (8) (8) (8) (8) (1) (8) -166,190 --484,500 227.480 82,930 49,080 109,240 -123,140 -156,230 -454,800 --235,100 -277,690 29,920 -52,630 -108,570 -200.660 -238,660 -154.770 - 190.160 147,360 50,170 - 128,860 - 389.900 209.970 129,665 124,520 149.795 31.920 26,850 -323,080 - 168,490 -174,780 130,890 - 13,010 -102,530 -161.960 - 166,270 27.480 20,560 213.900 122,050 113,630 (8) (8) (1) 12,180 687 Table C.4 (Continued) 4G NH3 NH3 CaC2 CaCO3 CaCl2 CaCl2 CaCl2.6H20 Ca(OH)2 Ca(OH)2 0 sesse . Chemical species State , 298 1298 Miscellaneous inorganics: (Note 2) (Note 1) (Note 1) Ammonia Ammonia (8) --46,110 - 16,450 Calcium carbide (aq) -- 26,500 Calcium carbonate -59,800 -64,900 Calcium chloride -1,206,920 -1.128,790 Calcium chloride ) - 795,800 -748,100 Calcium chloride () --8,101,900 Calcium hydroxide () -2,607,900 Calcium hydroxide -986,090 -898,490 Calcium oxide (aq) ---868,070 Carbon dioxide (3) CO2 --635,090 -604,030 Carbon monoxide (8) -393,509 -394,359 CO Hydrochloric acid (8) -110,525 -137,169 HCI Hydrogen cyanide (8) -92,307 --95,299 HCN (8) 135,100 124,700 Hydrogen sulfide HS Iron oxide -20,630 -33,560 Feo Iron oxide (hematite) (5) -272,000 Fe2O3 Iron oxide (magnetite) --824,200 - 742,200 Fe3O4 (5) Iron sulfide (pyrite) -1,118,400 -1,015,400 FeS2 (8) -178,200 - 166,900 Lithium chloride Lici -408,610 Lithium chloride LiCI-H20 (8) -712,580 Lithium chloride LiCl-2H20 (S) -1,012,650 Lithium chloride LiCl-3H20 (5) -1,311,300 Nitric acid HNO3 (1) -174,100 -80,710 Nitric acid HNO3 (aq) -111,250 Nitrogen oxides NO 90,250 86,550 NO2 33,180 51,310 N20 82,050 104,200 N204 9,160 97,540 Sodium carbonate Na2CO3 -1.130,680 -1,044,440 Sodium carbonate Na2CO3.10H20 -4,081,320 Sodium chloride NaCI --411,153 ---384,138 Sodium chloride NaCl (aq) -393,133 NaOH -425,609 -379,494 Sodium hydroxide Sodium hydroxide NaOH -419,150 SO2 - 296,830 -300,194 Sulfur dioxide SO3 -395,720 -371,060 Sulfur trioxide SO3 -441,040 Sulfur trioxide H2SO4 -813,989 -690,003 Sulfuric acid H2SO4 (aq) -744,530 Sulfuric acid -241,818 Water H2O -228,572 -285,830 Water H20 -237,129 From TRC Thermodynamic Tables--Hydrocarbons, Thermodynamics Research Cen- ter, Texas A&M Univ. System, College Station, TX; "The NBS Tables of Chemical Thermodynamic Properties," J. Phys. and Chem. Reference Data, vol. 11, supp. 2, 1982. Notes 5298 1. The standard property changes of formation AH;29, and AG are the changes occurring when I mol of the listed compound is formed from its elements with each substance in its standard state at 298.15 K (25C). 2. Standard states: (a) Gases (3): pure ideal gas at 1 bar and 25C. (b) Liquids (I) and solids (s): pure substance at 1 bar and 25C. (@Solutes in aqueous solution ...pothetical ideal 1-molal solution of solute in water at 1 bar and 25C. seISSSSSSSS@666 TABLE 1-7 Common Units and Conversion Factors Mass (M) 1 pound mass = 453.5924 grams =0.45359 kilograms 7000 grains 1 slug = 32.174 pounds mass 1 ton short) = 2000 pounds mass 1 ton (long) = 2240 pounds mass 1 ton (metric) = 1000 kilograms = 2204.62 pounds mass 1 pound mole = 453.59 gram moles Length (L.) 1 foot = 30.480 centimeters =0.3048 meters 1 inch = 2.54 centimeters = 0.0254 meters 1 mile (U.S.) = 1.60935 kilometers 1 yard = 0.9144 meters Area (L) 1 square foot = 929.0304 square centimeters =0.09290304 square meters I square inch = 6.4516 square centimeters 1 scuare yard = 0.836127 square meters Volume (L.) 1 cubic foot = 28,316.55 cubic centimeters = 0.02531685 cubic meters = 28.31685 liters = 7.451 gallons (U.S.) 1 gallon = 3.7853 liters = 231 cubic inches Time (O) 1 hour = 60 minutes = 3600 seconds Temperature (T) 1 centigrade or Celsius degree = 1.8 Fahrenheit degree Temperature, Kelvin = TC + 273.15 Temperature, Rankine =TF+ 459.7 Temperature, Fahrenheit =95 TC +32 Temperature, centigrade or Celsius = 5/9 (TF - 32) Temperature, Rankine = 1.STK Force (F) 1 pound force = 444,822.2 dynes = 4.448292 Newtons = 32.174 poundals Pressure (F/L) Normal atmospheric pressure latm = 760 millimeters of mercury at 0C (density 13.5951 g/cm) = 29.921 inches of mercury at 32F - 14.696 pounds force/square inch = 33.899 feet of water at 39.1F = 1.01325 x 10 dynes/square centimeter = 1.01325 x 10 Newtons/square meter Density (M/L) 1 pound mass/cubic foot = 0.01601846 grams/cubic centimeter = 16.01846 kilogram/cubic meter Energy (H or FL) 1 British thermal unit=251.98 calories = 1054.4 joules = 777.97 foot-pounds force = 10.409 liter-atmospheres = 0.2930 watt-hour Diffusivity (L) 1 square foot/hour=0.258 cm/s = 2.58 x 10 m/s Viscosity (M/LE) 1 pound mass/foot hour=0.00413 g/cm s. 0.000413 kg/ms 1 centipoise = 0.01 poise = 0.01 g/cms = 0.001 kg/ms = 0.000672 lbm/fts = 0.0000209 lbs/ft Thermal conductivity (H/OLAT/L)] 1 Btu/hr ft (Ft) = 0.00413 cal/s em (C/cm) = 1.728 J/ m (C/m) Heat transfer coefficient 1 Btu/hr ft F = 5.678 J/s m C Heat capacity (H/MT) 1 Btu/lbm F = 1 cal/g C = 4184 J/kg C Gas constant 1.987 Btu/bm mole "R= 1.987 cal/mol K = 82.057 atm cm/mol K =0.7302 atm ft/lb mole F = 10.73 (lb,/in.) (ftylb mole "R = 1545 (Ibe/ft) (ftlb mole R = 5.314 (N/m) (mmol K Gravitational acceleration g=9.8066 m/s = 32. 174 ft/s











