Question
Use the tables in your schema. 1) For each job, display the job title followed by the number of employees with that job title, then
Use the tables in your schema. 1) For each job, display the job title followed by the number of employees with that job title, then the min, max, and avg salary for that job. Format the results to display in dollars with no decimal places. Set the column headers to be NUM, MIN, MAX and AVERAGE and a report title of "Salaries Per Job". Use SQL/92 - Implement with USING statement. Hint: you will need to use a "group by" clause. Keep the ordering by ascending average salary. Clear the report header at the end.
2) Use the tables in your schema. Alter the previous query to only print out those job titles that have more than 1 employee for the job title.
Use the tables in your schema. 3) Show the last name, hire date, and use a case statement to form a third column labeled "Experience" If the employee was hired before 1990, they are an 'Old Timer', before 1994 'Senior', before 1997 'Experienced', before 1999 'Junior' and everyone else is a 'Rookie'. Only show employees whose name begins with B. (protect against case anomalies). Order by ascending last name.
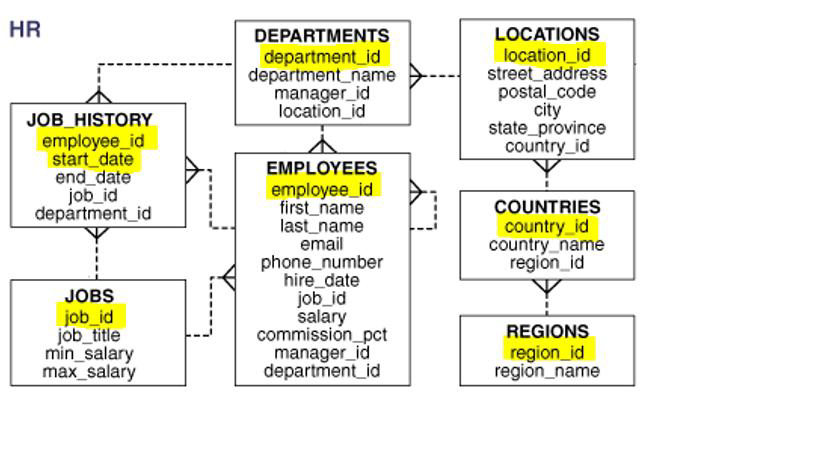
HR DEPARTMENTS department_id department_name manager_id location_id LOCATIONS location_id street_address postal_code city state_province country_id JOB_HISTORY employee_id start_date end_date job_id department_id EMPLOYEES employee_id first_name last_name email phone_number hire_date job_id salary commission_pct manager_id department_id COUNTRIES country_id country_name region_id JOBS job_id job_title min_salary max_salary REGIONS region_id region_name
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


