Question
use these methods : public int level(T el) { return level(el, root); } protected int level(T el, BSTNode p) { if(p == null) { return
use these methods :
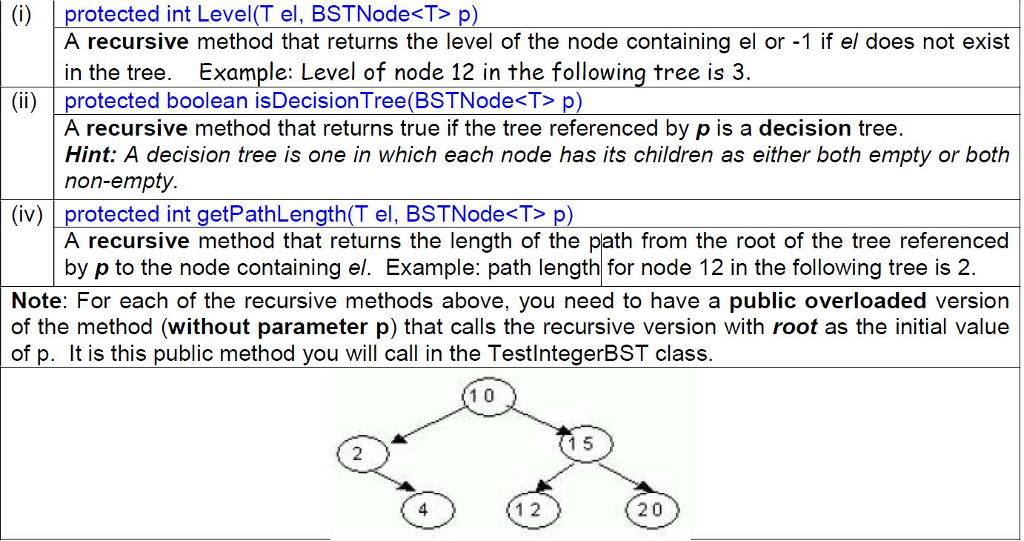
public int level(T el) { return level(el, root); } protected int level(T el, BSTNode p) { if(p == null) { return -1; } if(p.key.equals(el)) { return 1; } int l = level(el, p.left); int r = level(el, p.right); if(l != -1) { return 1 + l; } else if(r != -1) { return 1 + r; } else { return -1; } } this A recursive method that returns the level of the node containing el or -1 if el does not exist in the tree. Example: Level of node 12 in the following tree is 3.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
public boolean isDecisionTree() { return isDecisionTree(root); } protected boolean isDecisionTree(BSTNode p) { if(p == null || (p.left == null && p.right == null)) { return true; } else if(p.left != null && p.right != null){ return isDecisionTree(p.left) && isDecisionTree(p.right); } else { return false; } } this
A recursive method that returns true if the tree referenced by p is a decision tree. Hint: A decision tree is one in which each node has its children as either both empty or both non-empty.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
public int getPathLength(T el) { return getPathLength(el, root); } protected int getPathLength(T el, BSTNode p) { if(p == null) { return -1; } if(p.key.equals(el)) { return 0; } int l = getPathLength(el, p.left); int r = getPathLength(el, p.right); if(l != -1) { return 1 + l; } else if(r != -1) { return 1 + r; } else { return -1; } } this A recursive method that returns the length of the path from the root of the tree referenced by p to the node containing el. Example: path length for node 12 in the following tree is 2.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
add new case in this class to test these methods :
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.*;
public class TestIntegerBST {
public static void main (String[] args){
BST
int option, target;
Scanner reader = new Scanner(System.in);
do {
System.out.println(" ***************************");
System.out.println("* Testing Binary Search Tree *");
System.out.println("*************************** ");
System.out.println("1. Insert an element");
System.out.println("2. Search for an element");
System.out.println("3. Delete an element");
System.out.println("4. Print in Breadth-First-Order");
System.out.println("5. Print in Pre-Order");
System.out.println("6. Print in In-Order");
System.out.println("7. Print in Post-Order");
System.out.println("8. Print sum of the elements");
System.out.println("9. Quit");
System.out.print(" Select an Option [1...9] : ");
option = reader.nextInt();
switch (option) {
case 1 : System.out.print("Enter the element to insert: ");
tree.insert(reader.nextInt());
break;
case 2 : System.out.print("Enter the element to search for: ");
target = reader.nextInt();
Integer result = tree.search(target);
if (result != null)
System.out.println("Element, "+result+ " was found in the tree");
else
System.out.println("Sorry, the element was not found");
break;
case 3 : System.out.print("Enter the element delete: ");
tree.delete(reader.nextInt());
break;
case 4 : tree.breadthFirst();
break;
case 5 : tree.preorder();
break;
case 6 : tree.inorder();
break;
case 7 : tree.postorder();
break;
case 8 : System.out.print("Sum of the elements in the tree is: "+sum(tree));
break;
} //end of switch
} while (option != 9);
} //end of main
public static int sum(BST
int sum = 0;
for (int n : tree)
sum += n;
return sum;
}
}
(i) protected int Level(T el, BSTNode T> p) A recursive method that returns the level of the node containing el or -1 if el does not exist in the tree. Example: Level of node 12 in the following tree is 3. (ii) protected boolean isDecision Tree(BSTNodeStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


