Using Matlab
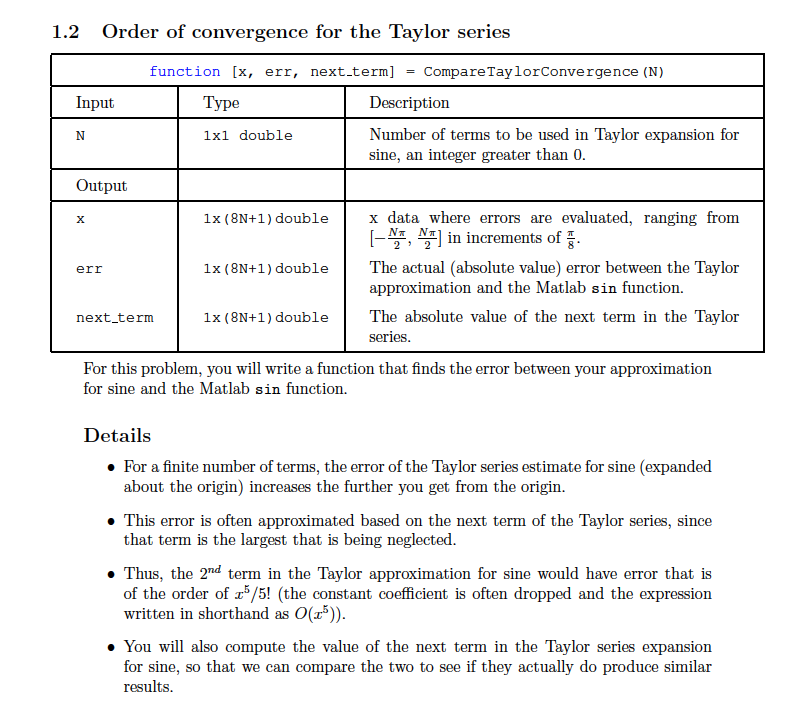
1.2 Order of convergence for the Taylor series function [x, err, next-term] CompareTaylorConve rge nce (N) = Input Type Description Number of terms to be used in Taylor expansion for sine, an integer greater than 0 1x1 double Output 1x (8N+1) doublex data where errors are evaluated, ranging from [?, ? in increments of 1x (8N+1) double The actual (absolute value) error between the Taylor err approximation and the Matlab sin function. next term 1x (8N+1) doubleThe absolute value of the next term in the Taylor series For this problem, you will write a function that finds the error between your approximation for sine and the Matlab sin function. Details For a finite number of terms, the error of the Taylor series estimate for sine (expanded about the origin) increases the further you get from the origin. that term is the largest that is being neglected of the order of x5/5! (the constant coefficient is often dropped and the expression This error is often approximated based on the next term of the Taylor series, since Thus, the 2nd term in the Taylor approximation for sine would have error that is written in shorthand as O(r5)) You will also compute the value of the next term in the Taylor series expansion for sine, so that we can compare the two to see if they actually do produce similar results 1.2 Order of convergence for the Taylor series function [x, err, next-term] CompareTaylorConve rge nce (N) = Input Type Description Number of terms to be used in Taylor expansion for sine, an integer greater than 0 1x1 double Output 1x (8N+1) doublex data where errors are evaluated, ranging from [?, ? in increments of 1x (8N+1) double The actual (absolute value) error between the Taylor err approximation and the Matlab sin function. next term 1x (8N+1) doubleThe absolute value of the next term in the Taylor series For this problem, you will write a function that finds the error between your approximation for sine and the Matlab sin function. Details For a finite number of terms, the error of the Taylor series estimate for sine (expanded about the origin) increases the further you get from the origin. that term is the largest that is being neglected of the order of x5/5! (the constant coefficient is often dropped and the expression This error is often approximated based on the next term of the Taylor series, since Thus, the 2nd term in the Taylor approximation for sine would have error that is written in shorthand as O(r5)) You will also compute the value of the next term in the Taylor series expansion for sine, so that we can compare the two to see if they actually do produce similar results







