Question
using namespace std; class SinglyLinkedListNode { // INSERT YOUR CODE HERE }; class SinglyLinkedList { public: SinglyLinkedListNode *head; SinglyLinkedListNode *tail; SinglyLinkedList() { this->head = nullptr;

using namespace std;
class SinglyLinkedListNode { // INSERT YOUR CODE HERE };
class SinglyLinkedList { public: SinglyLinkedListNode *head; SinglyLinkedListNode *tail;
SinglyLinkedList() { this->head = nullptr; this->tail = nullptr; }
void insert_node(int node_data) { // INSERT YOUR CODE HERE } };
void free_singly_linked_list(SinglyLinkedListNode* node) { // INSERT YOUR CODE HERE }
// Complete the has_cycle function below.
/* * For your reference: * * SinglyLinkedListNode { * int data; * SinglyLinkedListNode* next; * }; * */ bool has_cycle(SinglyLinkedListNode* head) { SinglyLinkedListNode* temp = head; bool isCycle = false; while (temp != nullptr) { // INSERT YOUR CODE HERE }
}
int main() {
// INSERT YOUR CODE HERE TO TEST YOUR CODE return 0; }
PLEASE FILL THE "INSERT YOUR CODE HERE" PARTS. according to 2 pictures. (C++)
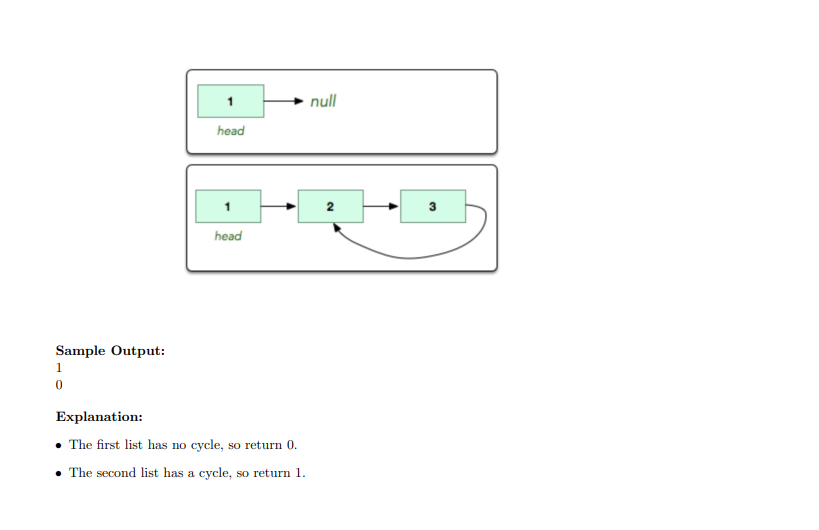
A linked list is said to contain a cycle if any node is visited more than once while traversing the list. Given a pointer to the head of a linked list, determine if it contains a cycle. If it does, return 1. Otherwise, return 0. Example: head refers to the list of nodes 1 +2+3+1+NULL. There is a cycle where node 3 points back to node 1, so return 1. Function Description: Complete the has_cycle function provided in the moodle assignment folder. It has the following parameter: SinglyLinkedListNode pointer head: a reference to the head of the list. Returns: int: 1 if there is a cycle or 0 if there is not. Note: if the list is empty, head will be null. Input Format: The code stub reads from stdin and passes the appropriate argument to your function. The custom test cases format will not be described for this question due to its complexity. Expand the section for the main function and review the code if you would like to figure out how to create a custom case. Constraints: List size can be minimum 0 and maximum 1000. Sample Input: References to each of the following linked lists in the figure above are passed as arguments to your function: null head N 3 head Sample Output: 1 0 Explanation: The first list has no cycle, so return 0. The second list has a cycle, so return 1Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


