Using the information above:
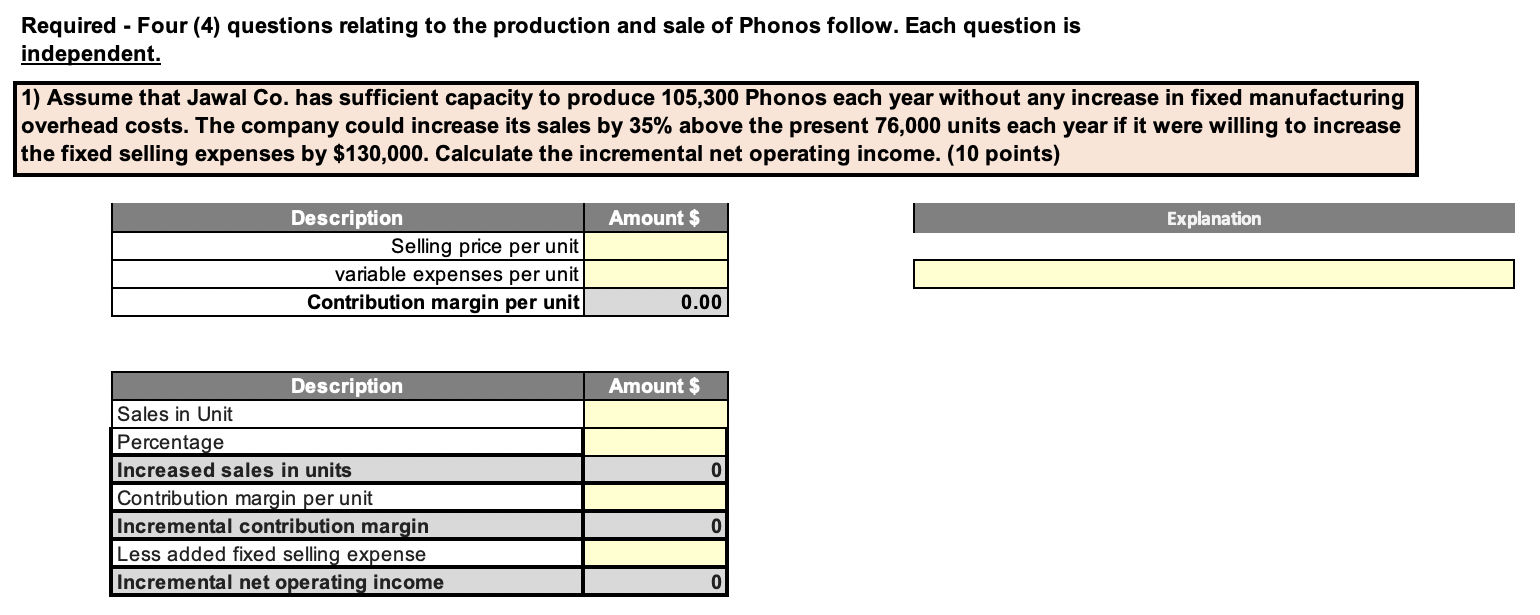
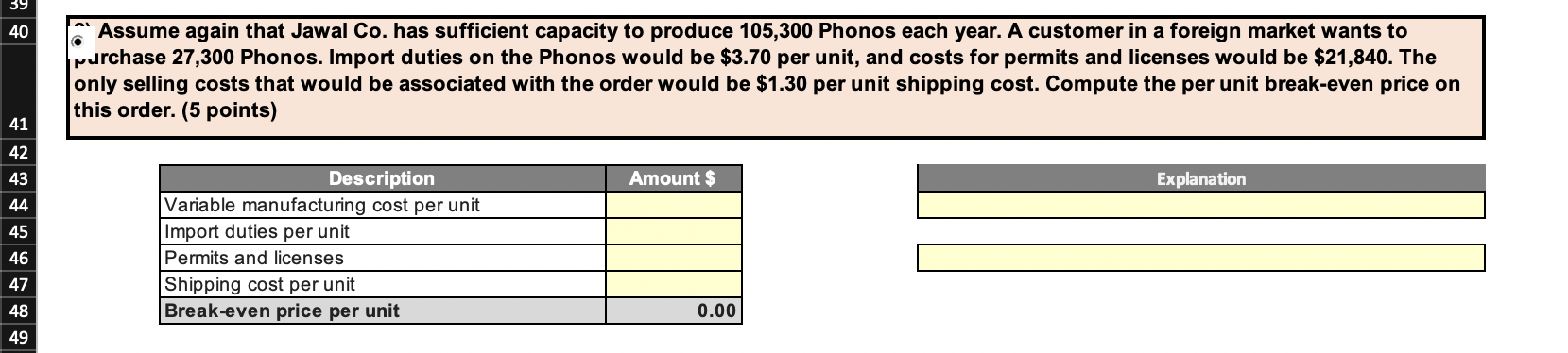
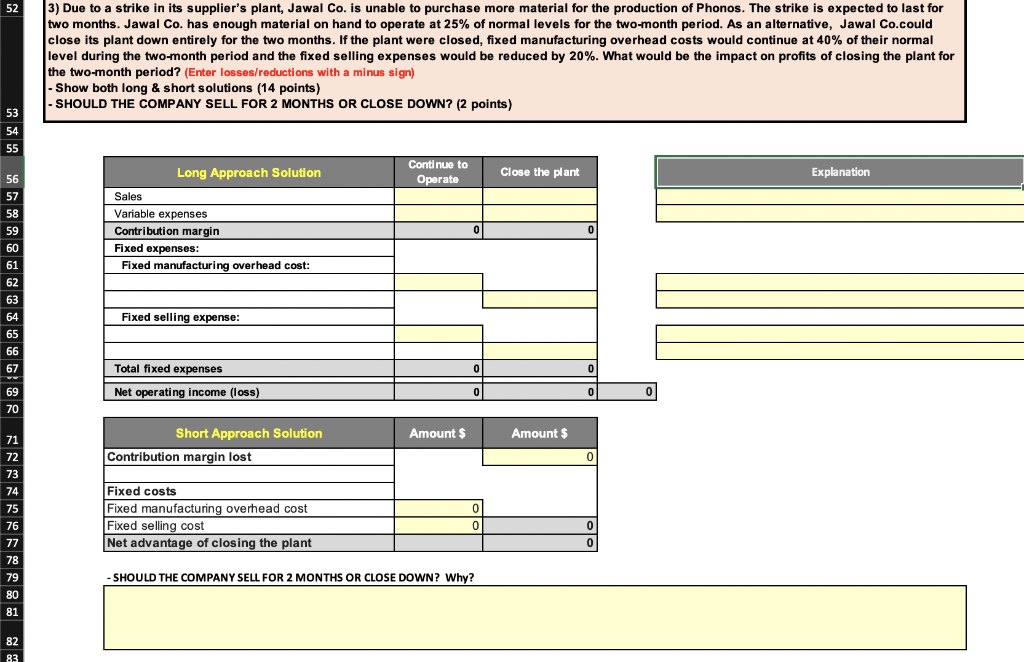
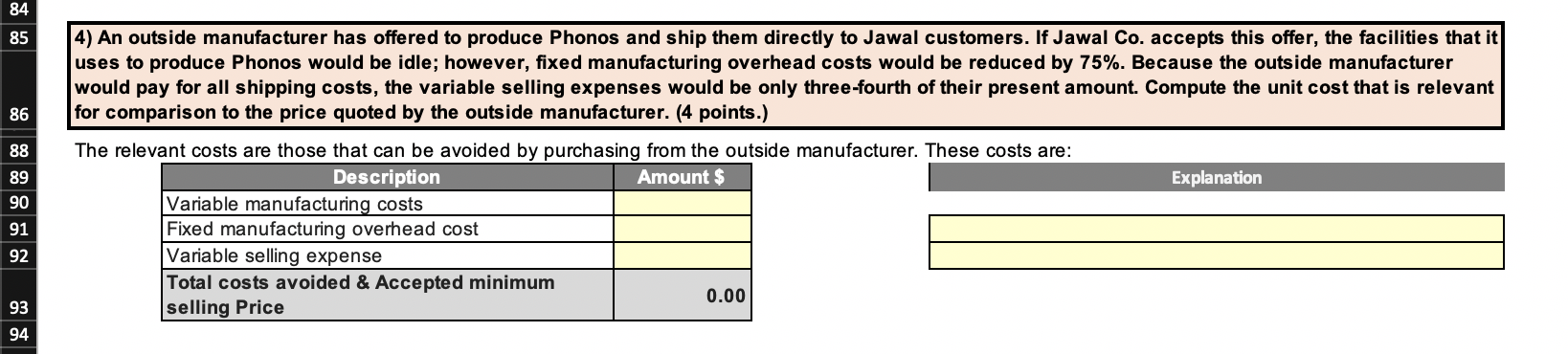
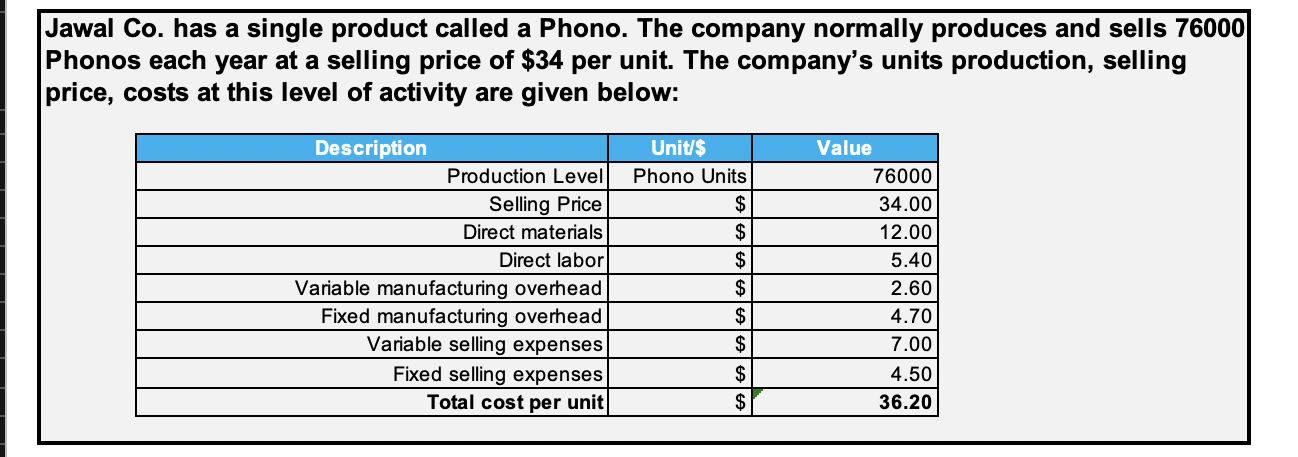
Jawal Co. has a single product called a Phono. The company normally produces and sells 76000 Phonos each year at a selling price of $34 per unit. The company's units production, selling price, costs at this level of activity are given below: Unit$ Phono Units $ Description Production Level Selling Price Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed manufacturing overhead Variable selling expenses Fixed selling expenses Total cost per unit Value 76000 34.00 12.00 5.40 2.60 4.70 7.00 4.50 36.20 $ Required - Four (4) questions relating to the production and sale of Phonos follow. Each question is independent. 1) Assume that Jawal Co. has sufficient capacity to produce 105,300 Phonos each year without any increase in fixed manufacturing overhead costs. The company could increase its sales by 35% above the present 76,000 units each year if it were willing to increase the fixed selling expenses by $130,000. Calculate the incremental net operating income. (10 points) Amount $ duon Description Selling price per unit variable expenses per unit Contribution margin per unit 0.00 Amount $ Description Sales in Unit Percentage Increased sales in units Contribution margin per unit Incremental contribution margin Less added fixed selling expense Incremental net operating income 39 40 Assume again that Jawal Co. has sufficient capacity to produce 105,300 Phonos each year. A customer in a foreign market wants to purchase 27,300 Phonos. Import duties on the Phonos would be $3.70 per unit, and costs for permits and licenses would be $21,840. The only selling costs that would be associated with the order would be $1.30 per unit shipping cost. Compute the per unit break-even price on this order. (5 points) 41 42 43 Amount $ Explanation 44 Description Variable manufacturing cost per unit Import duties per unit Permits and licenses Shipping cost per unit Break-even price per unit 46 47 48 0.00 52 3) Due to a strike in its supplier's plant, Jawal Co. is unable to purchase more material for the production of Phonos. The strike is expected to last for two months. Jawal Co. has enough material on hand to operate at 25% of normal levels for the two-month period. As an alternative, Jawal Co.could close its plant down entirely for the two months. If the plant were closed, fixed manufacturing overhead costs would continue at 40% of their normal level during the two-month period and the fixed selling expenses would be reduced by 20%. What would be the impact on profits of closing the plant for the two-month period? (Enter losses/reductions with a minus sign) - Show both long & short solutions (14 points) - SHOULD THE COMPANY SELL FOR 2 MONTHS OR CLOSE DOWN? (2 points) Long Approach Solution Continue to Operate Close the plant Explanation Sales Variable expenses Contribution margin Fixed expenses: Fixed manufacturing overhead cost: 0 Fixed selling expense: Total fixed expenses Net operating income (loss) Amount $ Amount $ Short Approach Solution Contribution margin lost Fixed costs Fixed manufacturing overhead cost Fixed selling cost Net advantage of closing the plant 0 01 - SHOULD THE COMPANY SELL FOR 2 MONTHS OR CLOSE DOWN? Why? 84 85 4) An outside manufacturer has offered to produce Phonos and ship them directly to Jawal customers. If Jawal Co. accepts this offer, the facilities that it uses to produce Phonos would be idle; however, fixed manufacturing overhead costs would be reduced by 75%. Because the outside manufacturer would pay for all shipping costs, the variable selling expenses would be only three-fourth of their present amount. Compute the unit cost that is relevant for comparison to the price quoted by the outside manufacturer. (4 points.) 86 88 Explanation The relevant costs are those that can be avoided by purchasing from the outside manufacturer. These costs are: Description Amount $ Variable manufacturing costs Fixed manufacturing overhead cost Variable selling expense Total costs avoided & Accepted minimum 0.00 selling Price











