Question
Using the provided financial statements as a starting point: The DCF valuation and pro forma financials with five years of forecasted growth rates are provided
 Using the provided financial statements as a starting point:
Using the provided financial statements as a starting point:
- The DCF valuation and pro forma financials with five years of forecasted growth rates are provided in the original model. Please modify the model to consider a more successful scenario where Wok Yow's sales grow at a more aggressive pace of 40% for five years and then flatten to a more sustainable growth rate of 7%. What would the stock value per share be under the new scenario? What kind of strategic changes you would make in the business model to justify the growth assumption? How would you do things differently? You can use fictional events to justify your assumptions.
2.Prepare and present DCF valuations and pro forma financial statements (five-year explicit period) that justify a $31 and a $56 share price. You can play with the model assumptions to get to these valuations. Propose two different business plans that would be targeting these two different outcomes. Make sure the ratios embedded in your projections conform to reasonable operating ratio assumptions in the models. Also remember that higher risk business strategies come with higher expected returns.
3.Discuss the $31 and $56 IPO prices for Wok Yow within the context of comparable firms and their multiples. You can use some outside reference materials from companies in similar industries for comparison purposes. Then take a position on whether you would recommend the $31 or $56 IPO. Which one is more feasible? Take a position on which of the two business plans you would invest in as an investor, which financial instrument of the company you would want to invest in and what kind of a return you would expect on your money.
4.Prepare an executive summary discussing the events and decisions leading to its current situation, the options it currently has moving forward, and your recommendations for Wok Yow's near future. The events in the summary will be fictional.
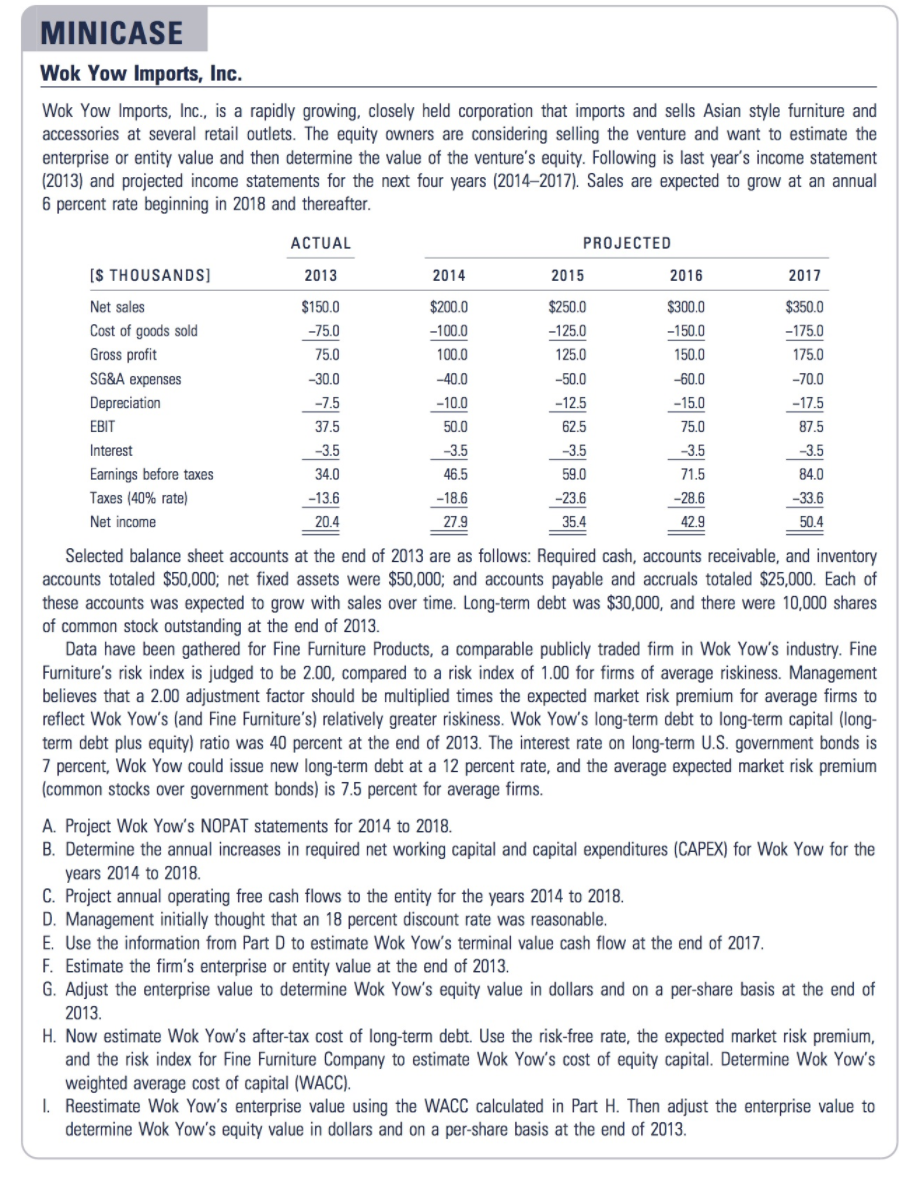
MINICASE Wok Yow Imports, Inc. Wok Yow Imports, Inc., is a rapidly growing, closely held corporation that imports and sells Asian style furniture and accessories at several retail outlets. The equity owners are considering selling the venture and want to estimate the enterprise or entity value and then determine the value of the venture's equity. Following is last year's income statement (2013) and projected income statements for the next four years (2014-2017). Sales are expected to grow at an annual 6 percent rate beginning in 2018 and thereafter. ACTUAL PROJECTED [S THOUSANDS] 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 $150.0 $300.0 -150.0 $350.0 -175.0 -75.0 75.0 150.0 175.0 $200.0 -100.0 100.0 -40.0 -10.0 50.0 Net sales Cost of goods sold Gross profit SG&A expenses Depreciation EBIT Interest Earnings before taxes Taxes (40% rate) Net income $250.0 -125.0 125.0 -50.0 -12.5 62.5 -30.0 -7.5 37.5 -3.5 -70.0 -17.5 87.5 -3.5 84.0 -33.6 -3.5 -60.0 -15.0 75.0 -3.5 71.5 -28.6 42.9 -3.5 34.0 -13.6 20.4 46.5 -18.6 27.9 59.0 -23.6 35.4 50.4 Selected balance sheet accounts at the end of 2013 are as follows: Required cash, accounts receivable, and inventory accounts totaled $50,000; net fixed assets were $50,000; and accounts payable and accruals totaled $25,000. Each of these accounts was expected to grow with sales over time. Long-term debt was $30,000, and there were 10,000 shares of common stock outstanding at the end of 2013. Data have been gathered for Fine Furniture Products, a comparable publicly traded firm in Wok Yow's industry. Fine Furniture's risk index is judged to be 2.00, compared to a risk index of 1.00 for firms of average riskiness. Management believes that a 2.00 adjustment factor should be multiplied times the expected market risk premium for average firms to reflect Wok Yow's (and Fine Furniture's) relatively greater riskiness. Wok Yow's long-term debt to long-term capital (long- term debt plus equity) ratio was 40 percent at the end of 2013. The interest rate on long-term U.S. government bonds is 7 percent, Wok Yow could issue new long-term debt at a 12 percent rate, and the average expected market risk premium (common stocks over government bonds) is 7.5 percent for average firms. A. Project Wok Yow's NOPAT statements for 2014 to 2018. B. Determine the annual increases in required net working capital and capital expenditures (CAPEX) for Wok Yow for the years 2014 to 2018 C. Project annual operating free cash flows to the entity for the years 2014 to 2018. D. Management initially thought that an 18 percent discount rate was reasonable. E. Use the information from Part D to estimate Wok Yow's terminal value cash flow at the end of 2017. F. Estimate the firm's enterprise or entity value at the end of 2013. G. Adjust the enterprise value to determine Wok Yow's equity value in dollars and on a per-share basis at the end of 2013 H. Now estimate Wok Yow's after-tax cost of long-term debt. Use the risk-free rate, the expected market risk premium, and the risk index for Fine Furniture Company to estimate Wok Yow's cost of equity capital. Determine Wok Yow's weighted average cost of capital (WACC). Reestimate Wok Yow's enterprise value using the WACC calculated in Part H. Then adjust the enterprise value to determine Wok Yow's equity value in dollars and on a per-share basis at the end of 2013 MINICASE Wok Yow Imports, Inc. Wok Yow Imports, Inc., is a rapidly growing, closely held corporation that imports and sells Asian style furniture and accessories at several retail outlets. The equity owners are considering selling the venture and want to estimate the enterprise or entity value and then determine the value of the venture's equity. Following is last year's income statement (2013) and projected income statements for the next four years (2014-2017). Sales are expected to grow at an annual 6 percent rate beginning in 2018 and thereafter. ACTUAL PROJECTED [S THOUSANDS] 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 $150.0 $300.0 -150.0 $350.0 -175.0 -75.0 75.0 150.0 175.0 $200.0 -100.0 100.0 -40.0 -10.0 50.0 Net sales Cost of goods sold Gross profit SG&A expenses Depreciation EBIT Interest Earnings before taxes Taxes (40% rate) Net income $250.0 -125.0 125.0 -50.0 -12.5 62.5 -30.0 -7.5 37.5 -3.5 -70.0 -17.5 87.5 -3.5 84.0 -33.6 -3.5 -60.0 -15.0 75.0 -3.5 71.5 -28.6 42.9 -3.5 34.0 -13.6 20.4 46.5 -18.6 27.9 59.0 -23.6 35.4 50.4 Selected balance sheet accounts at the end of 2013 are as follows: Required cash, accounts receivable, and inventory accounts totaled $50,000; net fixed assets were $50,000; and accounts payable and accruals totaled $25,000. Each of these accounts was expected to grow with sales over time. Long-term debt was $30,000, and there were 10,000 shares of common stock outstanding at the end of 2013. Data have been gathered for Fine Furniture Products, a comparable publicly traded firm in Wok Yow's industry. Fine Furniture's risk index is judged to be 2.00, compared to a risk index of 1.00 for firms of average riskiness. Management believes that a 2.00 adjustment factor should be multiplied times the expected market risk premium for average firms to reflect Wok Yow's (and Fine Furniture's) relatively greater riskiness. Wok Yow's long-term debt to long-term capital (long- term debt plus equity) ratio was 40 percent at the end of 2013. The interest rate on long-term U.S. government bonds is 7 percent, Wok Yow could issue new long-term debt at a 12 percent rate, and the average expected market risk premium (common stocks over government bonds) is 7.5 percent for average firms. A. Project Wok Yow's NOPAT statements for 2014 to 2018. B. Determine the annual increases in required net working capital and capital expenditures (CAPEX) for Wok Yow for the years 2014 to 2018 C. Project annual operating free cash flows to the entity for the years 2014 to 2018. D. Management initially thought that an 18 percent discount rate was reasonable. E. Use the information from Part D to estimate Wok Yow's terminal value cash flow at the end of 2017. F. Estimate the firm's enterprise or entity value at the end of 2013. G. Adjust the enterprise value to determine Wok Yow's equity value in dollars and on a per-share basis at the end of 2013 H. Now estimate Wok Yow's after-tax cost of long-term debt. Use the risk-free rate, the expected market risk premium, and the risk index for Fine Furniture Company to estimate Wok Yow's cost of equity capital. Determine Wok Yow's weighted average cost of capital (WACC). Reestimate Wok Yow's enterprise value using the WACC calculated in Part H. Then adjust the enterprise value to determine Wok Yow's equity value in dollars and on a per-share basis at the end of 2013Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


