Using two important instructions of MARIE (JnS and JumpI ), implement a subroutine (a function) such that when this function is called, it will calculate, print and save the next element in a Fibonacci series. As you know, Fibonacci numbers can be calculated based on the following equations.

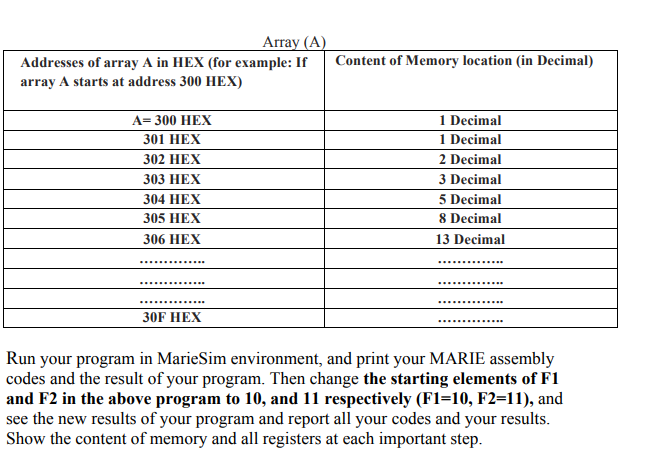
Part 4: Subroutine call and return Using two important instructions of MARIE (JnS and JumpI), implement a subroutine (a function) such that when this function is called, it will calculate, print and save the next element in a Fibonacci series. As you know, Fibonacci numbers can be calculated based on the following equations. Formulas for Fibonacci series In this Part, you should implement a subroutine and a program that calls that subroutine. Assume your subroutine is called FIBO, such that when FIBO is called it will first calculate the next element in Fibonacci series, then it will print and save the calculated Fibonacci number in an array in MARIE memory. At the beginning, the first two elements in your array will be one (1) and all other elements will be zero, and then at the end of the program your array will have 16 elements of Fibonacci series including those two initial values of 1. (Hint: you can implement the following Pseudo code that will call your FIBO subroutine. You also should implement FIB0 subroutine to calculate next Fibonacci number.) F1 := 1; // FI: Starting element 1 F2:-1 // F2: Starting element 2 FOR X := 1 to 10 DO FIBO Call which Calculates, prints and then save the next FIBONACCI number in your array) (this part calls your FIBO subroutine, ENDFOR If Fl 1 and F2-1, at the end of your program, array (A) will look like as follows: Part 4: Subroutine call and return Using two important instructions of MARIE (JnS and JumpI), implement a subroutine (a function) such that when this function is called, it will calculate, print and save the next element in a Fibonacci series. As you know, Fibonacci numbers can be calculated based on the following equations. Formulas for Fibonacci series In this Part, you should implement a subroutine and a program that calls that subroutine. Assume your subroutine is called FIBO, such that when FIBO is called it will first calculate the next element in Fibonacci series, then it will print and save the calculated Fibonacci number in an array in MARIE memory. At the beginning, the first two elements in your array will be one (1) and all other elements will be zero, and then at the end of the program your array will have 16 elements of Fibonacci series including those two initial values of 1. (Hint: you can implement the following Pseudo code that will call your FIBO subroutine. You also should implement FIB0 subroutine to calculate next Fibonacci number.) F1 := 1; // FI: Starting element 1 F2:-1 // F2: Starting element 2 FOR X := 1 to 10 DO FIBO Call which Calculates, prints and then save the next FIBONACCI number in your array) (this part calls your FIBO subroutine, ENDFOR If Fl 1 and F2-1, at the end of your program, array (A) will look like as follows








