Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
2.26. Measurement error in which of the variables in Eq. (2.4) (air temperature, relative humidity, or wind velocity) will yield the largest relative error


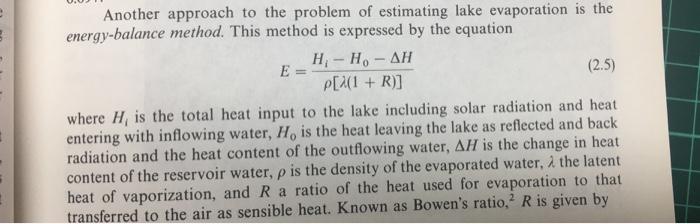
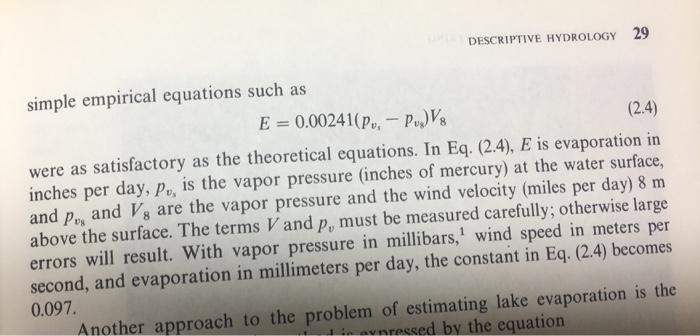
2.26. Measurement error in which of the variables in Eq. (2.4) (air temperature, relative humidity, or wind velocity) will yield the largest relative error in the estimated evaporation rate? Assume the conditions of Prob. 2.25 and a 10 percent relative measurement error for each of the variables. 2.25. What evaporation rate would be indicated by Eq. (2.4) when the reservoir water surface is 60'F, the air temperature at 8 m is 70 F, the relative humidity is 85 percent, and the wind velocity at 8 m is 9 mph? If the relative humidity at 8 m were only 20 percent, what would be the evaporation rate, all other factors being the same? -77 Another approach to the problem of estimating lake evaporation is the energy-balance method. This method is expressed by the equation H- Ho-AH E = (2.5) P[(1 + R)] where H, is the total heat input to the lake including solar radiation and heat entering with inflowing water, H, is the heat leaving the lake as reflected and back radiation and the heat content of the outflowing water, AH is the change in heat content of the reservoir water, p is the density of the evaporated water, the latent heat of vaporization, and R a ratio of the heat used for evaporation to that transferred to the air as sensible heat. Known as Bowen's ratio, R is given by DESCRIPTIVE HYDROLOGY 29 simple empirical equations such as E = 0.00241(p,, - Pu)Vs (2.4) were as satisfactory as the theoretical equations. In Eq. (2.4), E is evaporation in inches per day, Po, is the vapor pressure (inches of mercury) at the water surface, and and Vs are the vapor pressure and the wind velocity (miles per day) 8 m Pe above the surface. The terms V and p, must be measured carefully; otherwise large errors will result. With vapor pressure in millibars,' wind speed in meters per second, and evaporation in millimeters per day, the constant in Eq. (2.4) becomes 0.097. Another approach to the problem of estimating lake evaporation is the vnressed by the equation
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.47 Rating (177 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
day lorresbonds to ttin milib...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


