Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
What is the main difference between hot and cold deformation? Why annealing is applied to cold worked metals? Please explain the annealing steps. The hypothetical
What is the main difference between hot and cold deformation? Why annealing is applied to cold worked metals? Please explain the annealing steps.
The hypothetical binary phase diagram is given below. According to this diagram, determine the which material or materials with given compositions are agehardenable and explain your answer in detail. Also, write why age hardening cannot be applied in other compositions.
Please explain the "strain hardening" mechanism by using stressstrain diagram. Do you think this mechanism could be used at high temperatures or not?
a What is the difference between homogeneous and heterogeneous nucleation?
b How does cooling rate affect the microstructure? Explain.
and display unlimited complete solid solubility.
a Draw a hypothetical binary phase diagram for system, and label the curves, regions, etc. Melting temperatures of and are and respectively
b Which requirements should be satisfied to obtain a complete solid solubility?
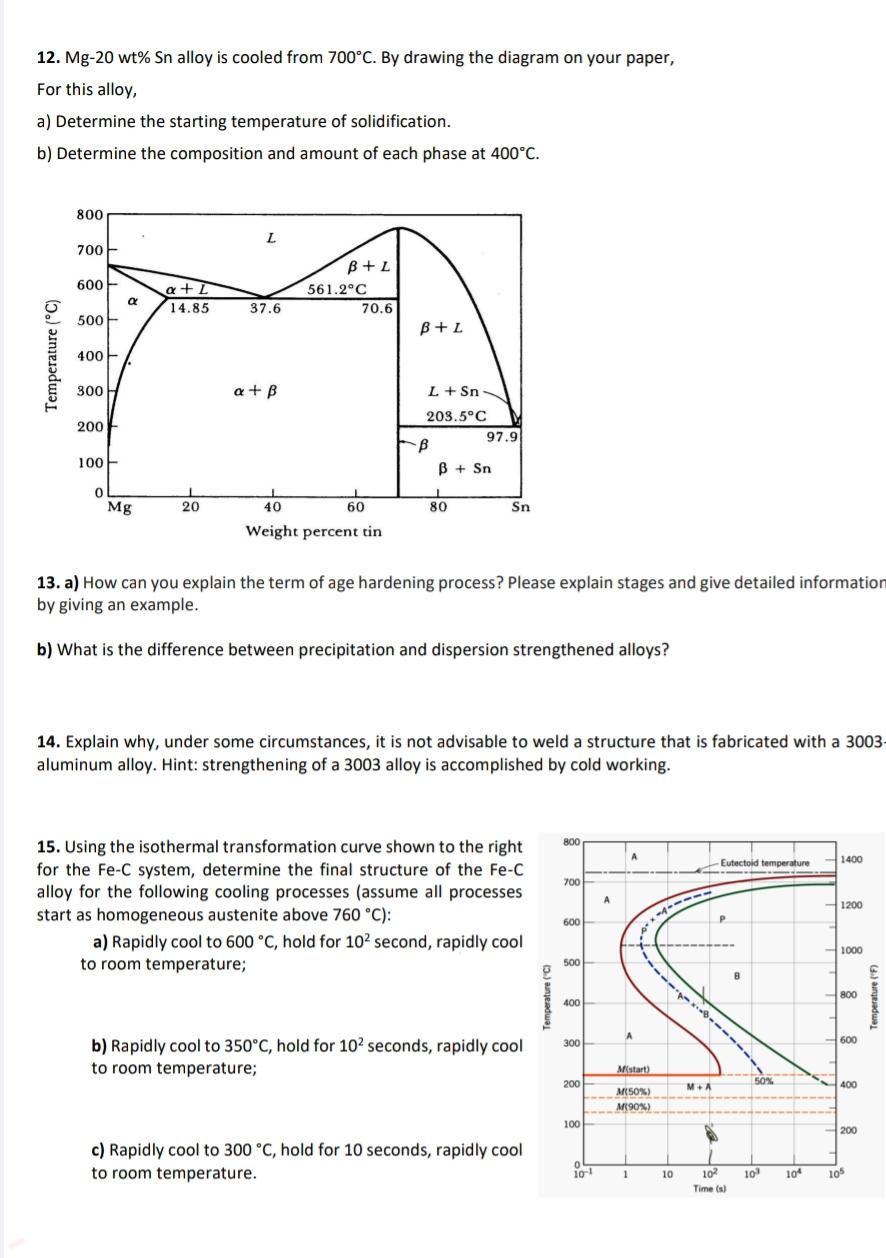
Mg wt alloy is cooled from By drawing the diagram on your paper, For this alloy,
a Determine the starting temperature of solidification.
b Determine the composition and amount of each phase at
a How can you explain the term of age hardening process? Please explain stages and give detailed information by giving an example.
b What is the difference between precipitation and dispersion strengthened alloys?
Explain why, under some circumstances, it is not advisable to weld a structure that is fabricated with a aluminum alloy. Hint: strengthening of a alloy is accomplished by cold working.
Using the isothermal transformation curve shown to the right for the FeC system, determine the final structure of the FeC alloy for the following cooling processes assume all processes start as homogeneous austenite above :
a Rapidly cool to hold for second, rapidly cool to room temperature;
b Rapidly cool to hold for seconds, rapidly cool to room temperature;
c Rapidly cool to hold for seconds, rapidly cool to room temperature.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


