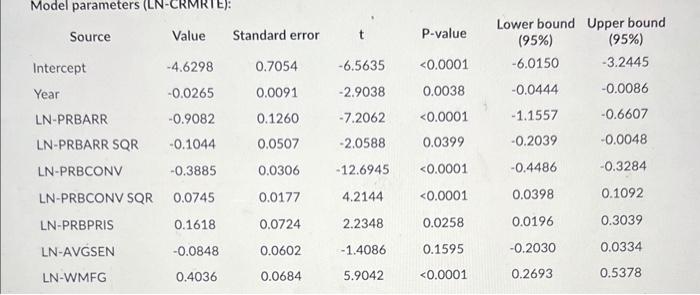
What is the relationship between crime and punishment? This important question has been examined by Cornwell and Trumbull 1 using a panel of data from North Carolina. The data are annual for the years 1981 to 1987. The data are in the file Crime Data for Exam.x/sx, which is posted in the Some Datasets folder on the course Contents page. (You don't actually need to download the data for anything.) [1] "Estimating the Economic Model of Crime with Panel Data," Review of Economics and Statistics, 76, 1994. Consider a regression model in which the crime rate (LN-CRMRTE) is a function of the probability of arrest (LN-PRBARR), the probability of conviction (LN-PRBCONV), the probability of a prison sentence (LN-PRBPRIS), the average prison sentence (LN-AVGSEN), and the average weekly wage in the manufacturing sector (LN-WMFG). The latter represents wages for work that is not illegal. Note that the natural log of all variables except Year are used in the model. Year is included in the model to sep if there is any change in the average crime rate over time. Due to potential nonlinearities indicated in the the scatter plots of some of the independent variables against the dependent, a squared term was added to the model for LN-PRBARR and for LN-PRBCONV. The results are given below: Mndel naramefers (LN-CRMRTEI? At a 1% significance level, are any of the parameter estimates NOT significantly different from zero (meaning they don't impact crime rates)? Yes or No? If so, which one(s)? Based on the results above and using a five percent significance level, what would be the impact of a one percentage point increase in the probability of a prison sentence? Based on the results above and using a five percent significance level, what would be the impact of a one percentage point increase in the probability of arrest if that probability were initially 0.24 ? A Based on the results above and using a five percent significance level, what would be the impact of a one percentage point increase in the probability of arrest if that probability were initially 0.65 ? percentage point increase in the probability of conviction if that probability were initially 0.74 ? A Based on the results above and using a five percent significance level, what would be the impact of a one percentage point increase in the probability of conviction if that probability were initially 0.89 ? A What is the relationship between crime and punishment? This important question has been examined by Cornwell and Trumbull 1 using a panel of data from North Carolina. The data are annual for the years 1981 to 1987. The data are in the file Crime Data for Exam.x/sx, which is posted in the Some Datasets folder on the course Contents page. (You don't actually need to download the data for anything.) [1] "Estimating the Economic Model of Crime with Panel Data," Review of Economics and Statistics, 76, 1994. Consider a regression model in which the crime rate (LN-CRMRTE) is a function of the probability of arrest (LN-PRBARR), the probability of conviction (LN-PRBCONV), the probability of a prison sentence (LN-PRBPRIS), the average prison sentence (LN-AVGSEN), and the average weekly wage in the manufacturing sector (LN-WMFG). The latter represents wages for work that is not illegal. Note that the natural log of all variables except Year are used in the model. Year is included in the model to sep if there is any change in the average crime rate over time. Due to potential nonlinearities indicated in the the scatter plots of some of the independent variables against the dependent, a squared term was added to the model for LN-PRBARR and for LN-PRBCONV. The results are given below: Mndel naramefers (LN-CRMRTEI? At a 1% significance level, are any of the parameter estimates NOT significantly different from zero (meaning they don't impact crime rates)? Yes or No? If so, which one(s)? Based on the results above and using a five percent significance level, what would be the impact of a one percentage point increase in the probability of a prison sentence? Based on the results above and using a five percent significance level, what would be the impact of a one percentage point increase in the probability of arrest if that probability were initially 0.24 ? A Based on the results above and using a five percent significance level, what would be the impact of a one percentage point increase in the probability of arrest if that probability were initially 0.65 ? percentage point increase in the probability of conviction if that probability were initially 0.74 ? A Based on the results above and using a five percent significance level, what would be the impact of a one percentage point increase in the probability of conviction if that probability were initially 0.89 ? A