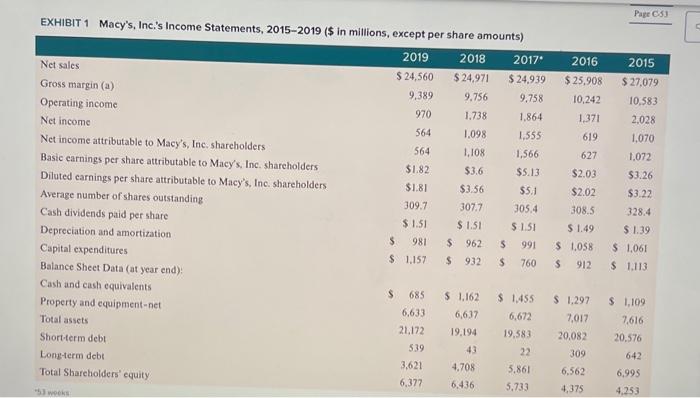
When analyzing the weekly case address the following issues: Provide a short background to the case and then explain: . What is the key decision to be made? Provide evidence - What is the key unit of analysis involved in this case? Provide evidence - Identify the stakeholders impacted by this decision. How are the impacted? Provide evidence. . What are some of the key facts? This might be financial, SWOT, Porter's, elements (Mission/vision/values) or strategies. -.What recommendation do you believe the company should make regarding its best path forward? Macy's, Inc.: Will Its Strategy Allow It to Survive in the Changing Retail Sector? Alen Badal University of Liverpool John E. Gamble Tecas AdM Universiry Corpus Christi The retail landscape in the United States in early 2020 may have been best characterized as rapidly changing with an uncertain future. The COVID-19 pandemic and stay-athome orders by state and local governments had created unprecedented challenges for all retailers, but traditional brick-and-mortar retailers had under pressure for at least a decade. The convenience of shopping for nearly every type of consumer good at Amazon or other online retailer sites had radically transformed the retail industry. Consumer needs continued to allow for variations in strategy that allowed for distinctive retailer approaches to meeting customer expectations. But consumers had become to expect even the most highly differentiated retailers to have an online presence in addition to their prestigious brickand-mortar locations. The change in consumer shopping preferences had especially impacted mallbased department stores. Nearly all shopping malls relied on strong department store anchor tenants to draw vast numbers of shoppers, who would also patronize smaller specialized retailers during their visits to a mall. The transition to online shopping had greatly damaged the business model of many shopping malls as smaller retailers failed along with department stores, both of whom had experienced a decline in sales per square foot resulting from reduced customer traffic. Macy's, Ine. had particularly struggled to adapt its business model to the online shopping environment with sales declining each year since its record sales of $28.1 billion generated in 2014. In 2018. Macy's turned to 34year company veteran Jeff Gennette to lead the company's turnaround and transformation as CEO. In early 2020, Gennette was in the second year of his five-point strategic plan designed to reinvent the company's business model and generate retail innovations. The key feature of the plan was its Growth50 initiative which strived for product and merchandising innovations in 50 stores that would establish a new retailing standard that could be rolled out to 50 to 100 additiotal stores per year. The company also implemented a direct vendor fulfillment model for online sales that nearly doubled the number of SKUs offered online since inventory could be maintained by vendors, not Macy's: Headquartered in Cincinnati, Ohio, Macy's, Inc, was the second-largest department store chain with a market share of approximately 16.3. percent in 2020. The company operated about 551 Macy's department stores, 53 Bloomingdales, and 171 Bluemercury businesses in early2020, and its retailing portfolio also included Bloomingdale's The Outlet, Macy's Backstage, and STORY and online businesses macys,com. bloomingdales.com, and bluemercury.com. The company also licensed Bloomingdale's stores in Dubai and Kuwait for operation by AI Tayer Group. Beginning in 2018, CEO Gennette and his chief lieutenants latunched a fivepoint turnaround plan to improve the company's performance. The Growth50 initiative was focused on 50 Macy's department stores to revitalize in 2018, including store remodels, improved customer service, and increased product assortment. The addition of STORY retail locations in 2018 supported sales growth for the company as well. STORY locations were much smaller stores with an inventory assortment that was refreshed with new items every six to eight weeks. The value proposition of the STORY business was keyed to engaging consumers through an opportunity to interact with products and collaborate. The value proposition for The Market @ Macy's was similar, but entailed departments located within select Macy's stores rather than operating as standalone locations. Revitalization of the customer experience at Bloomingdale's and Blumercury were also important elements of the turnaround efforts. Like Bloomingdale's, the Bluemercury business operated standalone stores but also was comprised of store-within-store locations inside Macy's stores. The Bluemercury division had achieved impressive sales growth for the company and an addition of 26 standalone locations. Additionally, Bluemercury online sales inereased by greater than 50 percent, accounting for double-digit inereases in total sales. The Bluemercury division increased its private brands Lune+Aster and M.61, which accounted for greater than 10 percent of total sales at Bluemercury per company. A focus on improvements in the online and mobile shopping experience was a second primary element of the plan and resulted in mobile representing the fastest growing channel for the company. The new practice of allowing Macy's customers to make purchases online and pickup merchandise in the store or buy online and ship to a store for pick-up resonated with consumers. The third primary element of the company's turnaround plan included an expansion of its loyalty program to increase customer traffic and average purchase amount. In 2018. Macy's Platinum customers generated about 30 percent of store sales, shopped with more frequency, and spent 10 percent more per store visit than other customers. The company launched a new Bronze loyalty level in 2018, which yielded 3 million new customers for Macy's by yearend. A focus on improvements in the online and mobile shopping experience was a second primary element of the plan and resulted in mobile representing the fastest growing channel for the company. The new practice of allowing Macy's customers to make purchases online and pick-up merchandise in the store or buy online and ship to a store for pickup resonated with consumers. The third primary element of the company's turnaround plan included an expansion of its loyalty program to increase customer traffic and average purchase amount. In 2018. Macy's Platinum customers generated about 30 percent of store sales, shopped with more frequency, and spent 10 pereent more per store visit than other customers. The company launched a new Bronze loyalty level in 2018, which yielded 3 million new customers for Macy's by yearend. The company's offprice retail brands Backstage and Bloomingdale's The Outlet were the fourth major element of the turnaround plan because of their ability to defend against online retailers. Macy's management planned to add up to 50 Backstage locations within existing Macy's store locations and construct seven free-standing stores, all to be opened by 2020. Direct vendor fulfillment was the fifth major element of the plan and was directed at reducing distribution costs across all Macy's retail operations. Engaging customers through destination departments such as housewares, furniture, and women's apparel were additional turnaround initiatives designed to keep customers shopping once inside store locations. Exhibit 1 presents Macy's. Inc.'s Income Statements for 2015 through 2019 and reflect the company's difficulty in sustaining a consistent improvement in performance. The company's Results of Operations shown in 6 Exhibit 2 and Balance sheets shown in [. Exhibit 3 provide additional operating and financial results. EXHIBIT 1 Macy's, Inc,'s Income Statements, 2015-2019 (\$ in millions, except per share amounts) Overview of the Department Store Industry The department store industry was under pressure not only from ecommerce, but also from discount retailers whose product lines encroached on traditional department store product categories. Women's clothing and footwear and home goods and appliances made up the two largest categories of products sold in department stores in 2019. Drugs and cosmetics made up the third largest category of department store sales in 2019. Men's clothing and footwear and children's clothing and footwear contributed the least to department store revenues in 2019. Most product categories sold in department stores could also be purchased at supercenter discount retailers such as Walmart and Target or wholesale clubs such as Sam's or Costco. The proliferation of such product categories both online and available in brick-and-mortar stores required mall-based department stores to offer a highly differentiated experience or distinctive product line. The shopping mall experience. The business model of online-only retailers such as Amazon that involved low costs for land and buildings, real estate leases, inventory, store furnishings and merchandise displays, and personnel put tremendous pricing pressure on brick. and-mortar retailers. The low prices offered by many online retailers coupled with consumers' desire for the convenience of online shopping has dramatically altered the value proposition for shopping malls and resulting customer experience. Malls, which once were a popular place to visit, shop, and pass time, were challenged as the closings of prestigious anchor stores and specialty stores made shopping at a mall less exciting for consumers. Physical malls were also expensive to build and just as costly to remodel as many had been open for some time. The aging nature of many malls also decreased consumer desire to visit a mall. There were some locations that were characterized by extreme temperatures that made shopping indoors more appealing, such as the Mall of America in Minneapolis. Minnesota. The most viable malls in 2020 tended to be upscale outdoor lifestyle malls that featured beautiful architecture and landscaping along with a strong mix of aspirational luxury brands. The overall ambiance of such malls recreated the excitement of shopping in a mall that had been common in the 1970s and 1980 s. Other malls that remained popular in 2020 were outdoor outlet malls that were located near major highways that provided deep discounts on such highly sought after brands as Gucci, North Face, Coach, Abererombie \& Fitch, Under Armour, Ralph Lauren Polo, and Tori Burch. Retail sector growth and the impact of COVID-19. The retail trade sector had grown at an average annual rate of 0.7 percent in the years 2015 -2020 to reach $5.3 trillion in industry revenues. In 2020, the U.S. retail sector was made up of 2.8 million enterprises and employed 17.6 million Americans. Total wages in the industry exceeded $476 billion. The growth rate in retail trade had also allowed for a 3.1 percent increase in retailer profit margins in 2020 and an 8.9 percent increase in wages as a share of revenues in 2020. The onset of the coronavirus in early-2020 was projected to lead to a 3.3 percent decline in revenues for the entire 2020 calendar year as retailers were required to temporarily close stores: Also, the spike in unemployment resulting from COVID-19 stayat-home orders and store closures was projected to result in an overall decrease in consumer spending which would harm the U.S. department store industry and other consumer sectors. Analysts believe that the retail sector would return to a strong 1.8 percent annual growth rate for 2021 through 2025 as COVID-19 became contained and mitigated. Industry revenues were projected to increase to nearly \$5.9 trillion by 2025. The declining sales of the department store segment of the retail industry. The $100 billion department store segment of the retail sector had fared far less well than retailers such as discount supercenters, wholesale clubs, and specialty retailers during the mid.2010s. While the entire retail sector had enjoyed a 0.7 percent annual growth rate between 2015 and 2020 , the department store segment of the retail sector had declined 11 percent annually during those years. The number of department stores deelined 4.9 percent between 2015 and 2020 , with COVID-19 hastening the decay of the industry with a projected 27.4 percent decline in department store revenues and a 3.2 percent decrease in protit margins for the industry segment. Analysts projected that the department store segment of the retail industry would continue to decline by 7.5 percent annually, falling from $100 billion in 2020 to $67.7 billion in 2025. Profiles of the Largest U.S. Department Store Chains Taract Corponation Target Corporation was the largest U.S. department store chain in 2020 with a market share of 50.1 percent and 2019 sales of $50.1 billion. Target has achieved explosive growth between 2015 and 2020, allowing its market share to increase from approximately 34 percent in 2015 to 50 pereent in 2020. The company operated 1.868 stores across the United States and recorded sales of \$78.1 billion in fiscal 2020. A large portion of the company's sales was comprised of groceries, which lowered its sales of department store items to $50.1 billion. In fact, the company's sales of department store items had declined at an annual rate of 2.2 pereent between 2015 and 2020. Profiles of the Largest U.S. Department Store Chains Tarset Corporation Target Corporation was the largest U.S. department store chain in 2020 with a market share of 50.1 percent and 2019 sales of $50.1 billion. Target has achieved explosive growth between 2015 and 2020 , allowing its market share to increase from approximately 34 percent in 2015 to 50 percent in 2020. The company operated 1,868 stores across the United States and recorded sales of $78.1 billion in fiscal 2020. A large portion of the company's sales was comprised of groceries, which lowered its sales of department store items to $50.1 billion. In fact, the company's sales of department store items had declined at an annual rate of 2.2 percent between 2015 and 2020. The company had been able to increase overall sales in its supercenter locations through a reimaging plan that included store remodeling projects and the introduction of perishable and nonperishable foods to more store locations. This introduction of grocery items produced a comparable store sales growth of 5 percent. Gains in every market category was achieved coupled with a record high earnings per share increases. Key elements of Target Corporation's retail strategy included: - Becoming the first U.S. retailer to offer sameday and drive-up fulfillment capabilities, coast-to-coast - Remodeled more than 400 store locations by 2019. - In 2018, opened more than 24 small-store formats, with 30 more planned in 2019, in high-traffic urban locations and college campuses. - Focused on better guest services increased minimum wage to $12/ hour: raising again in 2019 to $13/ hour, with a goal or $15/ hour by the end of 2020 . - Focused on digital channels, where in 2018 comparable digital sales grew 36 percent. - Introduction of more brands, more than doubling a goal of more than a dozen in 2017, which was one reason Target Corporation was named by Fast Company as one of the world's most innovative companies. Nonlstrom, Inc. Nordstrom Inc. was the third largest department store chain in the United States with 380 total stores in 2020 . Nordstrom Inc. had a diverse mix of retailing formats with 136 fill-line Nordstrom department stores, 244 off-price Nordstrom Rack stores, and multiple e-commeree sites. The company's greatest store concentration of Nordstrom department stores was in California with 35 full-price locutions followed by Texas with 10. Macy's, Inc. Strategic Situation in Mid-2020 With the company reporting a year-over-year sales decline of more than 45 percent from approximately $5.5 billion in Q1 2019 to approximately $3 billion in Q1 2020, there was tremendous uncertainty about the effectiveness of Macy's turnaround and its ability to absorb the impact of COVID-19 on the retail industry. However, in comments to analysts following the company's announcement of its First Quarter 2020 results, CEO Gennette saw several bright spots. A portion of the company's loss in Q1 2020 was a result of a $300 million charge on inventory that would have been marked down as sale items if stores had been open. Also, CEO Gennette believed that the company would be able to right-size its inventory during the second quarter of 2020 to reduce overhead. Macy's management was particularly encouraged by the company's 80 percent increase in online sales during the month of May 2020 as consumers were forced to shop online during stay-at-home orders. Gennette had commented to analysts that while sales might not stabilize until 2021 or 2022 , the company would be able to retire $1 billion in debt by 2022 . With so much unpredictability, coupled with changing consumer wants and needs, the retail arena was surely one that will continue to be a challenge moving forward