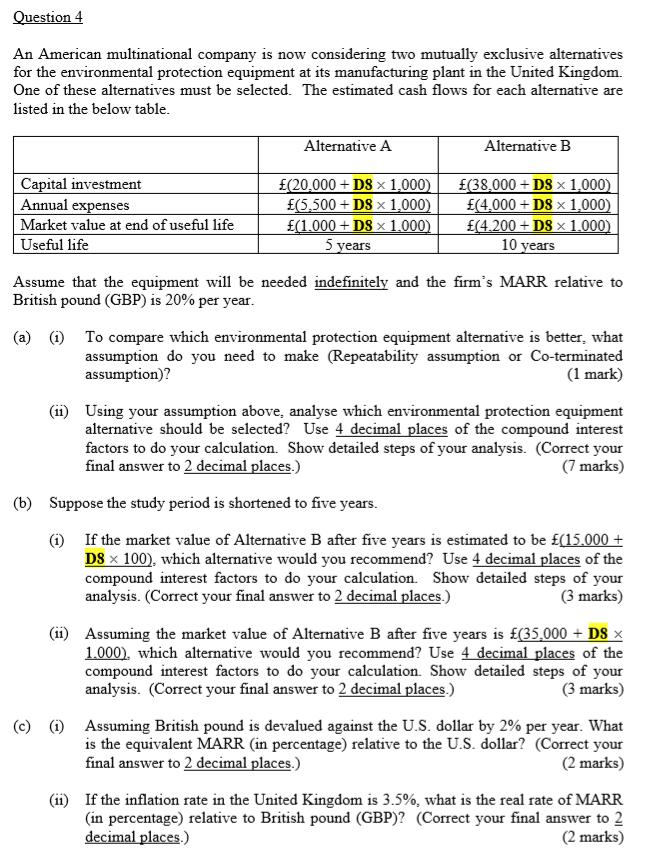
 Where D8 is equal to 4
Where D8 is equal to 4 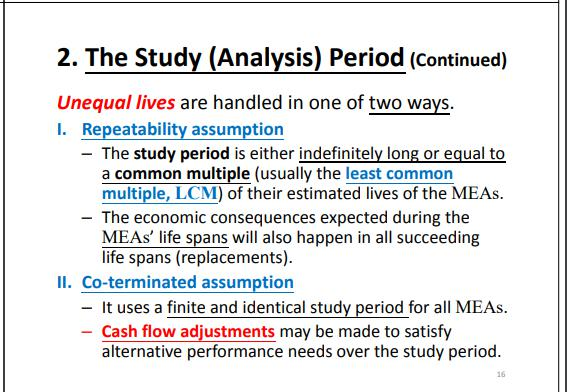
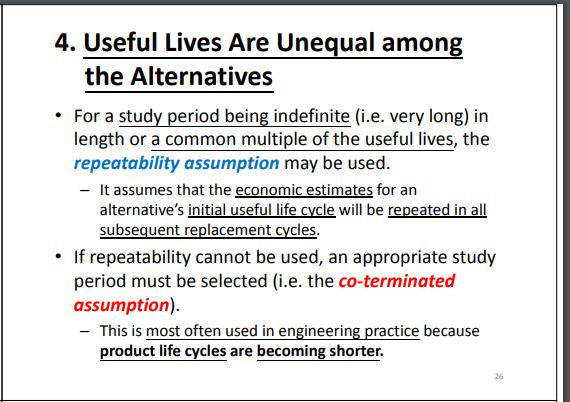
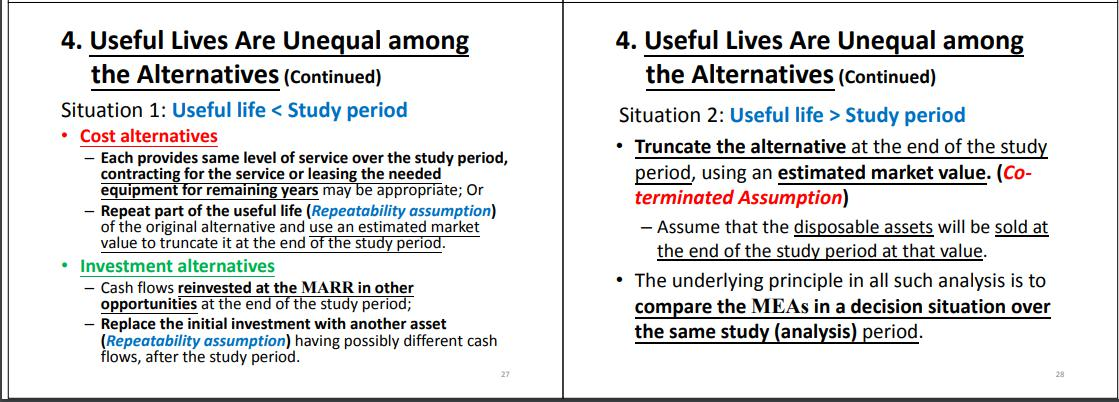
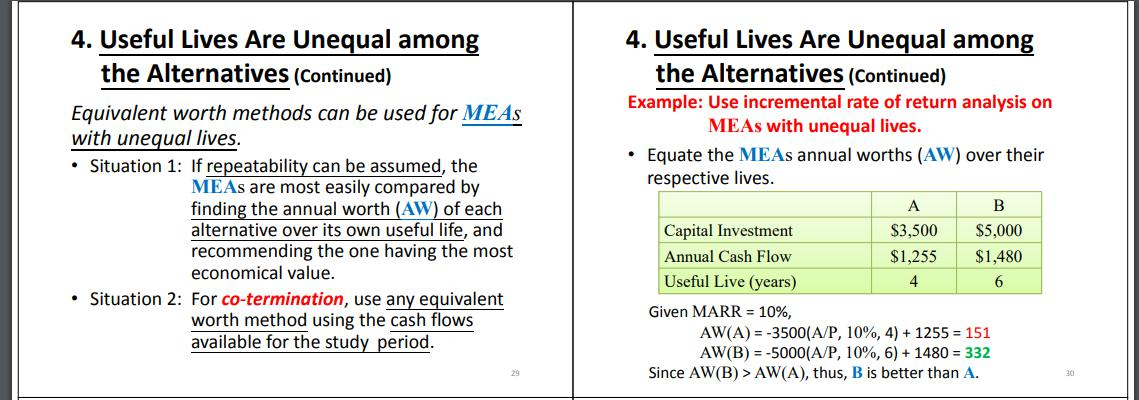
Question 4 An American multinational company is now considering two mutually exclusive alternatives for the environmental protection equipment at its manufacturing plant in the United Kingdom. One of these alternatives must be selected. The estimated cash flows for each alternative are listed in the below table. Alternative A Alternative B Capital investment Annual expenses Market value at end of useful life Useful life (20.000 + D8 x 1,000) (5.500 + D8 x 1,000) (1.000 + D8 x 1.000) 5 years (38,000 + DS X 1.000) (4.000 + DS X 1.000) (4.200 + D8 x 1.000) 10 years Assume that the equipment will be needed indefinitely and the firm's MARR relative to British pound (GBP) is 20% per year. (a) (1) To compare which environmental protection equipment alternative is better, what assumption do you need to make (Repeatability assumption or Co-terminated assumption)? (1 mark) Using your assumption above, analyse which environmental protection equipment alternative should be selected? Use 4 decimal places of the compound interest factors to do your calculation. Show detailed steps of your analysis. (Correct your final answer to 2 decimal places.) (7 marks) (b) Suppose the study period is shortened to five years. (1) If the market value of Alternative B after five years is estimated to be (15.000 + D8 x 100), which alternative would you recommend? Use 4 decimal places of the compound interest factors to do your calculation. Show detailed steps of your analysis. (Correct your final answer to 2 decimal places.) (3 marks) (ii) Assuming the market value of Alternative B after five years is (35,000 + DS X 1.000), which alternative would you recommend? Use 4 decimal places of the compound interest factors to do your calculation Show detailed steps of your analysis. (Correct your final answer to 2 decimal places.) (3 marks) c) (1) Assuming British pound is devalued against the U.S. dollar by 2% per year. What is the equivalent MARR (in percentage) relative to the U.S. dollar? (Correct your final answer to 2 decimal places.) (2 marks) (11) If the inflation rate in the United Kingdom is 3.5%, what is the real rate of MARR (in percentage) relative to British pound (GBP)? (Correct your final answer to 2 decimal places.) (2 marks) 2. The Study (Analysis) Period (Continued) Unequal lives are handled in one of two ways. 1. Repeatability assumption - The study period is either indefinitely long or equal to a common multiple (usually the least common multiple, LCM) of their estimated lives of the MEAs. The economic consequences expected during the MEAs' life spans will also happen in all succeeding life spans (replacements). II. Co-terminated assumption - It uses a finite and identical study period for all MEAs. - Cash flow adjustments may be made to satisfy alternative performance needs over the study period. 16 4. Useful Lives Are Unequal among the Alternatives For a study period being indefinite (i.e. very long) in length or a common multiple of the useful lives, the repeatability assumption may be used. - It assumes that the economic estimates for an alternative's initial useful life cycle will be repeated in all subsequent replacement cycles. If repeatability cannot be used, an appropriate study period must be selected (i.e. the co-terminated assumption). - This is most often used in engineering practice because product life cycles are becoming shorter. 26 4. Useful Lives Are Unequal among the Alternatives (Continued) Situation 1: Useful life Study period Truncate the alternative at the end of the study period, using an estimated market value. (Co- terminated Assumption) - Assume that the disposable assets will be sold at the end of the study period at that value. The underlying principle in all such analysis is to compare the MEAs in a decision situation over the same study (analysis) period. 4. Useful Lives Are Unequal among the Alternatives (Continued) 4. Useful Lives Are Unequal among the Alternatives (Continued) Example: Use incremental rate of return analysis on MEAs with unequal lives. Equate the MEAs annual worths (AW) over their respective lives. A Capital Investment $3,500 $5,000 Annual Cash Flow $1,255 $1,480 Useful Live (years) Given MARR = 10%, AW(A) = -3500(A/P, 10%, 4) + 1255 = 151 AW(B) = -5000(A/P, 10%, 6) + 1480 = 332 Since AW(B) > AW(A), thus, B is better than A. Equivalent worth methods can be used for MEAS with unequal lives. Situation 1: If repeatability can be assumed, the MEAs are most easily compared by finding the annual worth (AW) of each alternative over its own useful life, and recommending the one having the most economical value. Situation 2: For co-termination, use any equivalent worth method using the cash flows available for the study period. B 4 6
 Where D8 is equal to 4
Where D8 is equal to 4 









